What Is Stromme Syndrome?
The DNA that makes up who we are is extremely complex. There is a vast amount of information involved and this means that there is also a lot that can go wrong when this information is being passed over. This does occasionally happen, and this can result in some rather profound conditions.
Stromme syndrome is a genetic condition that can lead to a number of genetic mutations. The severity of the symptoms can vary considerably, and some patients will not survive for long after being born. Here we take a closer look at what Stromme syndrome is, and some of the symptoms it causes.

1. Petter Stromme
Stromme syndrome is named after Petter Stromme. Stromme is a Norwegian pediatrician who first identified the condition in two siblings. It was named after him in 2008 when another case was being studied by Van Bever et al. The condition is very rare and, since 2017, only 13 people have been diagnosed to have the condition. Stromme syndrome is an autosomal recessive genetic condition. This means that in order for the syndrome to be present, the abnormal gene responsible must be present in both of the parents DNA. The gene must also be present in both copies in their offspring.
2. Physical Characteristics
Patients with Stromme syndrome will display a number of physical characteristics that will help medical professionals identify the condition. Patients with the syndrome are likely to be shorter than other people. In addition, they are likely to have a high nasal bridge, and a large mouth with a small jaw. They are also likely to have larger than usual ears that are set low down.
Epicanthal folds, which are folds of skin in the upper eyelid, are also a possibility and many patients with Stromme syndrome will have hair that is fine and sparse. A number of patients will have a cleft palate, and some will have skin tags.

3. Intestines
Patients with the condition will usually have intestinal problems. One such problem is intestinal atresia, which means that some parts of the intestine are narrower than usual, or even missing altogether. This will lead to an obstruction of the bowels and, in many cases, this will need to be operated on if the child is to survive. In some cases, there will be intestinal malrotation.
This means that instead of forming a coil as usual, the intestines will instead become twisted. This can also lead to blockages and must be operated on. Those with more severe intestinal conditions are less likely to survive.

4. Heart
Our heart has 4 chambers: 2 ventricles and 2 atria. The smaller chambers, the atria, are separated by a wall known as a septum. This wall prevents the blood in either atria from mixing as the atria fill. In some instances of Stromme syndrome, the patient will have an atrial septal defect, which means that there is a hole in the wall. Patent foramen ovale, a particular type of atrial septal defect, can also occur.
This condition can also occur in the ventricles. Heart problems like this can lead to neonatal peripheral edema (swelling). Some patients will have smaller than usual heart muscle cells and less muscle tissue in the heart.
5. Skeletal
Stromme syndrome can also lead to problems with the patients skeleton. One example is hip dysplasia. This is a condition in which the bone of the hip socket does not cover the ball of the upper thigh bone. This means that dislocation of the joint is very easy, and dislocations can be very painful for patients.
Metopic craniosynostosis can also occur, which leaves the patient with a ridge at the front of their head. A sternal cleft is also a possibility, while some patients will have platyspondyly (flattened vertebrae). Some of these conditions are operable to help restore some of their quality of life.

6. Kidneys
Healthy kidneys are extremely important to us because they help to remove toxins from the body. Without them, our bodies will become increasingly toxic until we simply die. Dialysis can help, while kidney transplants are a possibility in some cases.
Stromme syndrome can cause kidneys to be malformed and underdeveloped. Hydronephrosis is also a possibility, which means that urine will build up in the bladder because it has no passage out of the body. Depending on the cause, surgery may be necessary to save the patients life. This can occur because the ureter, which channels urine from the bladder, is underdeveloped or blocked.
7. Blood
Healthy blood is also essential for our well-being because it transports oxygen and essential nutrients around the body to where they are needed. This includes the ability for the blood to clot when the blood vessels are damaged, otherwise the patient might bleed to death even from the smallest of cuts.
Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which the patient has fewer platelets than usual. Platelets are cells that bind together when needed to form a clot, thus blocking damage in blood vessels and preventing blood from escaping. This condition has only been found in one patient with Stromme syndrome so far.

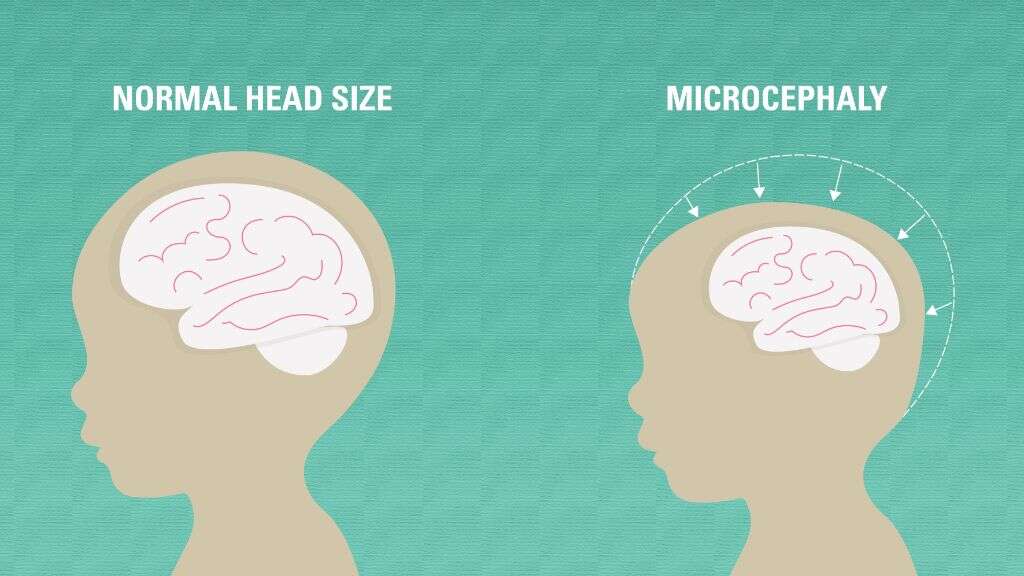
8. Brain
The majority of patients with Stromme syndrome will have microcephaly. This is a condition where the circumference of the patients head is considerably smaller than usual. The patient might also have shallower ridges in the brain than usual (lissencephaly), and/or fewer ridges (pachygyria). The severity of these conditions will vary from patient to patient.
Hydrocephalus is also a possibility. This is a condition in which there is a build up of fluid within the brain. This can cause the skull to be larger than usual, while it will also place more pressure on the brain. This latter condition is not necessarily dangerous provided the patient is operated on in time.
9. Eyes
Patients with Stromme syndrome can also find that they are born with problems with their eyes. Quite often, their eyes will be underdeveloped and smaller than usual. It is usually the case that one eye is more affected than the other. Other problems can include cataracts, leukoma, which is an opaque cornea, coloboma, which is a hole in the iris, and sclerocornea, which is when the cornea blends in with the whites of the eyes.
There are a number of other conditions that patients can have, and their impact can range from causing a slight decrease in their quality of vision, to making the patient blind.

10. Treatment
There is as yet no cure available for Stromme syndrome, but the patient can often be treated to at least help ensure their survival and/or enhance their quality of life. Many patients will need to undergo surgery on their digestive system, and/or on their heart. Sadly, many children with the condition will die shortly after they have been born or even before they are born.
With medical assistance, however, the majority will survive and will even manage to live well into their adolescence at least. Their condition, however, will make it very difficult for the patient to lead a normal life.