What Is Histoplasmosis?
Fungi are a life form that is neither animals nor plants. There is a huge variety of them, many of which will even end up on your dinner table. Some varieties are extremely small – so small that they could cause an infection in your body if you were unfortunate enough.
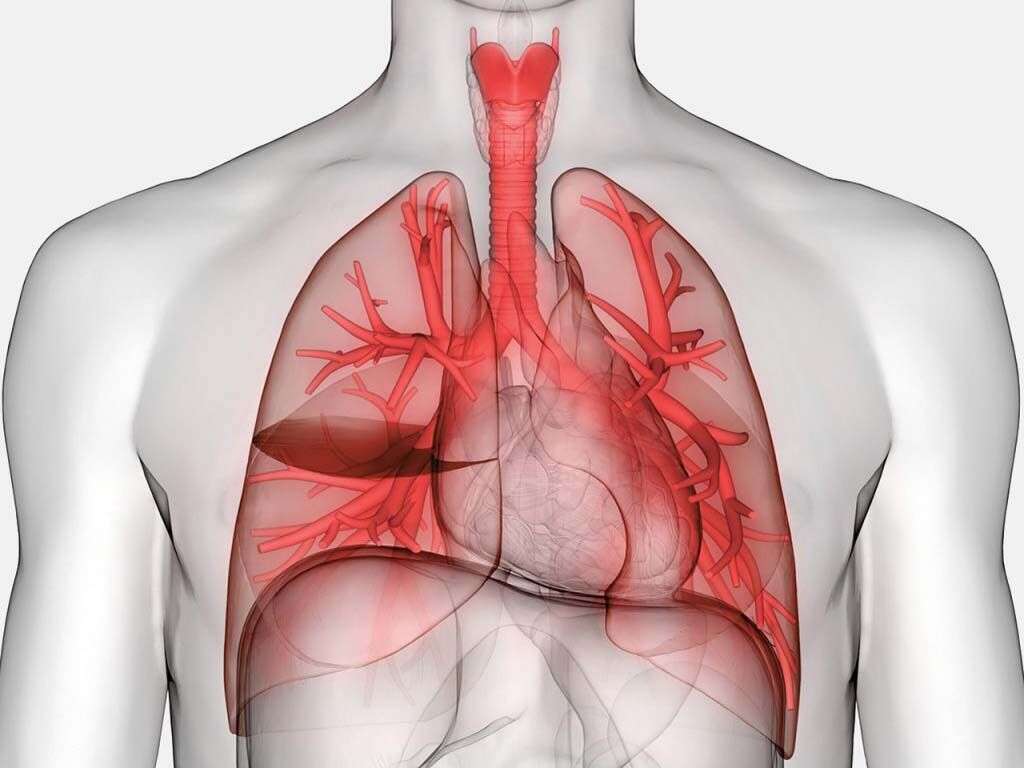
Fungi reproduce by releasing tiny spores into the atmosphere, and these spores will then drift away before settling and growing elsewhere. These spores are so small that they can be inhaled and they can settle in our lungs. This can result in a fungal lung infection, an example of which is histoplasmosis.

