10 Neurofibromatosis Symptoms
Neurofibromatosis is a group of genetic conditions where the affected individual develops tumor formation in their nervous system. There are three types of neurofibromatosis, each with different signs and symptoms: neurofibromatosis type 1, neurofibromatosis type 2, and schwannomatosis.
Neurofibromatosis is caused by a genetic mutation - approximately 50% of patients inherited these genes from their parents. These tumors are most commonly seen in the nervous system instead of the neurons. In neurofibromatosis type 1, tumors that appear in the peripheral nerves are called neurofibromas while in neurofibromatosis type 2 and schwannomatosis, tumors of Schwann cells are much more common. The diagnosis of neurofibromatosis is achieved based on the patient’s symptoms and signs. Genetic testing can help support the diagnosis.
There is no cure or prevention for neurofibromatosis. Treatment involves surgery to remove the tumors that are causing issues or that are cancerous. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be involved if there is cancer. Those with hearing loss can opt for an auditory brainstem implant or cochlear implant. In the United States, it has been estimated that there is approximately 1 per 3,500 individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1 and 1 per 25,000 individuals with neurofibromatosis type 2. Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 often experience symptoms at birth or before 10 years of age while those with neurofibromatosis type 2 may not experience symptoms until they reach early adulthood.
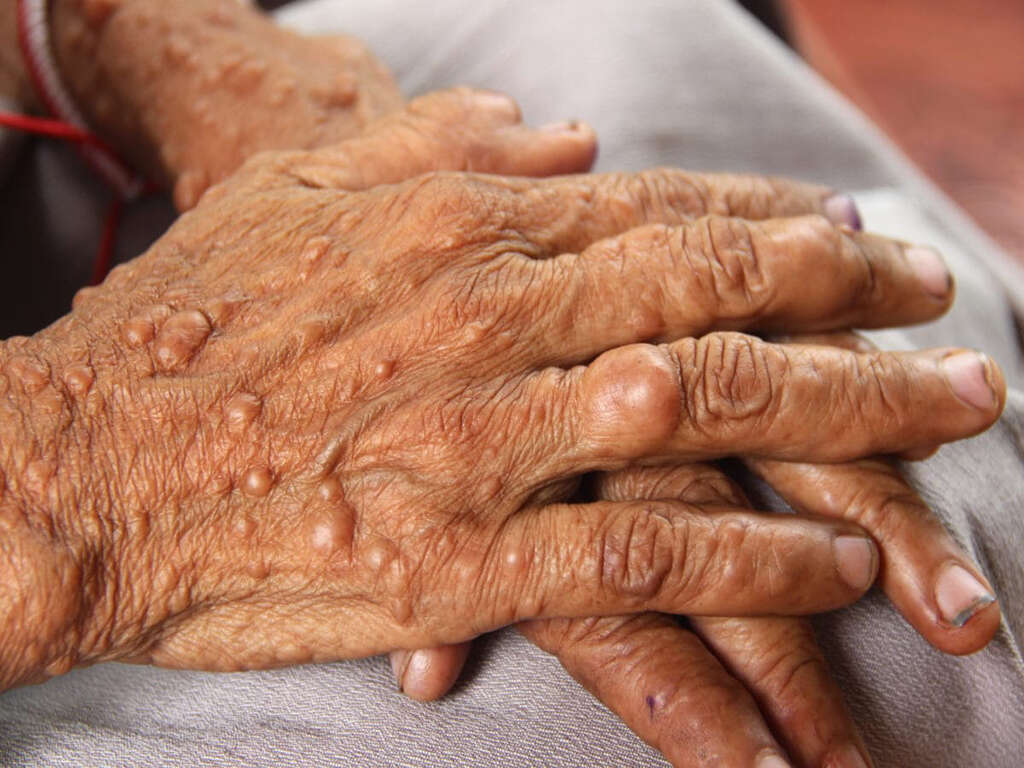

Symptom #1: Café au Lait Spots
The name café au lait (coffee with milk) refers to the flat pigmented birthmarks that are light brown in color. The difference in skin color is caused by a collection of melanocytes that are present in the epidermal layer of the skin. These spots can grow or increase in size and are usually permanent.
While harmless, they can be associated with syndromes like McCune-Albright syndrome, Chediak-Higashi syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Noonan syndrome, Watson syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, and more. Having six or more café au lait spots is one of the diagnostic features of neurofibromatosis type 1.

Symptom #2: Freckles In the Armpit and Groin
Freckles are clusters of pigmented skin that are most visible among people with fair complexion. It occurs in all individuals regardless of skin tone. The melanocytes present overproduce melanin which changes the coloration of the outer skin cells.
Freckles appear in neurofibromatosis type 1 patients by the ages of three to five years old. These freckles are typically present at birth or develop during the first few years of life.

Symptom #3: Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves sideways into an “S” or “C” shape. The degree of curvature can be stable or gradually increasing with time. Mild cases of scoliosis do not usually cause issues, but severe cases can lead to issues with respiration. Pain is not typically present. In most cases, the cause of scoliosis is unknown, but it has been thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
It can also be seen in conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscle spasms, Marfan syndrome, and more. The treatment of scoliosis depends on the location, cause, and degree of curve. Scoliosis is seen in neurofibromatosis type 1.
Symptom #4: Hearing Loss
Hearing loss or hearing impairment refers to the partial loss of the ability to hear. In younger children, it can affect their ability to learn and speak a language. In adults, it can cause difficulties in daily routines. Some conditions that can cause hearing loss for a child in utero are rubella and syphilis.
With neurofibromatosis, hearing loss usually occurs with type 2. The tumors grow and affect the nerve that carry sound from the ear to the brain. The hearing loss in type 2 is usually gradual.

