Causes of Swollen Tonsils
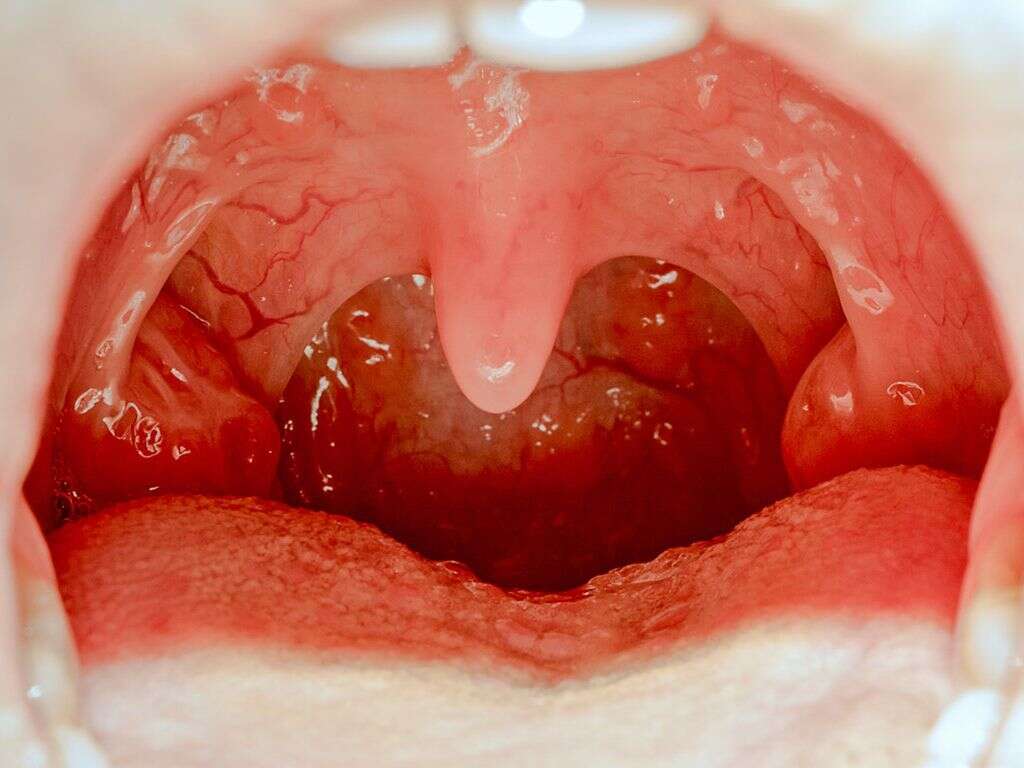
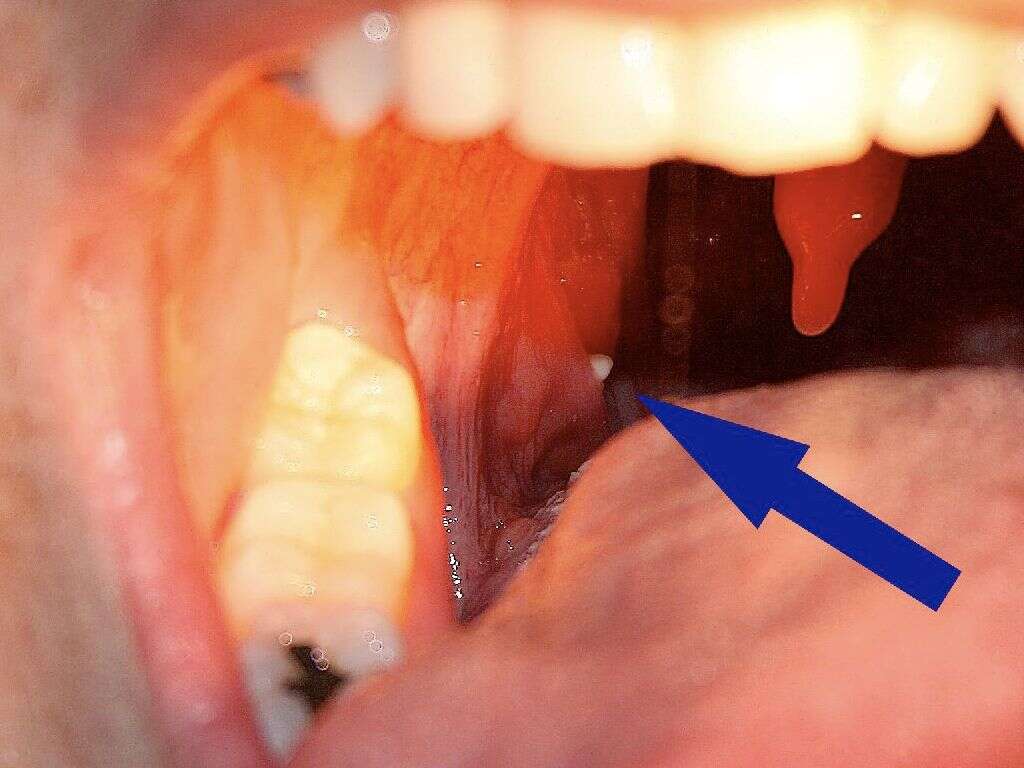
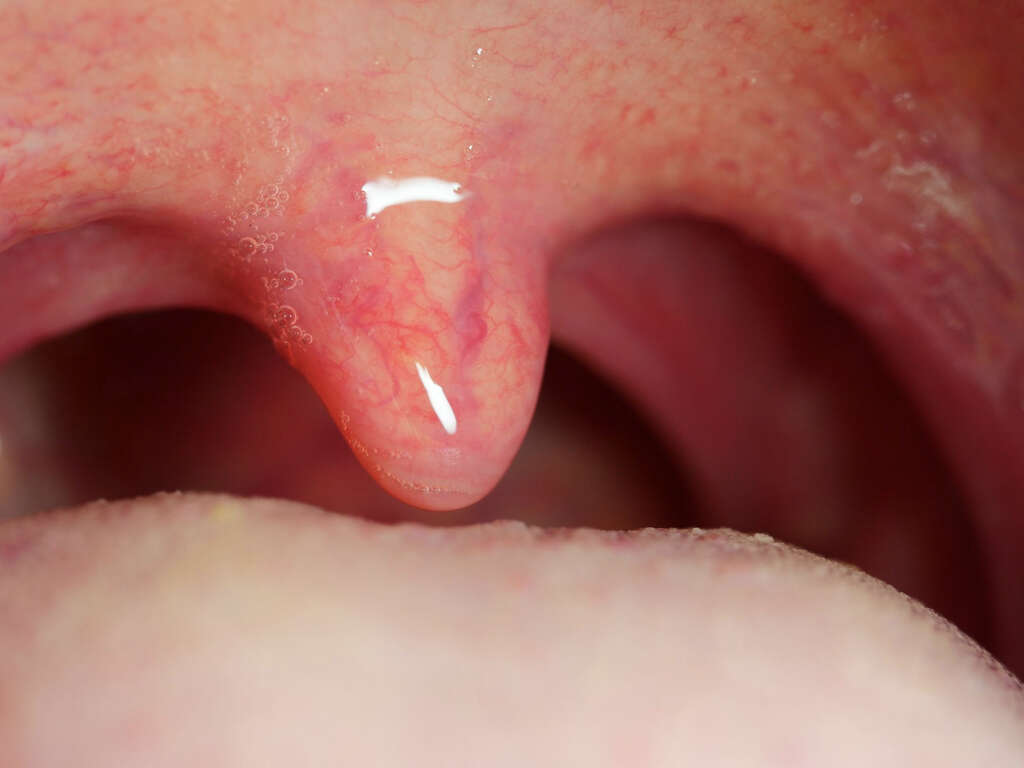
Tonsillitis is the medical term given for the inflammation of the tonsils. It can be very painful for the patient and will often come with a host of other symptoms that help make the patient feel even worse. Thankfully, depending on the causes of the inflammation, tonsillitis is not usually serious and will pass with no permanent harm being done.
The causes of tonsillitis tend to be either bacterial or viral. What other symptoms the patient will have will depend on what is causing the inflammation. Here’s a look at some of the most common causes, and at some of the symptoms they cause.
