10 Symptoms of TB
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. World Health Organization. (2020). Tuberculosis (TB). Retrieved November 13, 2020, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis
- 2. Rosha, D. (2002). Prolonged Fever During The Treatment Of Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Medical Journal Armed Forces India, 58(2), 127-129. doi:10.1016/s0377-1237(02)80045-4
- 3. Mahmoudi, A. (1993). Pitfalls in the Care of Patients With Tuberculosis. Jama, 270(1), 65. doi:10.1001/jama.1993.03510010071032
- 4. Hernández-Garduño, E., & Pérez-Guzmán, C. (2007). Appetite and tuberculosis: Is the lack of appetite an unidentified risk factor for tuberculosis? Medical Hypotheses, 69(4), 869-872. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2007.02.006
- 5. Saloman, L. (2016). Examining Disease Characteristics and Patterns of Weight Gain in Tuberculosis Treatment. Retrieved November 13, 2020, from https://www.contagionlive.com/view/examining-disease-characteristics-and-patterns-of-weight-gain-in-tuberculosis-treatment
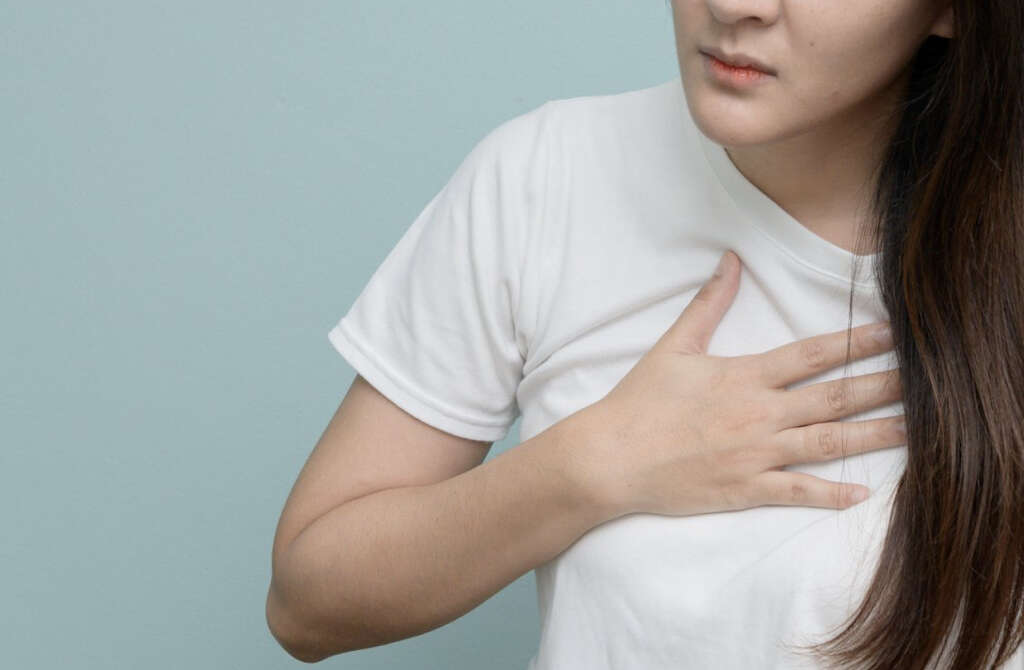
10. Chest Pains
Chest pain is occasionally the presenting symptom in a TB diagnosis. It can be directly related to lung damage, but it is more commonly associated with muscular pain and discomfort. In some patients, it may be due to nerve damage in the area of infection.
Chest pain can range from mild discomfort to intense, sharp pains. The violent coughing associated with TB only exacerbates the discomfort. While it is not the primary cause, lung involvement in pulmonary tuberculosis can also lead to chest pains.
Advertisement



-06.jpg)