10 Side Effects of Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a well-known over-the-counter (OTC) non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is widely used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. It comes in a wide array of presentations, including tablets, capsules, and oral suspensions. Ibuprofen works by blocking the production of certain chemical compounds in our body known as prostaglandins, which are associated with the process of inflammation.
Even though ibuprofen is an OTC drug, this doesn’t mean that it is harmless. NSAIDs are associated with many side effects and can damage your kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and they may increase the risk for serious cardiovascular diseases as well. It is important to follow your doctor’s prescription and avoid self-medication to prevent complications.
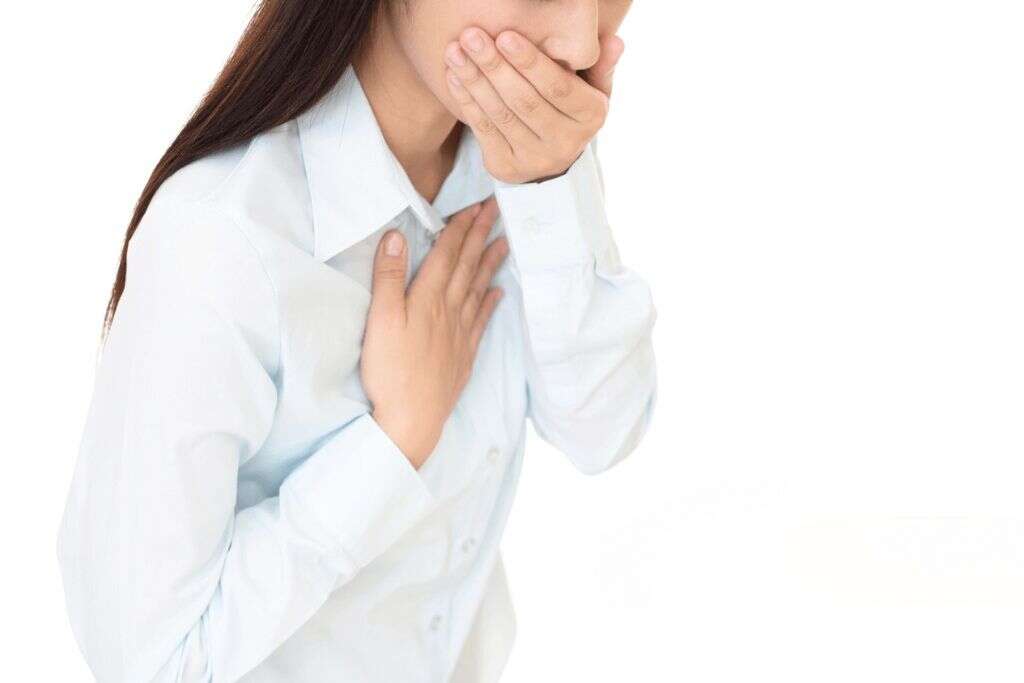
1. Nausea
Nausea is commonly defined as the urge to vomit. It can appear suddenly but in some cases, it has an insidious onset. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions, but it can also be triggered by certain events or things in our surroundings.
Nausea is a fairly common side effect associated with Ibuprofen. It is seen in almost 10% of the patients and it rarely results in vomiting. As with many drugs, side effects tend to appear with longer treatment duration, therefore, it is important not to abuse this drug and follow your doctor’s orders.

2. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
Ibuprofen like many other NSAIDs can cause damage to our gastrointestinal tract. One of the first signs associated with this side effect is the appearance of pain in the upper region of the abdomen, also known as epigastrium. It is important to keep your doctor informed of any side effects that you may encounter, especially abdominal pain as it can be a sign of a more serious condition.

3. Dizziness
Dizziness is defined as the loss of balance and/or the feeling of being lightheaded. It is a subjective sensation that can show up suddenly and may cause a person to feel ill. It is important to try to sit down as soon as possible to prevent falls that could result in serious complications.
Due to the subjective nature of the feeling, dizziness is often seen as a side effect of many drugs, and Ibuprofen is no different. It is important to notice if this symptom develops shortly after the administration of the ibuprofen and if it comes with other symptoms like a skin rash or difficulty breathing, as it may be a sign of a hypersensitivity reaction which means that person might be allergic to the drug.

