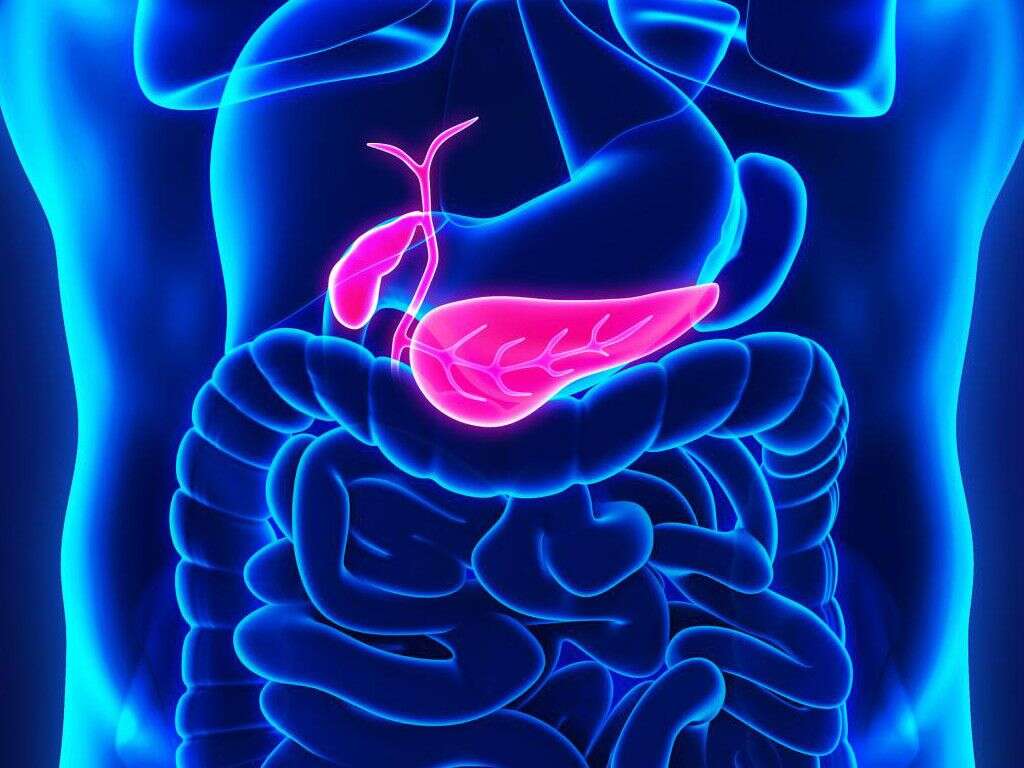
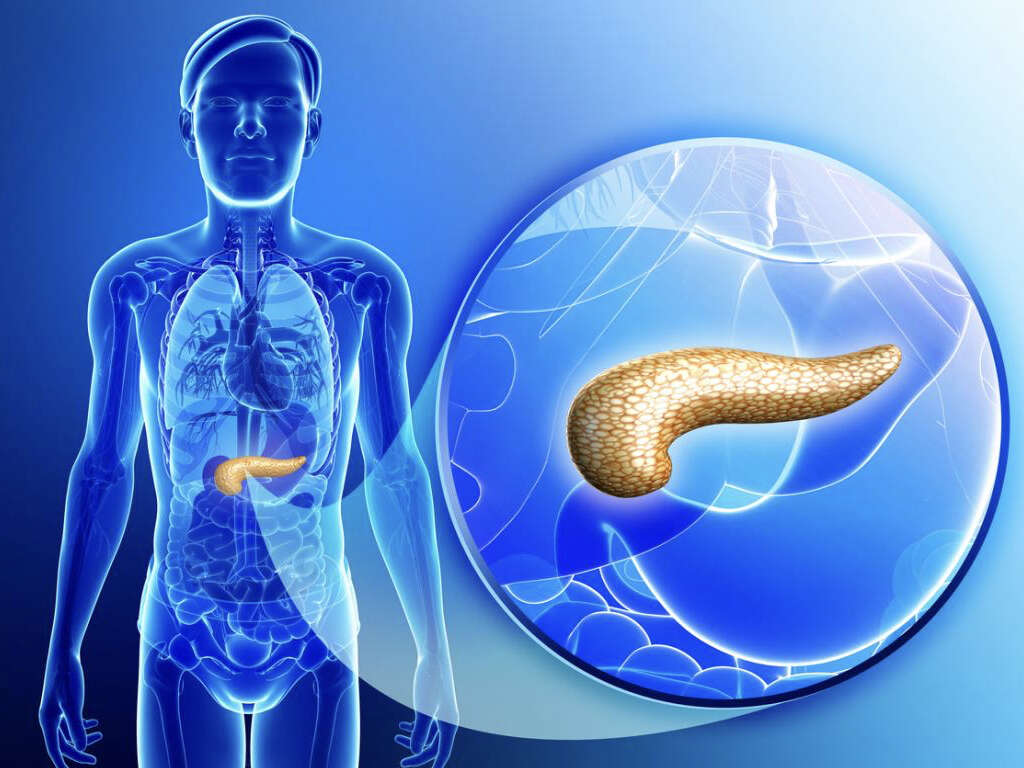
What Is Pancreatic Cancer?
The pancreas is an organ that is a part of the digestive system. It is roughly pear shaped and is around 6 inches long. One of its functions is to secrete enzymes that help us digest our food. It also secretes insulin, which is needed to help us process sugar in our body.
Cancers can affect all of our body parts, and pancreatic cancer is no different. Although we are able to survive without a pancreas with help from medicine, pancreatic cancer will spread to other essential organs also. Pancreatic cancer is especially difficult to treat, and survival rates are very low.
1. Pancreatic Cancer
As with so many other parts of the body, the pancreas can develop different types of growth. Some of these can be cancerous. When they do cause cancer, the most common type is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. This type affects the cells in tubes that allow digestive enzymes to pass out of the organ.
As is the case with other types of cancer, pancreatic cancer is easier to treat the sooner it is diagnosed. However, pancreatic cancer tends not to cause any symptoms in the early stages, meaning it will often go missed until the cancer has progressed. This makes it one of the more dangerous types of cancer, with a fatality rate of approximately 95%.
2. Causes
The causes of pancreatic cancer are not clearly understood. However, some factors have been associated with the disease, including smoking. Some genetic mutations that have been inherited are also associated with pancreatic cancer. We do also know that mutations in the patient’s DNA cause cancer to develop.
When a cell has reached the end of its life, it is usually processed by the body and replaced by a new cell. With cancers, however, cells will begin to grow out of control, resulting in what is known as tumors. Tumors are not usually cancerous, but when they are, they will spread to other parts of the body as they grow.

