10 Jaundice Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Jaundice.' NHS.uk, 30 Jan. 2018, www.nhs.uk/conditions/jaundice
- 2. Gillott, Caroline. 'Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.' Medical and Health Information, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165749#symptoms
- 3. 'Jaundice.' Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/jaundice
- 4. 'Stools - Pale or Clay-colored.' MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003129.htm
- 5. 'Common Characteristics of Liver Disease.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/common-characteristics-of-liver-disease
- 6. Bassari, Ramez, and Johnathan B. Koea. 'Jaundice Associated Pruritis: A Review of Pathophysiology and Treatment.' PubMed Central (PMC), Feb. 7, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4316083/
- 7. Suely Falcão de Oliveira Melo, Norma, et al. 'Green Teeth Resulting from Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Report of a Case.' ScienceDirect.com | Science, Health and Medical Journals, Full Text Articles and Books, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031393914003199
Jaundice is a medical condition that primarily affects the color of the skin and eyes. It's caused by a buildup in the blood of a substance called bilirubin. There are several signs and symptoms, both common and less-typical, associated with jaundice.
Jaundice is fairly common in newborn babies. While it often resolves by itself, parents should consult a doctor if their baby is jaundiced. For adults, there are a range of possible causes of bilirubin buildup leading to jaundice, including problems with the gallbladder, pancreas, liver or blood. People should seek prompt medical advice if they notice jaundice.1‘Jaundice.’ NHS.uk, 30 Jan. 2018, www.nhs.uk/conditions/jaundice
Yellow Skin
