10 Symptoms of TB
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. World Health Organization. (2020). Tuberculosis (TB). Retrieved November 13, 2020, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis
- 2. Rosha, D. (2002). Prolonged Fever During The Treatment Of Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Medical Journal Armed Forces India, 58(2), 127-129. doi:10.1016/s0377-1237(02)80045-4
- 3. Mahmoudi, A. (1993). Pitfalls in the Care of Patients With Tuberculosis. Jama, 270(1), 65. doi:10.1001/jama.1993.03510010071032
- 4. Hernández-Garduño, E., & Pérez-Guzmán, C. (2007). Appetite and tuberculosis: Is the lack of appetite an unidentified risk factor for tuberculosis? Medical Hypotheses, 69(4), 869-872. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2007.02.006
- 5. Saloman, L. (2016). Examining Disease Characteristics and Patterns of Weight Gain in Tuberculosis Treatment. Retrieved November 13, 2020, from https://www.contagionlive.com/view/examining-disease-characteristics-and-patterns-of-weight-gain-in-tuberculosis-treatment
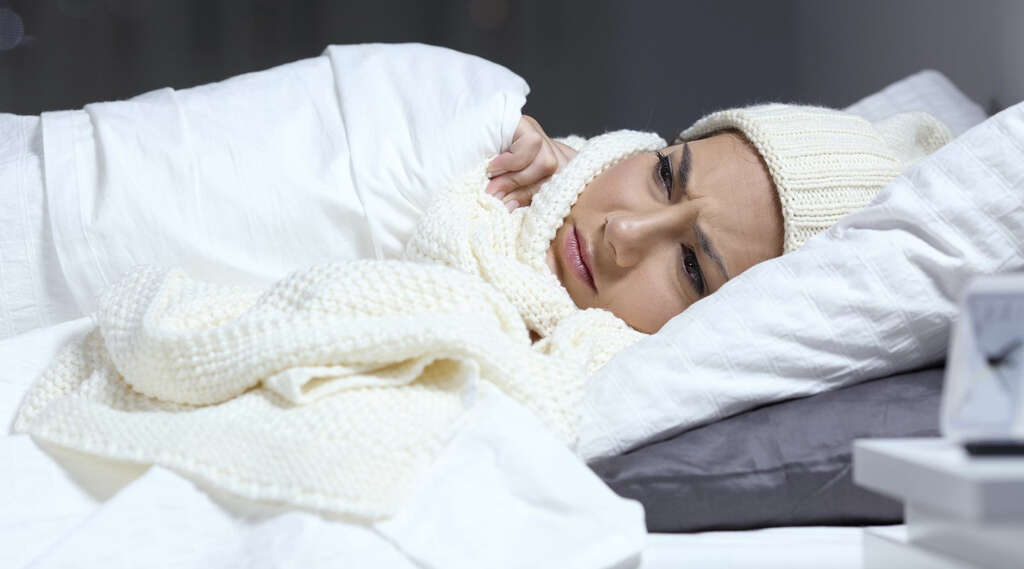
4. Chills
Chills are most commonly reported alongside a fever or just before one develops in tuberculosis patients. They happen as a result of rapid contractions and relaxation of muscles that the body performs to raise the core body temperature to a high enough level to fight off infection.
In addition to the trembling caused by muscle contractions, most patients who develop chills also become pale and feel cold. Bundling up or adding extra layers can make chills worse by further elevating core temperatures.
Advertisement



-06.jpg)