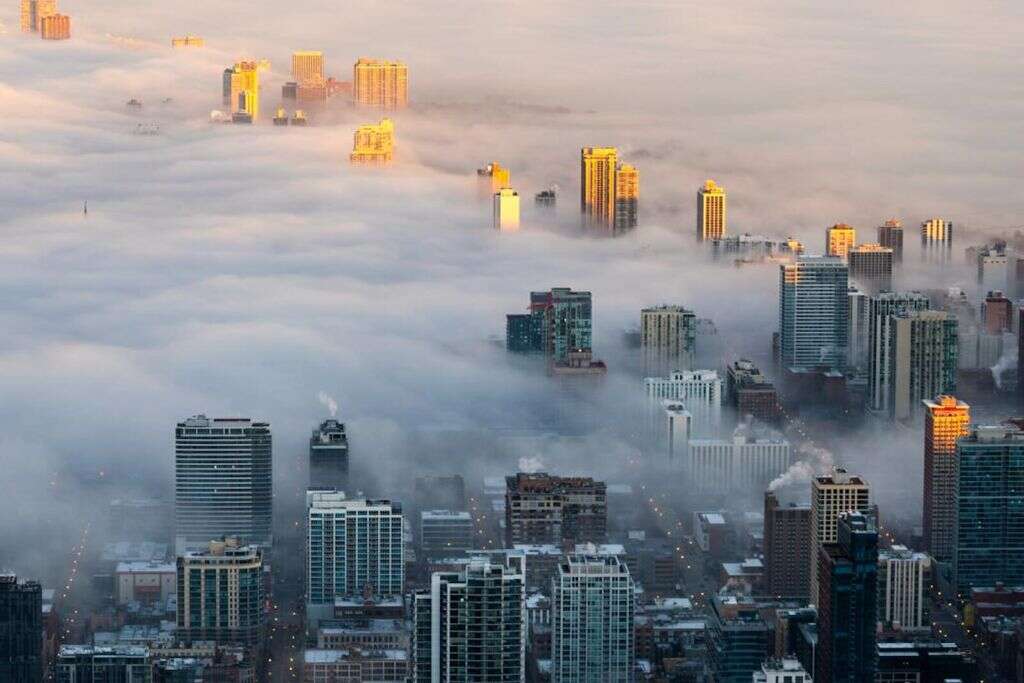
1. Environmental
Nowadays, many of our big cities are very polluted. Fumes from exhausts are pumped out from the countless vehicles on the road, while factories and other industries pump out vast amounts of pollution on their own. In the past, this pollution would simply have dissipated but there is often now so much produced that it lingers in the air. Inhaling this bad air can be a real problem for us, especially for younger people and others with more sensitive tissues.
The chemicals in the air can irritate and inflame the tissues, potentially leading to inflammation of the tonsils. In addition, polluted air can weaken the immune system, while there is more likely to be pathogens present in the polluted air.

2. Enterovirus
Most people have encountered the enterovirus at some point. There are many types and, thankfully, they only usually cause mild symptoms. In some instances, the host may not even experience any symptoms at all. When symptoms do arise, it is usually in young people, because adults have had time to develop an immunity.
The virus is usually contracted in summer and fall, and it can cause hand, foot, and mouth disease, as well as summer flu. Somebody with the virus can develop tonsillitis. While they are mostly harmless, some rarer types can be more severe, potentially causing illnesses such as polio and meningitis.
3. Influenza Virus
The influenza virus is among the best known of all viruses. It is responsible for the illness commonly known as the flu. In the past, the influenza virus has been responsible for countless deaths, but modern medicine means it is now nowhere near as dangerous as it once was.
The flu causes symptoms like fever, chills, aching joints, headache, and swollen tonsils. While it is not as dangerous as it used to be, it does still pose a risk for people who have a weakened immune system. People are encouraged to get regular flu shots in order to keep them protected against the virus as it evolves.
4. Parainfluenza Viruses
Despite similarities in their names, parainfluenza viruses are not related to the influenza virus. They are fairly common, and there are four types, all of which can infect people. They can spread from person to person and can also be contracted from surfaces on which the viruses can survive for hours.
HPIV-1 is the most common cause of croup in children. HPIV-2 also causes the same disease, but it is more likely to be encountered in fall. The HPIV-3 can cause bronchiolitis and pneumonia, and the HPIV-4 virus is known to cause some very serious illnesses but is, thankfully, rare. They can all cause tonsillitis.
5. Adenoviruses
Adenoviruses are a group of viruses that are often responsible for infections of the eyes, intestines, lungs, nervous system, and urinary tract. They tend to cause symptoms such as a fever, cough, diarrhea, pink eye, sore throats and, of course, inflamed tonsils.
The common cold is a type of adenovirus. Adenoviruses are very common and most people will have been infected by at least one variety by the time they are 10 years old. They do affect children more than adults, but they can affect people of any age. Adenoviruses are usually quite mild, but people who are particularly vulnerable should still be monitored closely.
6. Epstein-Barr Virus
The Epstein-Barr virus is another fairly common virus that is responsible for causing mononucleosis (often shortened to mono). Another name for mononucleosis is the kissing disease, so called because it is often transmitted by kissing. It is also often caught through sharing crockery, silverware, and similar.
The Epstein-Barr virus is common and it is estimated that up to 90% of adults in the United States have contracted it by the time they are 40 years old. For many people, the virus is contracted in their childhood but they never show symptoms. It is still contagious regardless of whether or not the patient is showing symptoms.
7. Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus is another common virus that is easily transmitted from person to person. The method of transmission is usually being in direct contact with an infected person, mainly through bodily fluids. There is as yet no known cure for the virus and, once contracted, the patient will remain infected for the rest of their life.
The good news is that many people will not even be aware they have the virus because it will cause no symptoms. When symptoms do arise, they are usually relatively mild and will usually pass within 3 weeks or so. Symptoms are more likely to show in people who have weakened immune systems and in pregnant women.
8. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1)
HSV-1 is a close relative of HSV-2, and the latter is a sexually transmitted disease that is known for causing sores and blisters on the genitals. HSV-1 is shared through contact such as kissing and sharing crockery, food, and utensils. It is a common virus, and around 67% of people are thought to have had it by the age of 50.
Many people with the HSV-1 virus will never experience an outbreak of symptoms. When they do, the symptoms typically include itching and sores around the mouth and elsewhere that blister. Other symptoms include fever, headaches, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and tonsillitis.
9. Rubeola
Rubeola, which is more commonly known as measles, is another fairly common virus. It is very contagious and it is an airborne transmitted disease, meaning it is mostly spread by infected people when they cough and/or sneeze.
It affects the respiratory system and the key symptoms are a rash, fever, Kopliks spots, lung infection, encephalitis, tonsillitis, and blindness. Measles is usually treatable and most people survive with no lasting damage done, but it can be fatal so it should be taken very seriously. Instances of measles have been increasing in recent years due to a trend toward children not being vaccinated.
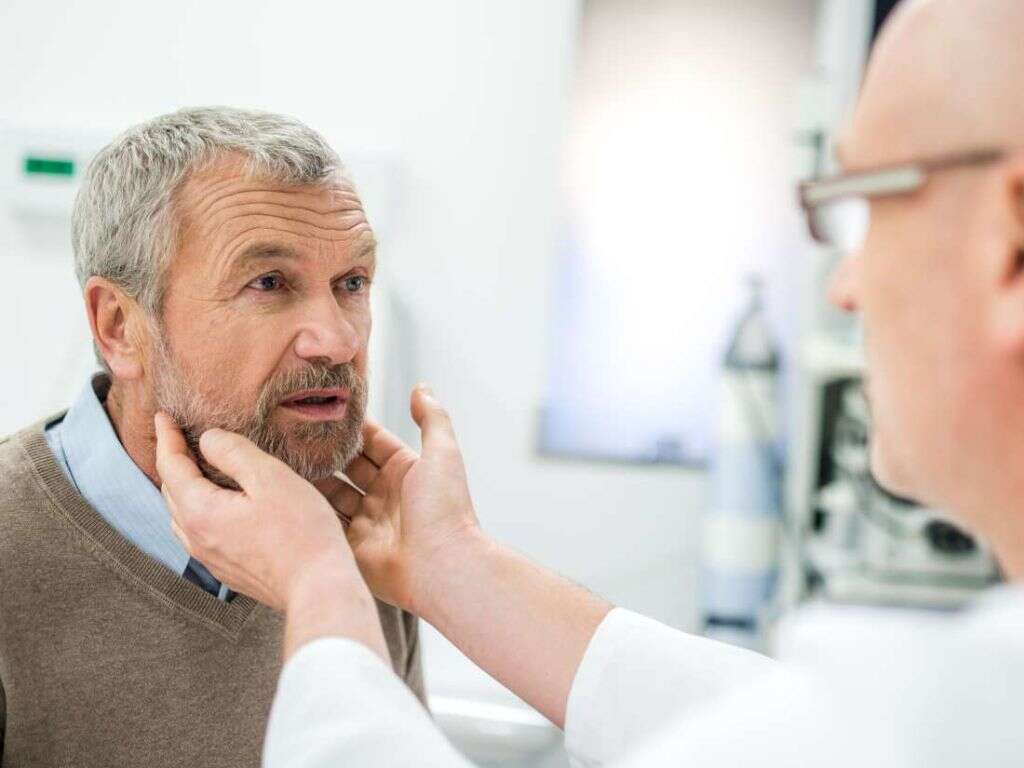
10. Treatment
Treatment for swollen tonsils will vary according to the underlying cause. In some instances, there is little that can be done but the condition will pass in a few days or so. In others, it can be important to treat the underlying cause because it can be severe, depending on what is causing it.
In addition, the patient can be treated for the symptoms of swollen tonsils. This will largely mean lozenges and similar to help ease the pain that inflamed tonsils can cause. In addition, other symptoms like headaches and fevers can also be treated to help make the patient feel more comfortable.