What Is Hypermobility Syndrome?
If you try to stretch your arm out straight, you will find that it will only extend so far. This is the same for everybody and most people will find that they can bend their joints to roughly the same amount. Some people can bend them more than others can, however.
Hypermobility syndrome is a condition where people are able to bend their joints more than other people can. It is often a harmless condition and can even be a sense of amusement. At other times, however, it can be more serious and can result in some very unwelcome complications.

1. Joints
Without joints, we would not be able to move around as we do. Without joints, our skeletons would remain rigid and we would not be able to bend our legs, our arms, and move other body parts. Some animal species that don’t have internal skeletons have no need for joints, but humans do need them.
Our joints are made up of several components. These include the ends of the bones where they meet each other. Joints also typically have relatively soft cartilage that helps provide a protective cushion. Many of our joints are also held together with the help of ligaments.
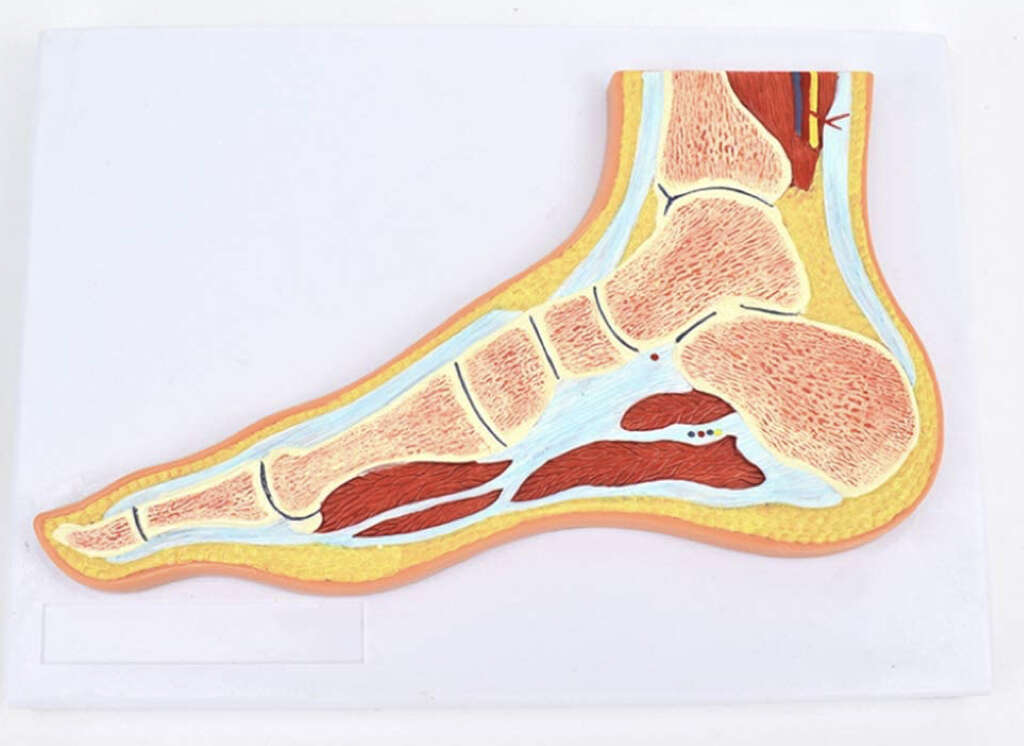
2. Ligaments
As mentioned, many of our joints are held together with the help of ligaments. These act as a type of biological rope that ties one body part to another. While helping to keep the joints held firmly together, they also allow us the flexibility we need in order to move our joints.
The ligaments still need to be made from strong materials, however, because they will need to be able to withstand a lot of force. They are given their strength thanks partly to collagen, which is a type of protein. If there was an abnormality with this protein, then the ligaments may not be as strong as they should be.
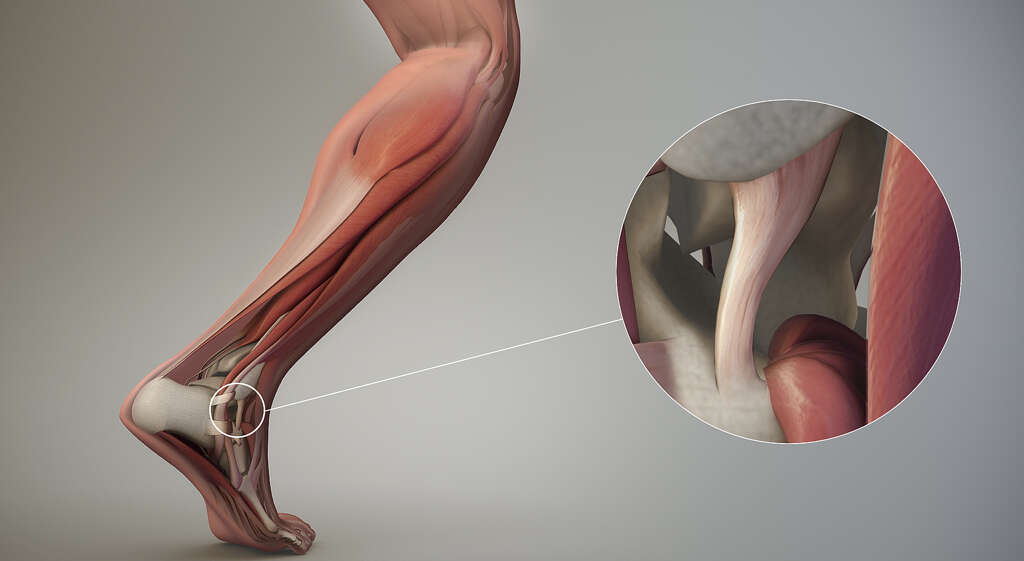
3. Benign Hypermobility Syndrome
