10 Fluid In Lungs Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Pulmonary Edema.' Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009
- 2. 'Pulmonary Edema.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000140.htm
- 3. 'Pulmonary Edema.' Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/condition/pulmonary-edema
- 4. Team, Heart and Vascular. 'Persistent Cough? It May Be a Sign of Heart Failure.' Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, health.clevelandclinic.org/persistent-cough-it-may-be-a-sign-of-heart-failure
- 5. Cyanosis By Rebecca Dezube, et al. 'Cyanosis - Lung and Airway Disorders.' Merck Manuals Consumer Version, www.merckmanuals.com/home/lung-and-airway-disorders/symptoms-of-lung-disorders/cyanosis
- 6. 'Pulmonary Edema.' Penn Medicine, www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/pulmonary-edema
- 7. Tidy, Dr Colin. 'Acute Pulmonary Oedema. What Is a Pulmonary Oedema?' Patient.info, 3 Jan. 2018, patient.info/doctor/acute-pulmonary-oedema
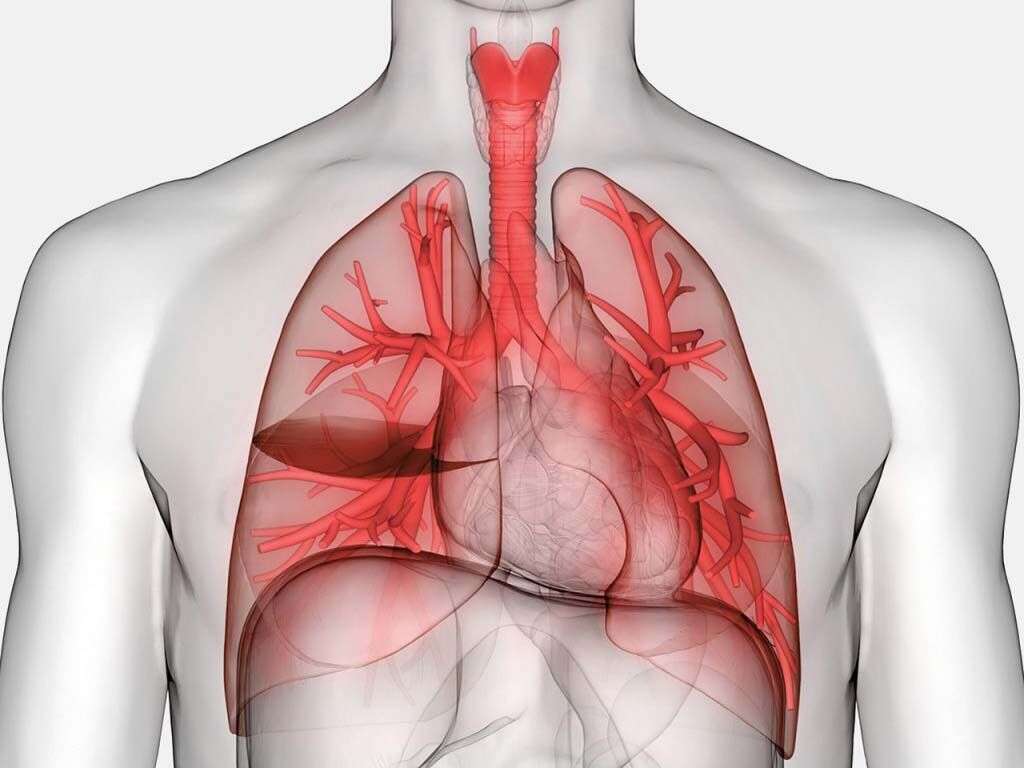
Fluid in the lungs, or pulmonary edema, is a condition in which the air sacs in the lungs fill with fluid. Issues involving the heart commonly cause fluid to develop in the lungs, but other causes may include injury to the chest wall, pneumonia and exposure to toxins, chemicals or medications. A person traveling to or exercising in high altitudes where the air contains less oxygen may also develop fluid in the lungs.
Sometimes fluid accumulates in the lungs slowly, causing few symptoms and dissipating without treatment. In other cases, pulmonary edema develops quickly and may be life-threatening, making immediate treatment critical.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009
Breathing Difficulty
A person with fluid in the lungs may experience a great deal of difficulty breathing or exhibit extreme shortness of breath, especially when lying down. The person may wheeze, grunt and gurgle, gasp for air and have trouble speaking in full sentences.
Pulmonary edema may cause a person to feel as if they're drowning or suffocating. Sometimes referred to as air hunger, this sensation may also worsen when lying down. Some people experience this feeling an hour or two after they fall asleep. It may cause them to wake up, struggling to breathe.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009,2‘Pulmonary Edema.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000140.htm

