What Is Jaundice?
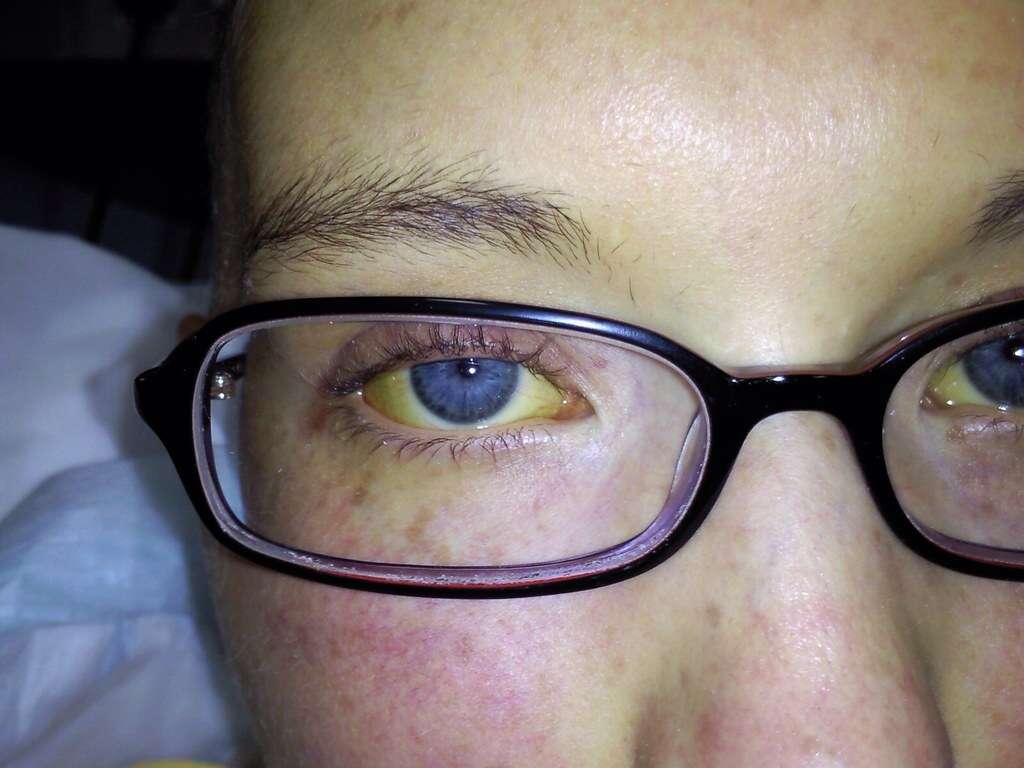
Jaundice is a relatively common condition that causes the patient to take on a noticeable yellow tinge. The yellow color is often more noticeable in the eyes and in parts where the skin is thin. While the yellow appearance can be quite startling, jaundice is not something that is necessarily dangerous in itself.
Although not usually dangerous, jaundice is often a sign of a potentially serious underlying problem so treatment should be sought. Depending on the underlying cause, treatment can be straightforward, while sometimes the cause can be a lot more difficult to deal with. Here’s a closer look at what jaundice is and what causes it.