One of the most common symptoms of jaundice is discolored skin that has a yellowish tinge. The abnormal color may darken to shades of brown and become more noticeable as jaundice worsens. People commonly notice this discoloration on the face and head first, although yellowing of the skin can occur anywhere on the body.
Bilirubin is a yellow-colored pigment that is naturally present in red blood cells. When cells die, the liver filters waste bilirubin out of the blood. When the liver is unable to effectively remove the substance, it builds up in the body and its distinct color is visible through the skin.2Gillott, Caroline. ‘Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.’ Medical and Health Information, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165749#symptoms
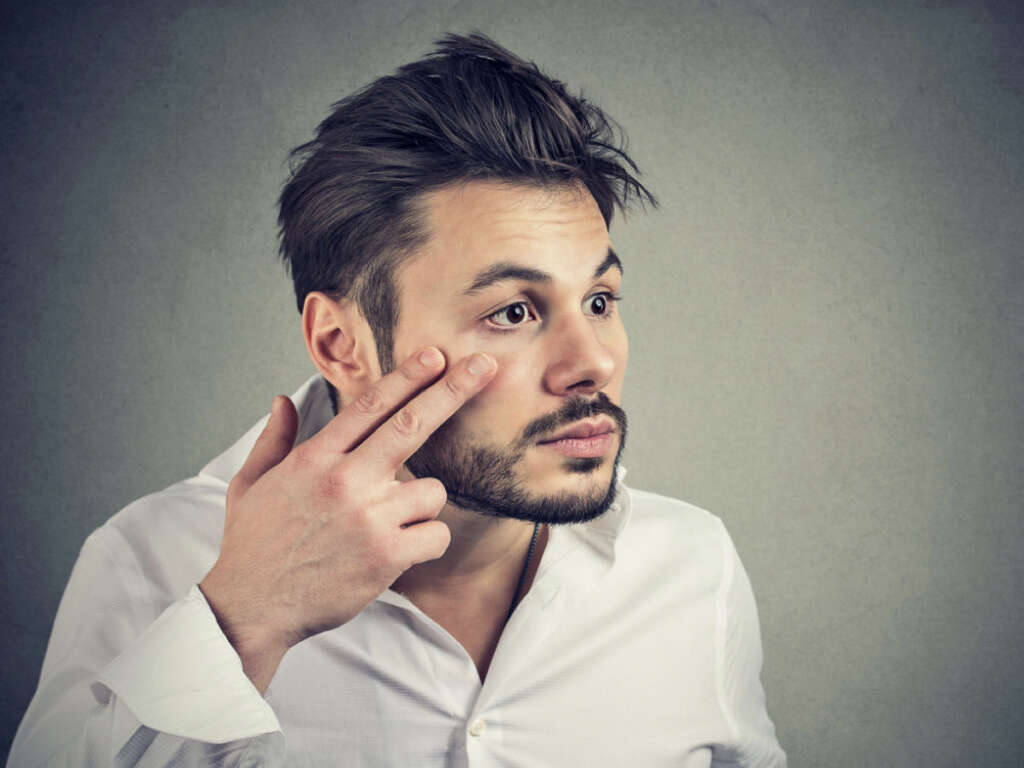
Yellow Eyes
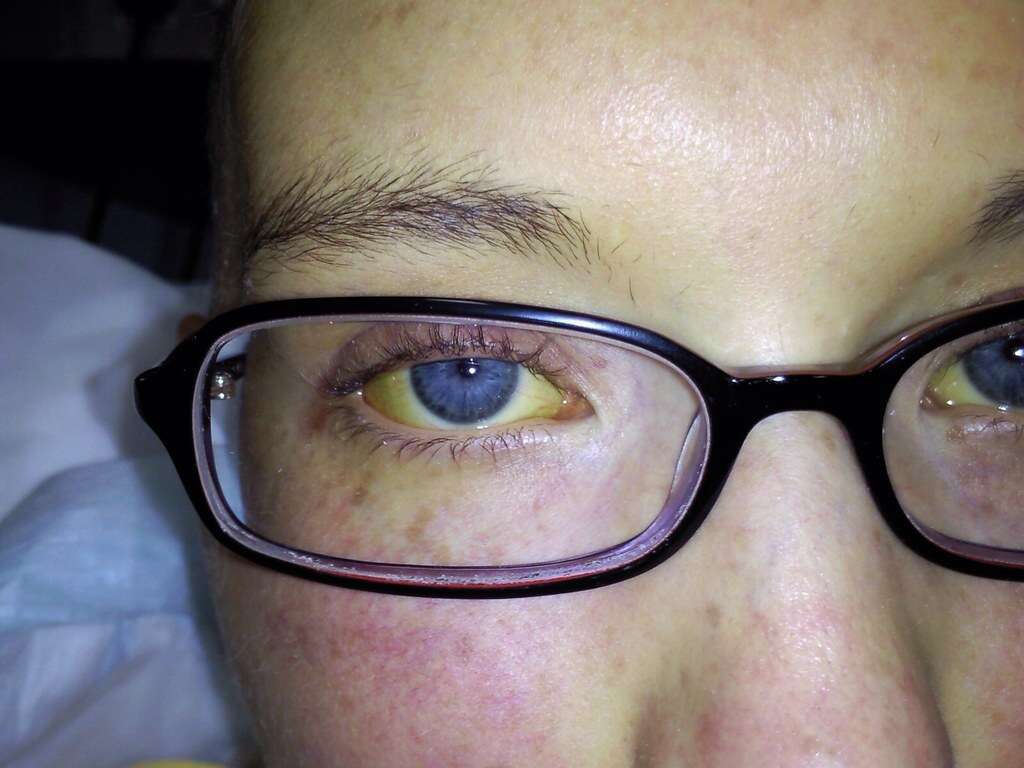
Yellow eyes is another common symptom of jaundice, where the white of the eye appears yellow. The discoloration normally starts at the outer edges of the eye, spreading inward toward the iris. In severe cases of jaundice, there may be no white visible.
Increased amounts of bilirubin in the body causes yellowing of the eyes. It's important to note that if a person has yellowing of the skin but not of the eyes, the discoloration is unlikely to be caused by jaundice.3‘Jaundice.’ Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/jaundice
Pale Feces
When jaundiced, a person may notice that their stools are paler than normal. Instead of waste matter being brown, it can become clay colored and much lighter than usual.4‘Stools - Pale or Clay-colored.’ MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003129.htm
The absence of normal color of the fecal matter may be due to the yellow-orange substance bilirubin not reaching the gastrointestinal tract via the biliary system. Bilirubin can't then be excreted from the body in the feces. This can occur when the liver fails to process the compound and it remains in the bloodstream.

