What Is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
9. Diagnosis
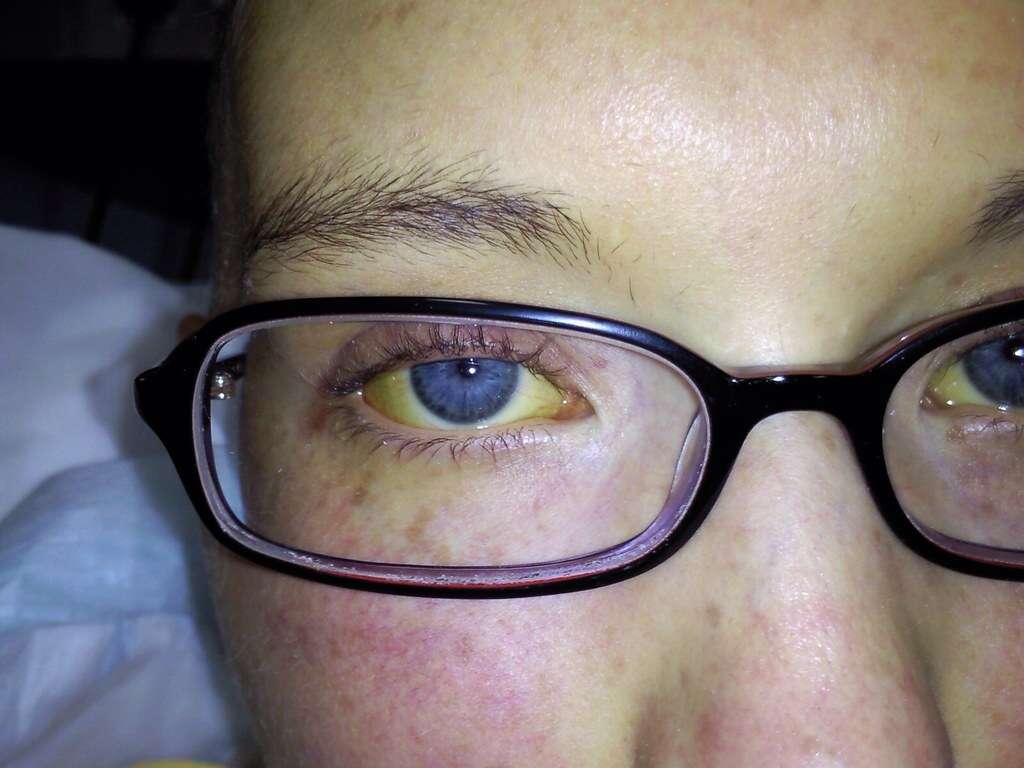
As mentioned above, some patients with primary biliary cholangitis are incidentally diagnosed during routine blood work. Physicians can be alerted by significant elevations of enzymes in liver function tests that signal liver disease and bile duct injury. Thus, aminotransferases (ALT and AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and ᵧ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP)can be high. Furthermore, as mentioned above patients with PBC can present with hypercholesterolemia. Thus, physicians should also measure lipid and cholesterol levels in the blood. Also, antibody tests for signs of autoimmune disease can be useful for diagnosis. Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) can be found in almost 95% of patients with primary biliary disease. These antibodies seldom occur in people without the condition. Thus, a positive anti-mitochondrial antibody test is a reliable sign of the disease. Nevertheless, a small number of patients with the condition don’t exhibit AMAs.
Imaging studies can be useful to exclude obstruction of the biliary tract (CT or MRI), to diagnose portal hypertension (a consequence of cirrhosis) and its consequences, and to evaluate liver tissue.
Advertisement