What Is Gestational Diabetes?
8. Medication
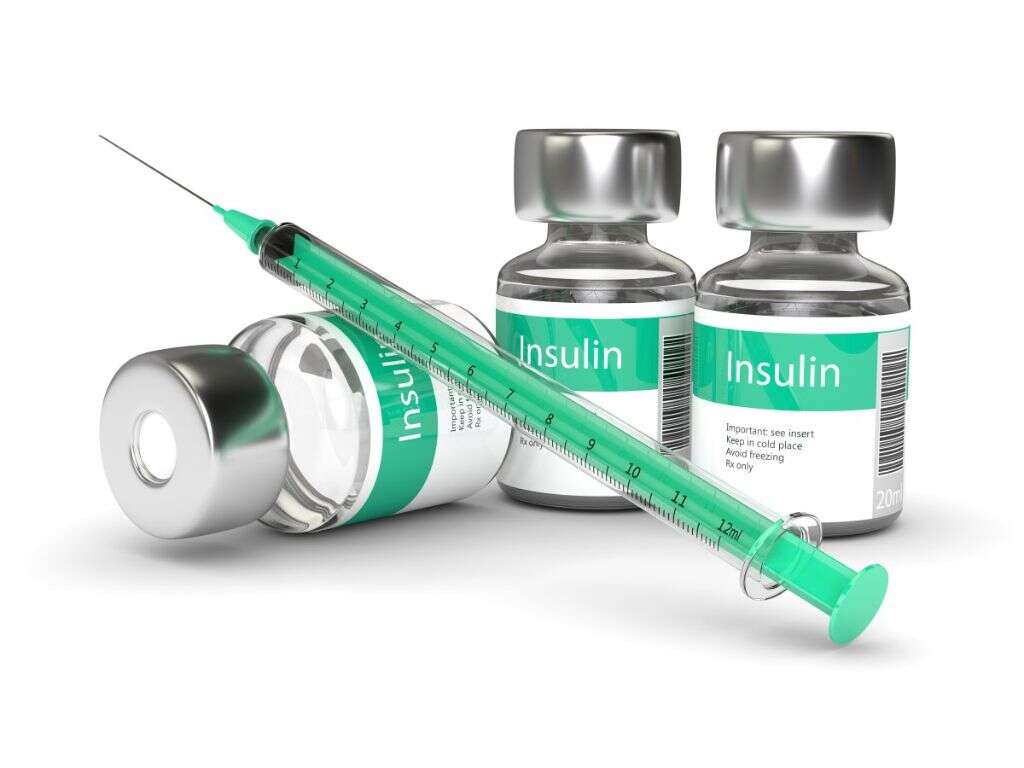
If lifestyle interventions are not adequate and observation and monitoring of the pregnancy reveals failure to control blood glucose levels or complications such as excessive fetal growth, treatment with insulin may be required. This is generally fast acting insulin that is administered before meals. Insulin can cause low blood sugar levels and should be avoided. There is also evidence of oral medications that may be safe or less dangerous compared to poorly controlled diabetes. However, due to lack of evidence, it is hard to recommend one medication over the other.
Metformin may be the best option. In cases where blood glucose levels cannot be controlled using insulin alone, a combination of insulin and metformin may be a better choice as some studies have reported that those treated with a combination of metformin and insulin gained less weight and required less insulin. Babies by mothers treated with metformin were also found to have less visceral fat, making them less likely to have insulin resistance in later life. However, it is important to know that there remains a possibility of long-term complications.
Advertisement