Symptom #5: Visual Problems
Cataracts are a condition where the lens of the eye is clouded, causing a decrease in vision. Symptoms include halos, blurry vision, trouble with seeing at night, trouble with bright lights, and faded colors.
They can lead to difficulty with daily activities such as reading, driving, or recognizing others. In neurofibromatosis type 2, cataracts occur at a young age as opposed to usually occurring among older individuals. Vision can also be affected if the growth of schwannoma tumors occurs in the optic nerve.
Symptom #6: Muscle Wasting
Muscle wasting or muscle atrophy occurs when there is decreased mass of the muscles. It is most commonly seen when there is are circumstances that cause an individual to be disabled, confined to bed, or have restricted movements. Muscle atrophy can lead to muscle weakness. It can be seen in various diseases such as congestive heart failure, cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In neurofibromatosis type 2, the growth of schwannomas in the various nerves of the body such as the optic nerve, cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and peripheral nerves can lead to issues such as pain, balance issues, vision loss, numbness, and atrophy/weakness of the muscles in the arms and legs.

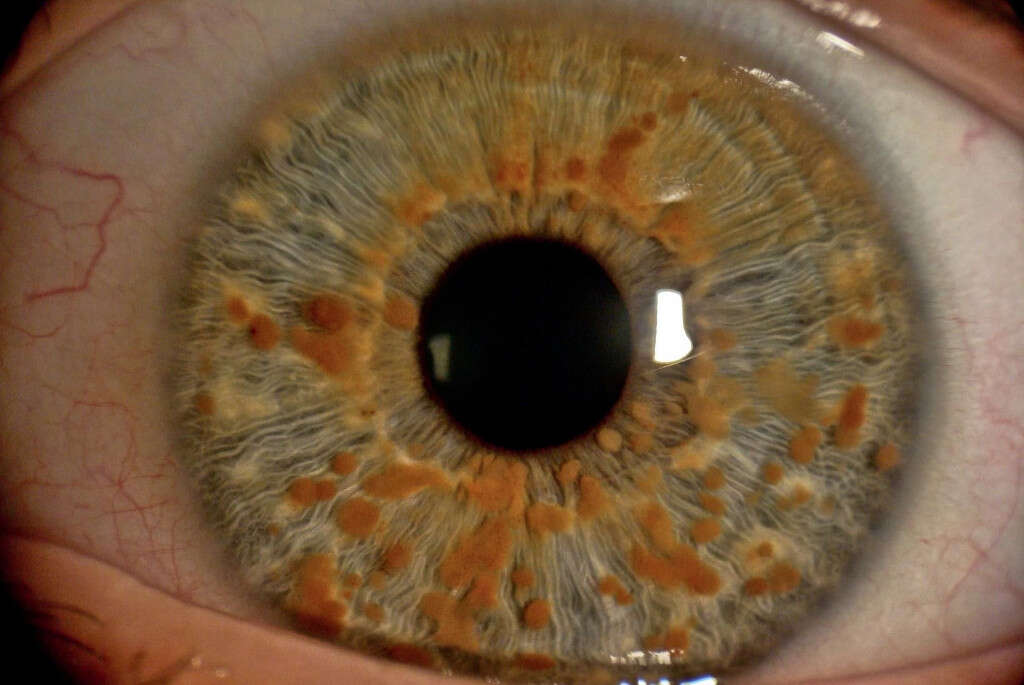
Symptom #7: Lisch Nodules
Lisch nodules or iris hamartoma refers to a pigmented malformation in the iris portion of the eye. They are usually benign. This aggregate of melanocytes is named after the Austrian ophthalmologist Karl Lisch who discovered them in 1937. Lisch nodules are usually found in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. As many as 94% of neurofibromatosis type 1 patients over the age of 6 have Lisch nodules.
These nodules are described to be clear yellowish-brown papules that can be oval, round, or dome-shaped. Lisch nodules project from the surface of the iris. While it does not affect vision, it is very helpful in the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 1.
Symptom #8: Learning Difficulties
As many as 50 to 60 percent of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 have learning difficulties. While they have normal intelligence, they may encounter issues with writing, reading, or the use of numbers. They may also have attention deficit issues leading to difficulties staying focused in school.
Affected children can often feel confused, frustrated, or anxious, which has a negative impact on their social interactions and school performance. Some children may also have issues with gym activities or writing as a result of motor output problems and can be regarded by others as uncoordinated or clumsy.

Symptom #9: Skin Bumps
As the name of the condition suggests, patients with neurofibromatosis develop tumors that arise from the nervous system. These neurofibromas can be visible on the skin and appear as small bumps that can be the size of a pencil eraser or mosquito bite.
Younger patients have few neurofibromas as the numbers may not be significant until they reach puberty. While some only have a few small neurofibromas, there are also others who can be covered with thousands.
Symptom #10: Ringing In The Ears
Patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 may develop tumor growths in their eras called acoustic neuromas.
These tumors are usually bilateral and may cause various symptoms such as headaches, ringing in the ears, loss of balance, and eventually lead to gradual hearing loss. The high pitched noise can be very uncomfortable and it usually starts in the late teenage years or early adulthood.