3. Symptoms
As mentioned, the symptoms of pancreatic cancer won’t show in the early stages of the disease. When they do show, they will typically include a pain in the abdomen which will radiate out to the back. The patient will also develop jaundice, giving them yellow skin which can also be itchy.
Pancreatic cancer will also cause the patient to lose their appetite, and they will also begin losing weight. Their urine will become darker and their stools will become lighter in color. The patient can start to develop blood clots and they can feel fatigued. They might also develop diabetes, and existing cases of diabetes can worsen.
4. Complications
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, pancreatic cancer will go on to develop severe complications. One of these is that as the tumor grows, it will begin to put pressure on surrounding tissues. This includes pressure on surrounding nerves, and this can become extremely painful for the patient.
Pancreatic cancer can also cause blockages of the digestive system, which can also be very dangerous. As the cancer spreads, it can begin to take over other nearby organs, including the liver. This will cause the liver to begin to fail, and liver failure is the most common cause of death in patients with pancreatic cancer.
5. Who’s At Risk?
Nobody is completely safe from pancreatic cancer, but some people are at a higher risk than others. Pancreatic cancer can affect people of all ages, but the over 65s are in a higher risk group. Somebody is also more likely to develop pancreatic cancer if there is a history of certain genetic mutations in their family.
A family history of pancreatic cancer will also make somebody more prone to the disease. Having pancreatitis, which is the chronic inflammation of the pancreas, will also make somebody more prone to pancreatic cancer. People who smoke are in a higher risk category, as are people who are obese, and those who eat a poor diet.
6. Prevention
You cannot make yourself completely safe from pancreatic cancer, but you can at least reduce your risk. One way to help achieve this is to eat a healthy diet. This means limiting how many processed foods you eat and eating plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Not smoking can also make a big difference.
You can also reduce your risk of pancreatic cancer by maintaining a healthy weight. This can be achieved with a healthy diet and plenty of exercise, and this will give you further health benefits also. If there is a history of the condition in your family, you can speak with a genetic counselor to see what your risks are.

7. Diagnosis
A doctor will need to ask you what your symptoms are, and also about history of the condition in your family. If pancreatic cancer or similar is suspected, there are tests that will help to confirm the diagnosis. A blood sample will likely be taken, and this will help the experts look for signs of pancreatic cancer.
Imaging technology may also be used to help get images of the pancreas and the surrounding organs. These include PET scans, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasound. Doctors will also often need to take a sample of the pancreas so it can be examined.
8. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves medication that will help to kill the cancerous cells. While it is not a cure for pancreatic cancer, it can at least help to slow the progress of the cancer. Chemotherapy medication can be taken orally, and it will also be administered intravenously in some cases.
Chemotherapy comes with some unpleasant side effects, and it will often cause the patient to feel even more fatigued than they are already. Hair loss is another symptom, as is pain, a loss of appetite, easy bruising, and bleeding. Chemotherapy can help to slow the progress of cancer, and it will often be used in combination with radiation therapy.

9. Radiation therapy
As mentioned, radiation therapy is a treatment method that is often used in combination with chemotherapy. It works by exposing the pancreas X-ray beams or proton beams, and these beams will contain particles that will help destroy cancerous cells.
Although radiation can be effective, its usage has to be limited. This is because, in addition to destroying cancer cells, the beams can also kill nearby healthy cells. Typical symptoms include fatigue, skin problems, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, bladder and bowel problems, and bleeding. Advances in technology mean that radiation is becoming more effective, and it is also likely to cause fewer symptoms.
10. Surgery
In many cases, surgery will be recommended, and there are different types of surgery available. Which type of surgery that’s recommended will depend on the nature of the condition. One option is for certain parts of the spleen to be removed, depending on where about the cancer is located.
In some cases, the Whipple procedure will be performed. This involves the removal of parts of several organs. Other procedures will involve reconstructing blood vessels that have been affected by the tumor. Surgical procedures involving pancreatic cancer tend to be very complex, and highly experienced surgeons will often be required to perform the procedure.