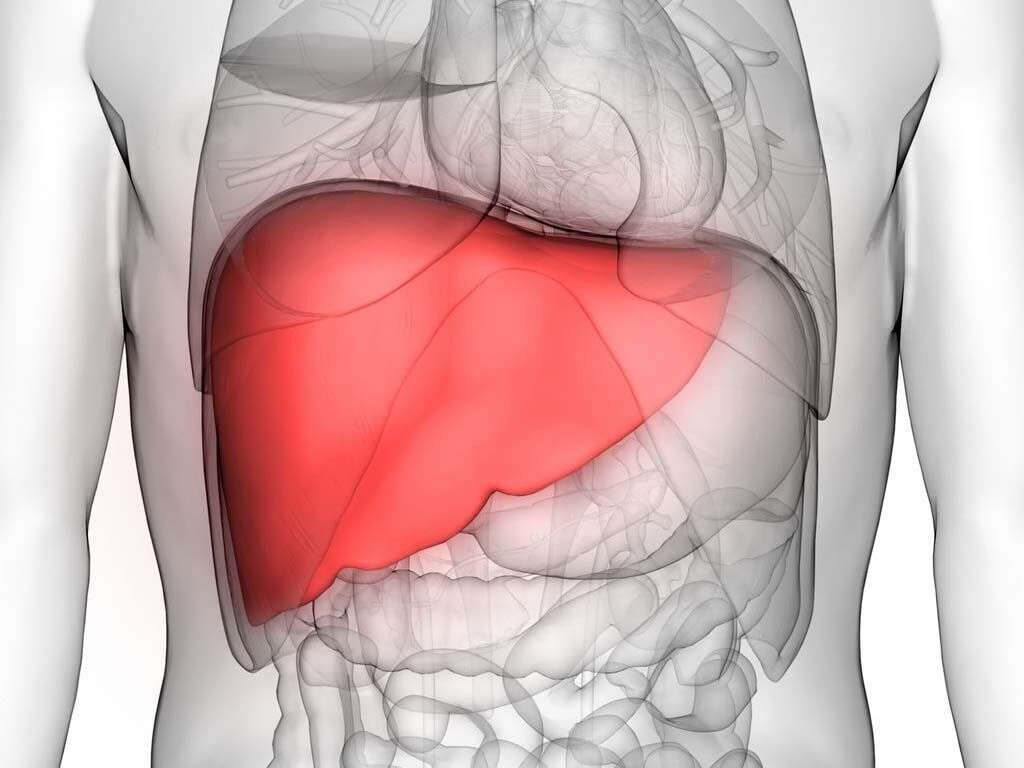
1. Bilirubin
Our red blood cells have a life span of approximately 4 months when they are in our body. When they have come to the end of their lives, they are broken down by our livers, and fresh blood cells will take their place. When blood cells are broken down in this way, a substance known as bilirubin is formed, and this bilirubin is used to help make bile. If there was something wrong with the liver then the bilirubin would not be processed normally. This can mean that bilirubin is found flowing through the blood and, considering bilirubins yellow color, the patient will take on a yellow color themselves.
2. Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
Jaundice can be broken down into different categories, one of which is pre-hepatic. The term applies to the fact that the issue occurs before the liver produces bile. It is caused when the rate of destruction of the red blood cells is considerably higher than it usually would be.
This increased rate of red blood cell breakdown results in a higher than usual volume of bilirubin, and the liver is sometimes unable to keep up with the increased workload. This then results in higher levels of bilirubin in the blood, giving the patient that characteristic yellow appearance that makes jaundice so recognizable.
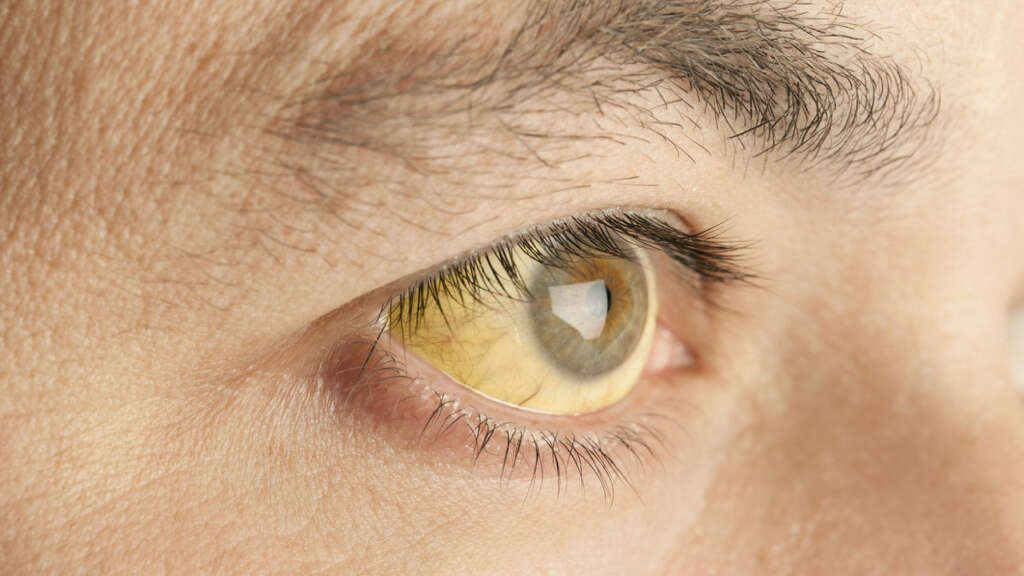
3. Hepatic Jaundice
Another category of jaundice is hepatic jaundice, and this refers to when the condition is caused by problems with the liver. In such instances, the livers ability to process the bilirubin is impaired, and this means that excess volumes of bilirubin are found in the patients blood. Among the most common causes of this is hepatitis, which is an inflammation of the liver.
This can be caused by a number of things, including infections and excess alcohol consumption. Cirrhosis (damage) of the liver is another potential cause, as is the use of some drugs. It could also be a sign that the patient has cancer.