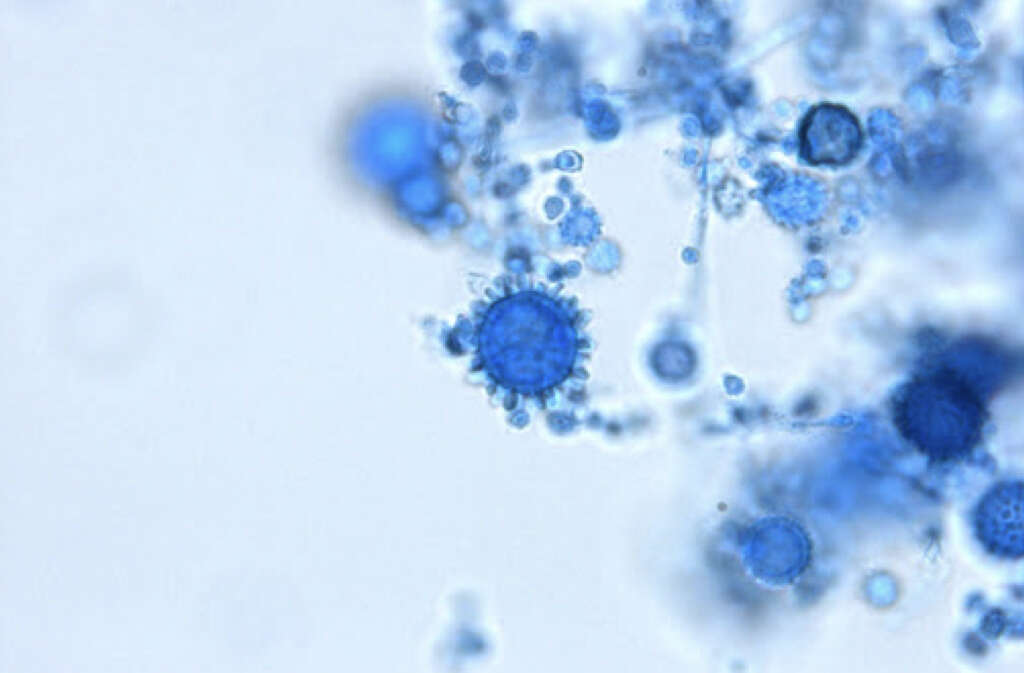
1. Histoplasma Capsulatum
Histoplasma capsulatum is the fungus responsible for histoplasmosis, which is an infection of the lungs. The fungus is often found in bat and bird droppings, and its spores are sometimes inhaled accidently. Then, they can make their way into our lungs where they can take hold and cause the infection.
The fungus exists in many parts of the world, including the United States, and it is often inhaled when soil or buildings have been disturbed. It is not usually a dangerous condition but it can be dangerous to people that are vulnerable. Treatment is available, but the condition can be fatal without treatment.
2. Causes
As mentioned, the infection is caused by the histoplasma capsulatum fungus. The fungus will thrive in soil and, when soil is disturbed, or buildings knocked down, the fungus can be flung into the air where it can hang for a long time before settling again. This makes it easy for it to be inhaled.
The fungus tends to be found in soil that is nutrient rich. The droppings from animals like bats and birds can enrich the soil. It is also sometimes known as the cave disease, because large colonies of bats will often make their homes in caves. It cannot be transmitted from person to person.

3. Symptoms
The majority of people with the disease will experience no symptoms whatsoever. In most cases, the patient won’t even be aware that they have it. When symptoms do show, they will usually appear between 3 and 17 days of the infection taking hold. Symptoms of the condition tend to be similar to pneumonia.
The symptoms typically include a fever, chills, and a headache. The patient can have a cough and feel some discomfort in their chest as well as breathing difficulties. Muscle aches and pains can also be experienced. While these symptoms are usually only mild, they can go on to develop into something more serious.