Dark Urine
Dark urine, as a sign of jaundice, commonly occurs along with pale stools. The color of a person's urine may appear as dark yellow or brown. When urine appears dark due to jaundice, the smell isn't affected.
Bilirubin normally exits the body in a person's fecal matter. However, if the liver is unable to remove the pigment, it can pass through the kidneys instead and its yellow-orange color can darken the urine that's excreted.5‘Common Characteristics of Liver Disease.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/common-characteristics-of-liver-disease

Itchiness
Many people experience severe itching when they're jaundiced. This itching may start before other jaundice symptoms. Itchiness, known medically as pruritus, can be one of the most bothersome and uncomfortable symptoms of jaundice. It can occur all over the body and is typically worse at night.
The exact cause of itchiness associated with jaundice isn't known, although some research suggests that an excess of bilirubin in the body stimulates sensory neurons close to the surface of the skin.6Bassari, Ramez, and Johnathan B. Koea. ‘Jaundice Associated Pruritis: A Review of Pathophysiology and Treatment.’ PubMed Central (PMC), Feb. 7, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4316083/

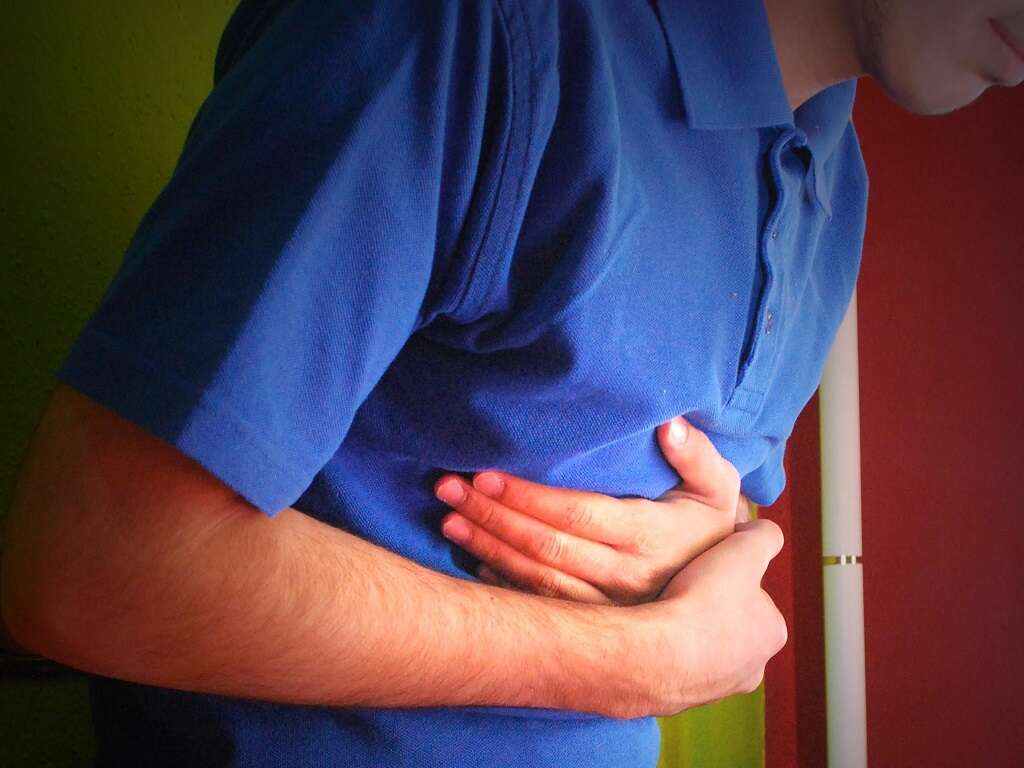
Abdominal Pain
Some people can experience pain in the abdomen when they have jaundice. The presence and severity of abdominal pain depends on the underlying cause of the condition. When present, pain can be constant or sporadic, and sometimes pain is only felt when the abdomen is touched.
Pain commonly occurs when jaundice is caused by cancer of the pancreas or in the biliary tract. Less commonly, pain may be an indication of an acute viral condition, such as hepatitis.

Fatigue
Sometimes, jaundice is accompanied by extreme tiredness. This fatigue can be severe enough to interfere with a person's quality of life and prevent them from performing their usual day-to-day activities. The presence of fatigue depends on the cause of the jaundice.
When a person experiences fatigue with jaundice, it commonly occurs when the condition is caused by a virus. Extreme fatigue may also be a symptom of the underlying cause of the jaundice, and not the jaundice itself.

Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting may occur with jaundice. As with other symptoms, whether a person experiences nausea or vomiting depends on the underlying cause of the jaundice. Severe liver disease or viral inflammation of the liver are two possible reasons why people may experience these symptoms when jaundiced.
Both nausea and vomiting cause discomfort. Excessive vomiting can lead to other issues if not promptly managed, such as dehydration and weight loss.

Yellow Inside the Mouth
A person with jaundice may notice the inside of their mouth turning yellow. This discoloration commonly affects the roof of the mouth more than the inside of the cheeks. Rarely, the tongue can look yellow as well. There's usually no associated pain in the mouth.
As with yellowing of the skin and eyes, jaundice causes changes to the color of the tissue inside the mouth due to raised levels of yellow-colored bilirubin in the body.

Discolored Teeth
Jaundice can cause a child's teeth to appear yellow or green. This rare symptom seems to affect young children and not adults.
The change in tooth color can occur during the baby's development when excess bilirubin is deposited on the tooth enamel during the calcification process. Because this discoloration occurs during the growth of the tooth, it appears to be permanent until the tooth falls out. The levels of bilirubin in the blood are higher than normal .7Suely Falcão de Oliveira Melo, Norma, et al. ‘Green Teeth Resulting from Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Report of a Case.’ ScienceDirect.com | Science, Health and Medical Journals, Full Text Articles and Books, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031393914003199