4. Post-Hepatic Jaundice
Post-hepatic jaundice, also known as obstructive jaundice, is a condition caused by an obstruction that prevents the bilirubin from draining into the intestines in the form of bile. One of the most common causes of this condition is gallstones located in the bile ducts.
Another potential cause of this condition is parasites that could physically block the bilirubin. Pancreatitis is also a potential cause, as is cancer of the gallbladder and/or pancreas. Because it can be a sign of something potentially serious, it is a good idea to see a doctor if your skin has taken on a yellow appearance.

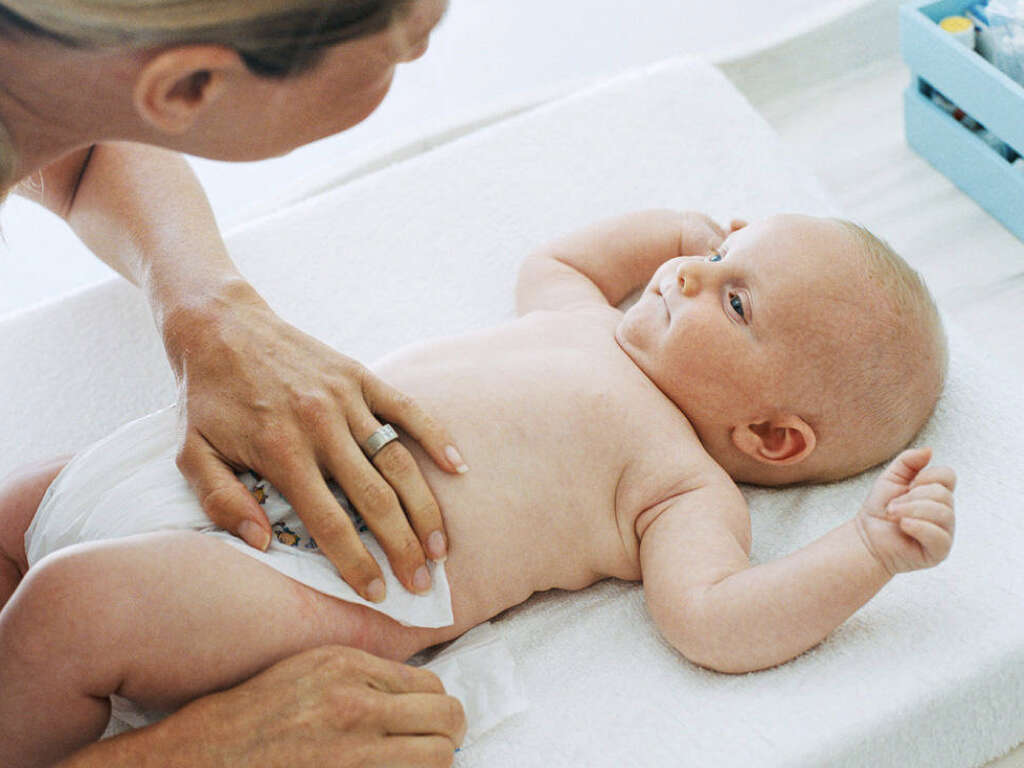
5. Physiological Jaundice
Jaundice is relatively common among newborn babies. It can, of course, be alarming for all involved, but the good news is that it is usually nothing to worry about. In many cases, it is simply a matter of the child’s young liver not yet being able to break down the bilirubin being produced. The symptoms of physiological jaundice will generally appear at around 2-3 days after birth. The condition will usually pass without having done any lasting damage once the liver is able to process the bilirubin as it is produced.
The condition is also unlikely to cause any other symptoms other than the yellow complexion; however, it is important to notify your child’s care provider if they exhibit jaundice because, unchecked, serious problems can ensue.