Some people have joints that are more flexible than usual in a condition known a hypermobility. In most cases, this is because the collagen in their ligaments is not the same as the collagen in other people. This makes the ligaments weaker, which also means that they can stretch further.
Hypermobility is not an uncommon condition. It is also sometimes known as being double-jointed or lose jointed. It is also usually quite harmless with no unwelcome symptoms or underlying health issues, although it might cause some mild pain in the joints and muscles. Such cases of hypermobility are known as benign hypermobility syndrome.
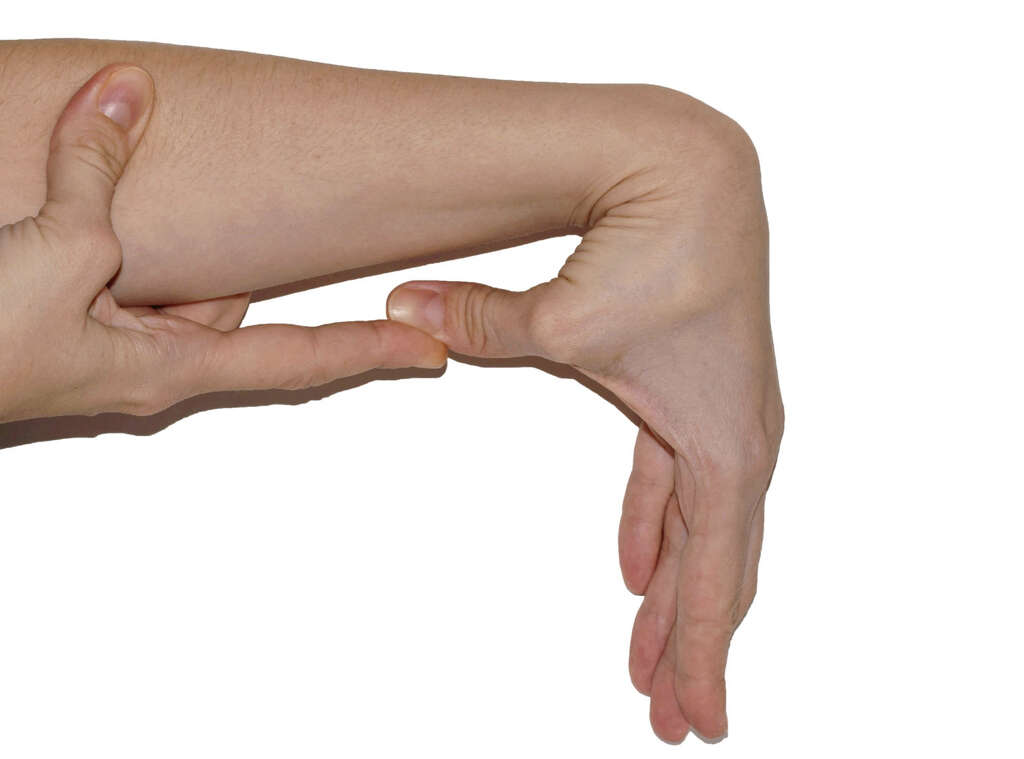
4. Joint Hypermobility Syndrome
Not all cases of hypermobility are so harmless for the patient. In some cases, it can cause considerable pain or stiffness in the muscles and joints. Some patients can also experience more severe symptoms that can even end up causing significant injuries. This is a condition that is known as joint hypermobility syndrome.
Joint hypermobility syndrome is a condition that can cause a significant drop in the patient’s quality of life, and it will need to be treated or at least managed in most cases. In some instances, it may be caused by an underlying health condition that can make matters even worse for the patient.
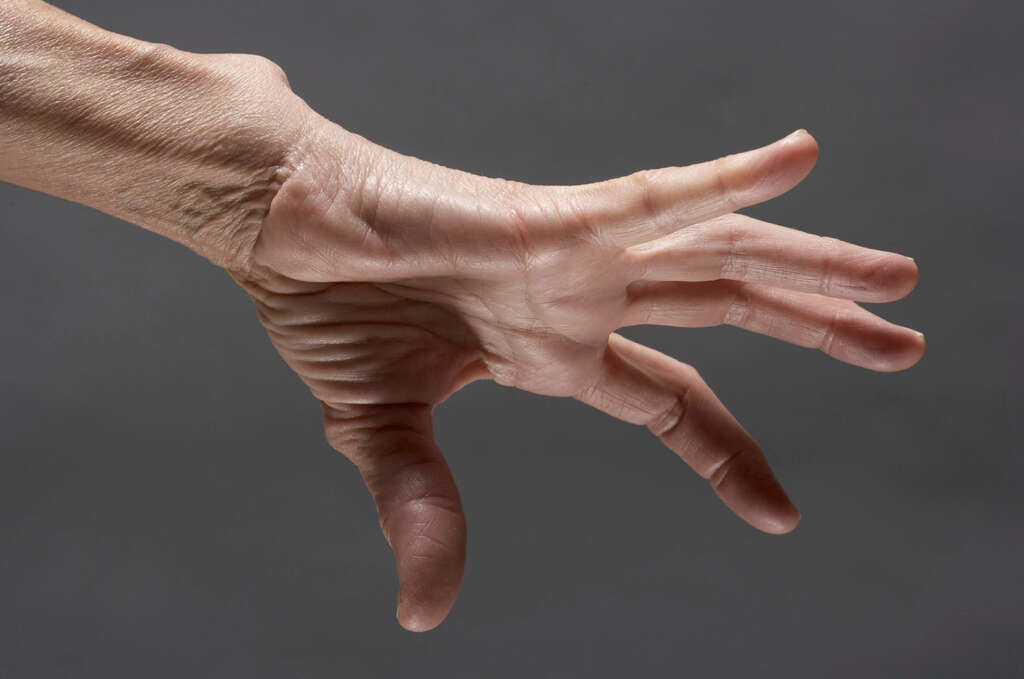
5. Physiological Causes
As mentioned, one of the main causes of hypermobility syndrome is that there is an issue with the patient’s ligaments. This is not the only cause of the condition, however. In some cases, for example, it may simply be the case that the patient’s joints are more flexible because of the physical shape of their bone at the joints.
In other instances, the condition may be a result of the patient’s muscles being weaker than usual. Exercises that help strengthen the muscles may overcome this in many cases. It is also a condition that tends to run in the family so if a parent has the condition, then their children are more likely to have it also.