Cough
Coughing may develop in a person with fluid in the lungs. They may cough up blood, their sputum may be tinged with blood or they may have pink, frothy mucus coming from their nose or mouth.2‘Pulmonary Edema.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000140.htm,3‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/condition/pulmonary-edema
This symptom commonly arises in people with heart failure. As the fluid builds up in the lungs, the body responds by coughing in an effort to expel the fluid from the lungs.4Team, Heart and Vascular. ‘Persistent Cough? It May Be a Sign of Heart Failure.’ Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, health.clevelandclinic.org/persistent-cough-it-may-be-a-sign-of-heart-failure

Appearance
A person with fluid in their lungs may look pale, and their skin may be cold and clammy. They may also perspire profusely.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009,2‘Pulmonary Edema.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000140.htm
Due to the diminished oxygen supply in the body, cyanosis may develop, causing the skin and lips to have a bluish tinge. It's usually caused by the low oxygen levels in the red blood cells or problems getting oxygenated blood to the body extremities.5Cyanosis By Rebecca Dezube, et al. ‘Cyanosis - Lung and Airway Disorders.’ Merck Manuals Consumer Version, www.merckmanuals.com/home/lung-and-airway-disorders/symptoms-of-lung-disorders/cyanosis

Behavioral Symptoms
Along with the feeling of air hunger, a person with fluid in their lungs may exhibit behavioral changes, such as anxiety and/or restlessness. They may also be less alert than usual.
People with fluid in the lungs usually receive emergency treatment that helps alleviate these symptoms. Administering oxygen through a face mask or ventilator is commonly necessary. Diuretics may help eliminate fluid in the lungs, but treatment of the underlying condition is necessary to resolve the symptoms.2‘Pulmonary Edema.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000140.htm

Heart-Related Symptoms and Chest Pain
When a person is experiencing symptoms resulting from fluid in their lungs, their heart rate is typically affected. The heart rate may be elevated, with very rapid heartbeats. Irregular heartbeats, known as palpitations, may also occur.
Chest pain or tightness may develop in people with fluid in their lungs. Weakness and fatigue are some other possible symptoms that may accompany the cough and breathing issues that people with fluid in their lungs experience.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009

Clinical Symptoms
To diagnose fluid in the lungs, a doctor notes the outward manifestations, such as breathing problems and bluish skin, and conducts a physical examination. They may note the distension of the neck veins, since abnormalities may indicate the presence of excess fluid in the body.
When using a stethoscope to listen to the lungs, they may hear crackling sounds, and a chest X-ray may confirm the presence of fluid in the lungs. They may also check for low blood oxygen levels with pulse oximeters.6‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Penn Medicine, www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/pulmonary-edema

Acute Pulmonary Edema Symptoms
Fluid in the lungs may develop quickly, known as acute pulmonary edema, and it can be a frightening experience for the person. Extreme breathing difficulty, profuse sweating and bluish skin, lips and nails are among the signs of acute pulmonary edema.
The person may feel nauseous and anxious and have a dry or productive cough. A health care provider's examination may reveal a fast heart rate, crackles in the lungs and congested neck veins.7Tidy, Dr Colin. ‘Acute Pulmonary Oedema. What Is a Pulmonary Oedema?’ Patient.info, 3 Jan. 2018, patient.info/doctor/acute-pulmonary-oedema

Chronic Pulmonary Edema Symptoms
Some people experience fluid in the lungs over a long period of time, which is known as chronic pulmonary edema. Breathing issues may develop when they're lying flat or engaging in physical exercise. They may experience shortness of breath or coughing that awakens them at night, and the symptoms may be alleviated when they sit up.
Other symptoms may include wheezing, a cough that worsens over time, fatigue and swelling of the lower extremities. Some weight gain may also be noticed.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009

High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema Symptoms
People who travel to or exercise in high-altitude areas may develop fluid in the lungs, also known as high-altitude pulmonary edema, or HAPE. Their symptoms may be worse at night.
A headache may be the first sign of HAPE, and the person may notice shortness of breath during exercise. They may feel weak and have chest pain and a low-grade fever. A dry cough may develop, later becoming productive with a frothy, pink sputum.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009

When To See a Doctor
When symptoms of fluid in the lungs develop quickly, a person should seek immediate medical attention. Significant shortness of breath, breathing difficulties, wheezing when breathing, profuse sweating and a bluish tinge to the skin and lips may indicate fluid in the lungs requiring emergency medical intervention.
Confusion or a major drop in blood pressure that causes dizziness, lightheadedness and weakness are also indications that medical care is necessary. A person whose pulmonary edema symptoms suddenly worsen should also obtain medical care.1‘Pulmonary Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009