6. Cephalohematoma
Newborn babies are very delicate and it can be very easy to rupture their fragile blood vessels. Regardless, some babies might have a relatively rough time during the birthing process, and this can lead to injuries. One example is cephalohematoma; usually a minor injury that results in blood collecting just beneath the scalp.
This pooled blood will then need to be broken down by the body, and this will result in a higher volume of bilirubin being produced. The livers of newborn babies are often unable to handle this extra bilirubin, meaning the baby is likely to develop jaundice as a result.

7. Maternal-Fetal Blood Group Incompatibility
There are 8 blood groups in total and, when getting a blood transfusion, it is important that the right type of blood is used to prevent the patient from getting problems. We don’t necessarily get the same blood type as our parents, and there are occasional incompatibility problems between mother and baby.
This is known as maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility and it can lead to a number of symptoms. One of these symptoms is jaundice as the incompatibility causes hemolysis, which is the breaking down of the child’s red blood cells. This can, in turn, cause the patient to develop jaundice.

8. Breastfeeding Jaundice
All people need nutrition, but newborn babies need it more than anybody else. They need the nutrition in order to grow as quickly as possible and they are also entirely dependent on their parents for food. In the majority of cases, this means drinking milk from their mothers breasts. It is important that the mother feeds the baby all the milk they need, but this does not always occur.
Some babies are, unfortunately, victims of neglect. In addition, some mothers are unable to produce the necessary volume of milk for their baby. This can result in a number of unwelcome symptoms, and jaundice is one of them.

9. Breast Milk Jaundice
As mentioned, a mothers milk is very important for the well-being of a newborn baby as it is packed full of the nutrition that they need. Sometimes, however, breast milk can cause unexpected symptoms when consumed by a baby. One such symptom is jaundice. Breast milk jaundice is thought to be down to the presence of certain chemicals in breast milk.
Thankfully it is not usually a harmful condition for the baby and it should go away with no harm being done. It is usually fine for the mother to continue breast feeding without risk to the baby; however, as with any signs of jaundice, it is important to alert the child’s care provider to ensure quick cessation of signs.

10. Other Symptoms
While yellow skin is perhaps the most recognizable symptom of jaundice, it is not the only symptom that comes with the condition. Other symptoms include fever, headache, confusions, swellings, nausea, weakness, loss of appetite, and pain in the abdomen. In newborns, yellow skin will generally be noticed in the head first and it will gradually move to the trunk and then onto the limbs.
Other symptoms include lethargy, high pitched crying, change in tone of the muscles, and a poor appetite. Some babies with jaundice might also experience seizures. Medical assistance should always be sought for any baby that is showing symptoms of jaundice.