4. Headache
A headache is described as the sensation of pain in any region of our head. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. Depending on the characteristics and nature of the headache, they can be classified into primary headaches (migraines and tension-type headaches to name a few), secondary headaches (traumatic, vascular, and substance-related headaches to name a few), and a third category reserved for neuropathies and other headaches.1Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (HIS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition (ICHD-3) – www.ichd-3.org
It is strange to think that a painkiller could cause a headache but it is a relatively rare side effect associated with ibuprofen and other NSAIDs. In this case, the headache usually does not last very long and it tends to be mild to moderate. If the pain persists, you should consider talking to a healthcare provider.

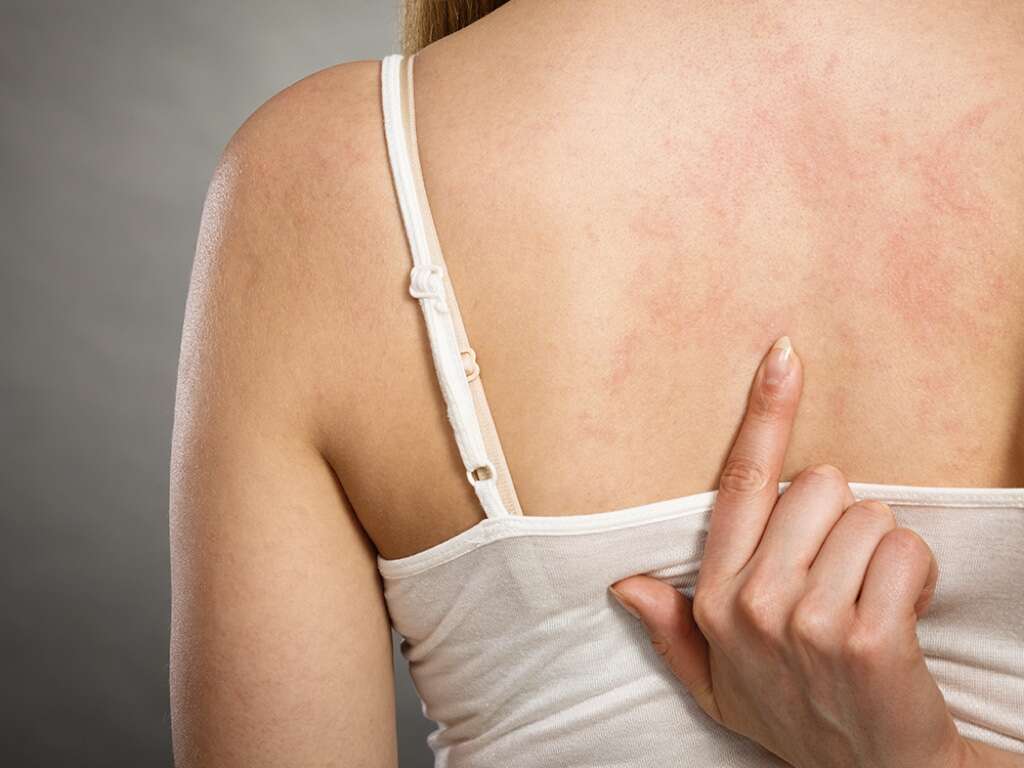
5. Rash
A rash is a disturbance in the normal structure of the skin, usually involving changes in the skin color and texture. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in many conditions. Usually, a rash can cause itchiness in the affected area, but this is not always the case.
Ibuprofen can cause a skin rash in less than 10% of the patients. It is usually seen as tinny red dots on the skin, also known as maculopapular rash, that may appear anywhere on the body. Itchiness has been described but it is not always associated.

6. Heartburn
Heartburn is described as a burning sensation felt in the chest or in the upper region of the abdomen called the epigastrium. It is a symptom seen in many conditions like acute and chronic gastritis. Pain is usually worse when lying down.
Ibuprofen causes heartburn in less than 10% of the patients. Prolonged treatments with NSAIDs are known to cause damage to our gastrointestinal tract (GI) and the stomach is often affected. It is important to use ibuprofen with caution, as it can cause serious GI events like ulcers, perforations, and bleeding, especially in the elderly.
7. Constipation
Constipation is defined as having less than 3 bowel movements a week. Other key features associated with constipation include hard and dry stools, and difficulty and/or pain during a bowel movement. Some people may experience tenesmus which is the feeling that you still need to empty your bowels even after you just had a bowel movement.
Ibuprofen is known to cause constipation in less than 5% of the patients taking it. This side effect is associated with longer treatment duration but it can appear anytime. Constipation may lead to other complications like hemorrhoids and anal fissures, therefore, it is important to seek medical attention to avoid these scenarios.