6. Proprioception
Proprioception is a sense that is considered by many to be our sixth sense. It is the sense that gives you awareness of the exact position of your body. Where your hands are, where your feet are, how far your knees are bent, and so on. It is a sense that comes to us with the help of neurons in our muscles that can relay messages to the brain.
Some people have a poor sense of proprioception, and this can cause a number of problems for them. One such problem is the inability to know how much a particular joint is bent, potentially resulting in it becoming more bent than it should be. Exercise and physiotherapy can help to improve somebody’s sense of proprioception.

7. Medical Causes
It is not common, but hypermobility syndrome is sometimes caused by other medical conditions. One of these is the relatively common Down syndrome that can cause significant development issues in patients. Another is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which is a condition that affects the elasticity of the patient’s ligaments.
There is also cleidocranial dysostosis, which is a disorder that affects the development of our bones, and Marfan syndrome, which is a disorder of our connective tissues. It can also be caused by a disorder that affects the metabolism, known as Morquio syndrome. While it may not be possible to cure the underlying cause, the symptoms at least can often be treated.

8. Complications
Joint hyper mobility syndrome can, as mentioned, cause some considerable pain and stiffness in the joints and muscles. In addition, it can also result in some other rather unwelcome symptoms, one of which is regular stomach problems, including constipation or diarrhea.
Other symptoms of joint hypermobility syndrome include skin that is thin and stretches more than it usually would be able to. The patient can also have poor coordination and balance, and they can also experience regular strains and sprains. Some patients will also experience regular dislocations of their joints, which can be very painful and can cause permanent damage.

9. Medical Treatment
Treating hypermobility syndrome largely involves treating the symptoms that are caused by the condition. Many patients will be experiencing pain and this can be treated with the help of pain killers. It is advisable to be cautious when using painkillers, however, because some can result in an addiction.
Other medical treatments can involve therapy, which will aim to increase the patient’s muscle strength and their coordination. More muscle strength also means that the patient is less likely to experience dislocations. Physical therapy can be hard work for the patient, but it can make considerable improvements so it is well worth the effort.

10. Other Treatment
In addition to professional, medical treatments available, patients can also help themselves with other treatments when at home. Some of these treatments can help to reduce pain and stiffness in joints, helping to make the patient a little more comfortable at least.
One such treatment is to have a bath in warm water, which can be a very relaxing experience regardless. Using heat-rub creams can also be beneficial, and applying hot water bottles onto aching joints can also give some relief from stiffness and pain. It is always a good idea to speak with a doctor about treatments you can use at home to help relieve some of the discomfort.