10 Mono Symptoms
Infectious mononucleosis is also known as glandular fever. The Epstein-Barr virus is the most common cause. Most people who are affected will start feeling better in two to four weeks. However, the residual effects (such as tiredness) can last for months. Infectious mononucleosis is most commonly spread through the saliva but can also spread through blood, semen, and contaminated objects.
Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis is based on the symptoms and confirmed with blood tests. While there is no vaccine available, individuals can prevent infectious mononucleosis by not kissing infected individuals or sharing personal items with them. The infection is usually self-limiting, but patients are encouraged to get sufficient rest, drink fluids, and take medications that can help with the symptoms (such as painkillers).
Most individuals are affected during childhood and have few (if any) symptoms. Mono symptoms are most apparent in adolescents and adults. Infectious mononucleosis often affects individuals who are between fifteen to twenty-four years old. Approximately 45 out of 100,000 individuals are affected by infectious mononucleosis annually in the United States. Almost 95 percent have had an Epstein-Barr virus infection by the time they reach adulthood.
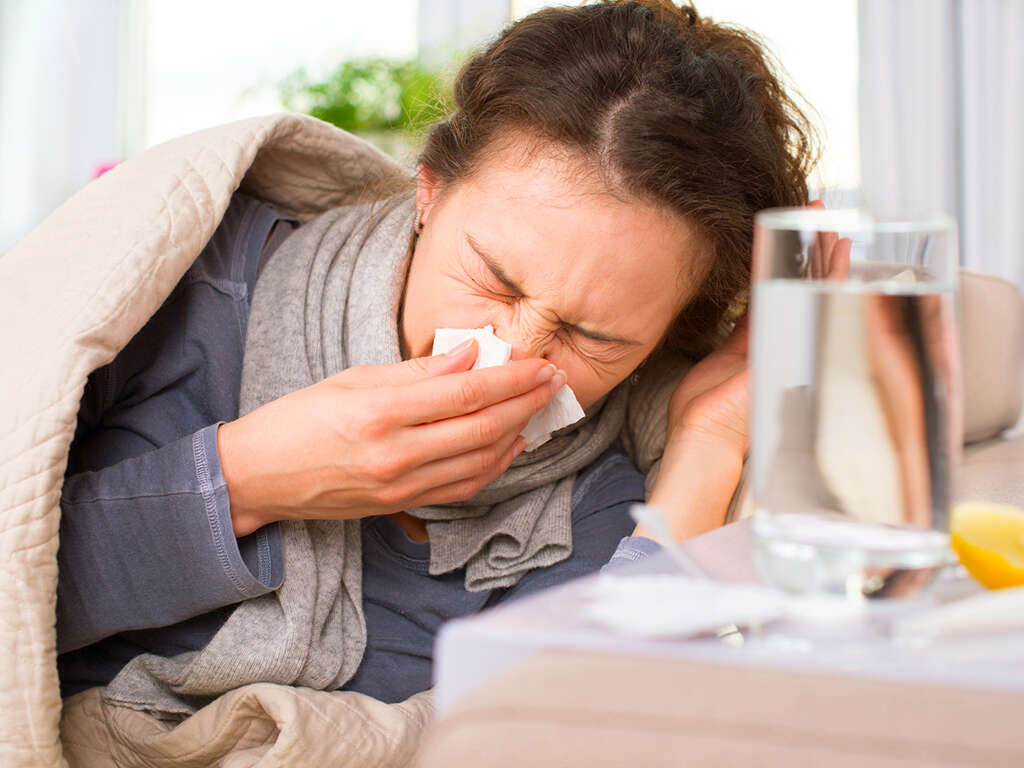

Symptom #1: Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the back of the throat or pharynx, which usually leads to a sore throat and fever. Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, resulting in a fever, enlargement of the tonsils, and a sore throat. Both pharyngitis and tonsillitis are upper respiratory tract infections that can occur because of either a viral or bacterial infection. A sore throat is one of the most common symptoms associated with mononucleosis.
Other symptoms associated with both conditions are fever, cough, hoarseness, headache, and runny nose. If the symptoms are severe (especially if they occur in younger children), seek medical attention since these symptoms may lead to difficulty breathing and swallowing.

Symptom #2: Fever
Fever, or pyrexia, is when the set point of body temperature increases. It is a nonspecific symptom that occurs in many conditions, such as viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections. It is the body’s natural way of helping the immune system fight an infection.
When the set point of body temperature increases, the body tries to reach a higher temperature. The repeated muscle contractions caused by shivering help increase body temperature as the body continuously tries to produce and conserve more heat. Mononucleosis usually causes a low-grade fever and chills are uncommon.

Symptom #3: Swollen Lymph Nodes
The lymph nodes are the part of the body’s immune system that filters foreign pathogens and helps fight off infection. Lymphadenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes where the number, size, or consistency of the lymph nodes is abnormal. It is a nonspecific symptom that can occur due to infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancers.
In infectious mononucleosis, inflammation causes the lymph nodes to swell and enlarge, and the disease usually affects the cervical lymph nodes.
Symptom #4: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a sensation of unease and discomfort that often includes an urge to vomit. Vomiting is the involuntary and forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth and sometimes the nose. It is also known as puking, barfing, emesis, or throwing up.
Both nausea and vomiting are nonspecific symptoms that are often seen in various conditions, such as pregnancy, food poisoning, gastroenteritis, and infections, or as side effects of medications or chemotherapy. Even though, patients with mono usually present nausea, vomiting is very rare.

Symptom #5: Headaches
A headache is pain or discomfort anywhere in the neck or head. It is a common and nonspecific symptom seen in various conditions and diseases. Types of headache include migraines, tension headaches, and cluster headaches.
Causes of headaches include stress, overwork, sleep deprivation, dehydration, brain tumors, high blood pressure, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Headaches can usually be managed symptomatically using painkillers, such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).

Symptom #6: Fatigue and Malaise
Fatigue is a feeling of tiredness that can be alleviated with periods of rest. Malaise is a general feeling of unease or discomfort. It is one of the first indications of disease or infection. Both fatigue and malaise are common and nonspecific symptoms.
These are the most common symptoms associated with mononucleosis and almost all symptomatic patients suffering from this condition will experience fatigue and malaise in varying degrees. Symptoms can last for several days and even weeks.

Symptom #7: Red Spots On The Palate
Palatal enanthem is a rash or spots that can be seen on the mucous membranes, especially on the roof of the mouth (palate).
It is a characteristic symptom in patients with measles, smallpox, chickenpox, roseola infantum, and, in some cases, infectious mononucleosis (it is a relatively uncommon symptom of infectious mononucleosis). It may also indicate hypersensitivity. This symptom usually resolves once the infection resolves.

Symptom #8: Rash
A rash is a change in the appearance, color, or texture of the skin. In infectious mononucleosis, the rash has a papular appearance. A papule is a circumscribed and solid elevation of the skin ranging from 5 to 10 mm in diameter where there is no visible fluid present.
The rash can be flat or slightly elevated. There are many other causes of papular rash, such as allergies, Kawasaki disease, roseola, and dengue infection.
Symptom #9: Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is usually a late symptom associated with severe complications like liver and/or spleen enlargement (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly respectively).
It is usually a doll and non-localized pain. Rest is mandatory for patients presenting with an enlarged spleen as the risk of rupture is high and could lead to a very unfavorable outcome.

Symptom #10: Muscle Aches
Myalgia is the medical term used to describe muscle aches. Myalgia is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions like viral infections.
This is not a very common symptom associated with mononucleosis but if muscle aches appear they are usually mild and go away as the diseases resolve over time.