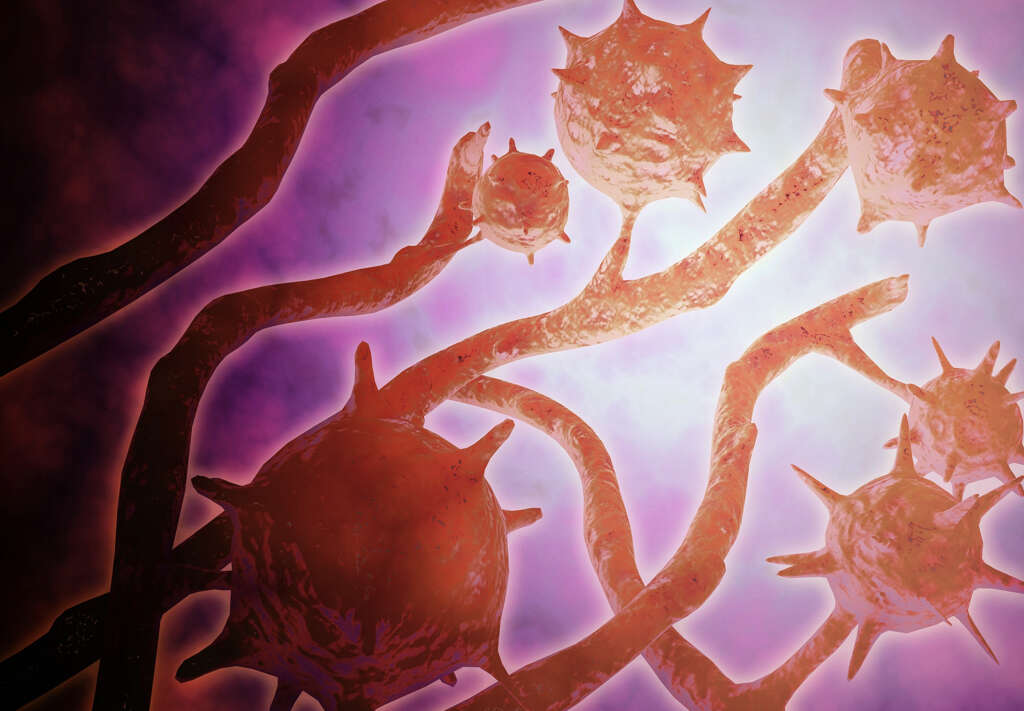
4. Disseminated Histoplasmosis
As mentioned, histoplasmosis can be severe in some cases. Indeed, it can develop into a condition known as disseminated histoplasmosis. This occurs where the fungus spreads and begins to infect other parts of the body as well as the lungs. It tends to infect infants more often than any other age group, and those with a weakened immune system are especially at risk.
Disseminated histoplasmosis can affect the central nervous system, the adrenal glands, the skin, liver, mouth, and just about any other part of the body. The condition is likely to be fatal if treatment is not sought in time.
5. Risk Factors
Anybody that lives in an area where the fungus is present stands a chance of contracting it. However, people that take part in certain activities are more likely to catch it than others are. This largely means people that are more likely to be exposed to the soil that can contain the spores.
This tends to include farmers and landscape gardeners. People that work in construction are also going to be more exposed to the spores, while people that enjoy caving as a hobby are also in a higher risk bracket. If you are in one of the higher risk categories, it is a good idea to take precautions such as wearing protective masks.

6. Immunity Risks
As mentioned, people that have a weakened immune system are more likely to develop serious problems due to disseminated histoplasmosis. It is usually young children that develop serious problems, but older people are also in a higher risk group.
There are numerous reasons why somebody might have a weakened immune system, one of which is HIV/AIDS. Some medications can also result in a weakened immune system as an unwelcome side effect. Other medication can weaken the immune system by design, such as those given to patients that have just received organ transplants. Chemotherapy and other cancer treatments can also result in a weakened immune system.

7. Complications
Histoplasmosis can result in acute respiratory distress syndrome. This is a very dangerous condition where damage to the lungs causes the alveoli to fill with fluid, thus preventing the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The condition can also cause damage to the adrenal glands, which can affect the function of the patient’s organs.
The infection can also cause pericarditis, which is a type of heart condition that causes swelling of the heart. Meningitis is another possibility, which is the inflammation of the membrane that helps to protect the spinal cord and the brain. These complications can usually be prevented with treatment.
8. Prevention
It can be all but impossible to make yourself completely safe from histoplasmosis; the spores can easily be in the air you are breathing. We can still make ourselves significantly safer from the condition, however. One way to do this is to avoid places like caves and farms where the fungus is more likely to exist.
If you are expecting to be exposed to the spores, then wearing a mask can help. Another method of keeping safe is to spray surfaces and soil first before disturbing them because this will make the spores less likely to be released into the air.

9. Diagnosis
In many cases, histoplasmosis will go undiagnosed because of the lack of symptoms that would otherwise encourage patients to get medical advice. Even when it is suspected, diagnosis is not always considered necessary. It will be deemed necessary in more serious examples, however, because of the severity of the patient’s symptoms.
Diagnosing the condition is not easy and several tests may be required. This can include blood and urine tests and also tests of secretions from the lungs. The patient’s bone marrow may also need to be investigated, and a biopsy of the patient’s lung tissue might also be deemed necessary.

10. Treatment
Treatment for histoplasmosis will usually not be considered necessary because of the mildness of the symptoms in the majority of cases. If the patient’s symptoms are on the more severe side, however, then treatment should be deemed a necessity and a medical emergency.
Thankfully, treating the condition is relatively easy and effective. Treatment is even available for disseminated histoplasmosis, and it will likely involve antifungal drugs. It is likely that more than one variety can be used. Depending on the severity of the condition, it might be necessary for the patient to continue taking medication for a year or so.