8. Edema
Edema is defined as fluid accumulation that leads to swelling of the affected tissue. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. Depending on the location and the nature of the edema, it can be a very dangerous sign like in pulmonary edema or an annoying symptom like the one seen in venous insufficiency.
Due to its mechanism of action, ibuprofen may cause peripheral edema in the legs in less than 3% of the patients taking it. This is a rare side effect associated with ibuprofen but the longer the treatment, the greater the chances of seeing side effects.

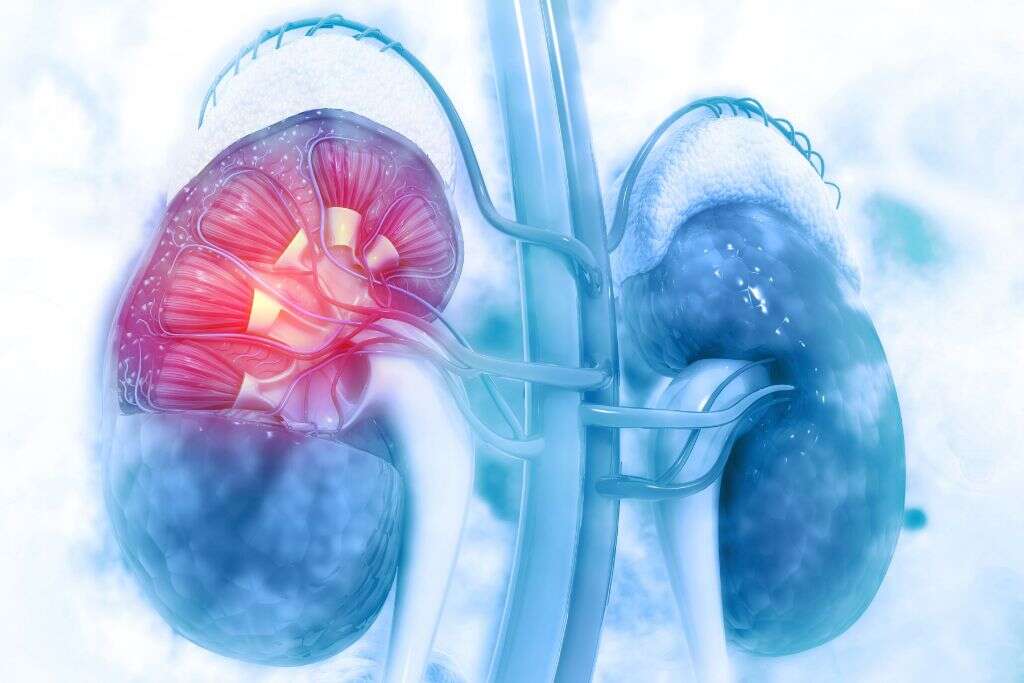
9. Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is defined as a sudden impairment or decline in renal function. Previously known as acute renal failure (ARF), this is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if left undiagnosed. One of the key symptoms associated with this condition is the decline in urine output, also known as oliguria.
NSAIDs like ibuprofen are known causes of Acute Kidney Injury. Even though it is not a common side effect, chronic use of ibuprofen increases the risk of developing this condition. This is especially important in patients taking ibuprofen with underlying kidney disease.
10. Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is the medical term used to describe a low platelet count. Platelets are blood cells that help the blood clot. This is vital to avoid losing too much blood due to wounds and other injuries. When the platelet levels are too low, we may find it harder to form a clot and bleeding becomes a problem.
Ibuprofen as well as other NSAIDs are known to cause thrombocytopenia in less than 1% of the patients taking it. It usually manifests as easy bruising and/or bleeding gums, but it can cause bleeding of other tissues like the gastrointestinal tract.