10 Vitiligo Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Vitiligo - Symptoms and Causes.' Mayo Clinic, 10 Apr. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/symptoms-causes/syc-20355912
- 2. 'Vitiligo.' Nhs.uk, 20 Oct. 2017, www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitiligo
- 3. 'Can Hair Dye Cause Vitiligo or Make It Worse?' Living Dappled, 21 Mar. 2021, livingdappled.com/can-hair-dye-cause-vitiligo-or-make-it-worse
- 4. 'Oral Manifestations of Vitiligo.' PubMed Central, Jan. 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4318026
- 5. 'Vitiligo: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Recovery.' Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12419-vitiligo
- 6. 'What is the Psychological and Social Effect of Vitiligo?'Medscape, 19 Oct. 2020, www.medscape.com/answers/1068962-87954
- 7. 'The Problems in Sexual Functions of Vitiligo and Chronic Urticaria Patients.' ResearchGate, 1 Jan. 2007, www.researchgate.net/publication/6638246
- 8. Vitiligo: Patient Stories, Self-esteem, and the Psychological Burden of Disease.' PubMed Central, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986114
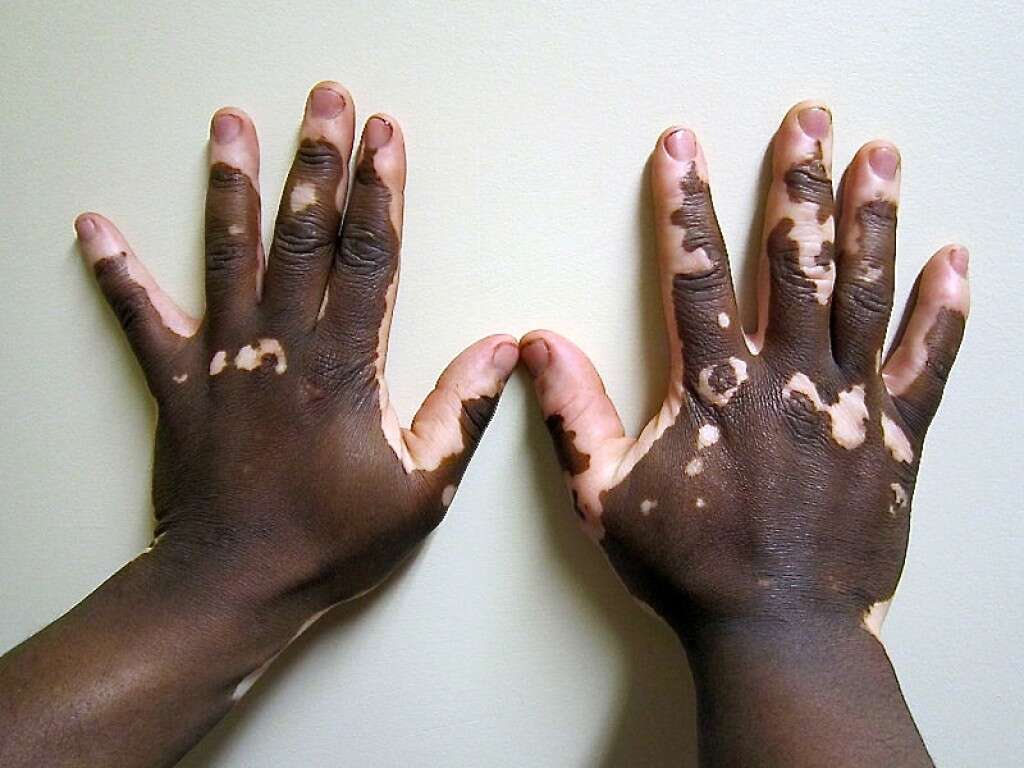
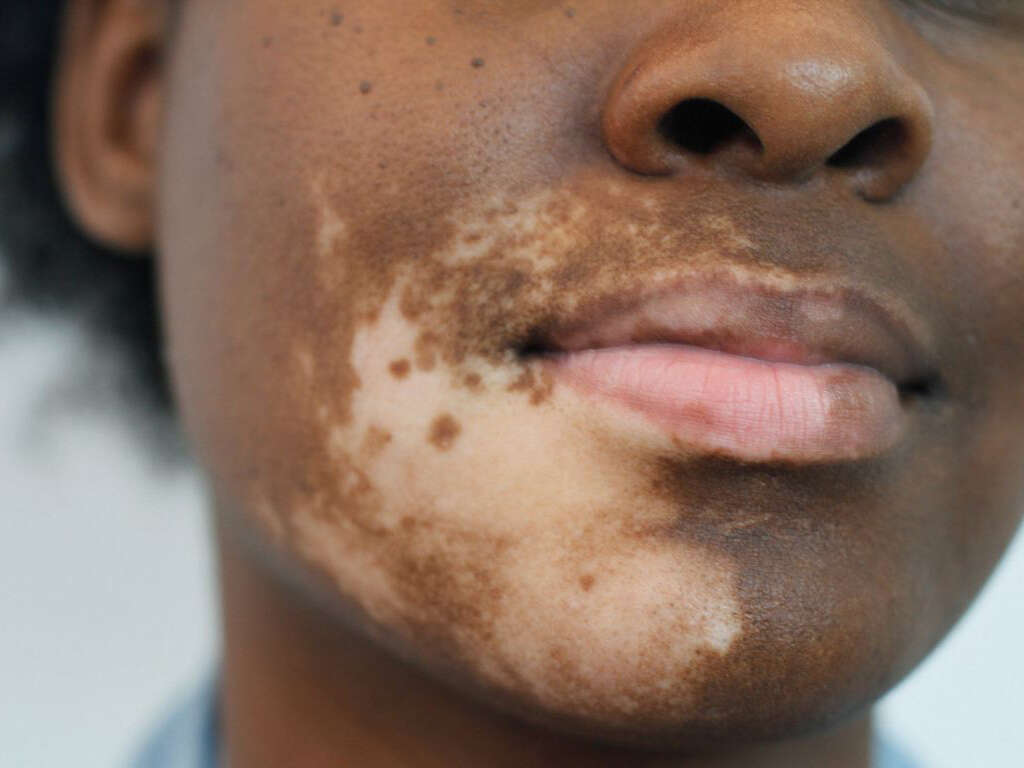
Depigmentation in Mucous Membranes
The resulting depigmentation from the lack of available melanin is also responsible for the loss of color in the mucous membranes of the mouth. It's estimated that 55 percent of those with vitiligo experience this symptom, with the lips affected in around 40 percent of people with the condition.
Studies suggest that depigmentation of mucous membranes is more likely to occur in women, with 27 percent experiencing the symptom, compared to 18 percent of men.4‘Oral Manifestations of Vitiligo.’ PubMed Central, Jan. 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4318026
Advertisement