What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
Our livers are the second largest organ in our body, and one of the most important. They help to prevent toxins and impurities from our food doing us any harm. Without them, toxins will accumulate in our blood, and this will be fatal if it is left unaddressed.
Our livers also do a lot of hard work and are exposed to multiple potential problems. This includes the possibility of fat accumulating in the organ, and this can affect how well it is able to perform its main tasks. For many people, however, the disease will cause no side effects, and it is often only noticed when doctors are looking for other conditions.
1. Fatty Liver Disease
It is not uncommon for us to have fat deposits on our livers and, for the most part, it is quite harmless. If the fat deposits are able to accumulate significantly enough then they can cause the liver to begin to lose its effectiveness. This, in turn, can result in some rather unwelcome symptoms.
There are two main types of fatty liver disease. These are alcohol related, and non-alcohol related. It is a relatively common condition worldwide, especially in countries where people tend to enjoy unhealthy diets and lifestyles. In some parts of the world, around 25 percent of the population will be affected by non-alcoholic related fatty liver disease.
2. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
If left untreated, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease can develop into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. This is a more aggressive form of the disease and it can cause the liver to become inflamed. This inflammation, if left untreated, can cause damage to the liver, potentially causing the liver’s tissues to become damaged.
Damage to the liver tissues can cause scarring to form a condition known as cirrhosis. The same condition is sometimes caused by excessive alcohol consumption, which can also cause damage to the liver. Cirrhosis of the liver can affect the liver’s ability to perform to the point where it becomes dangerous.

3. Causes
The causes of fatty liver disease are not well understood. But we do know the disease is linked with certain factors. One of these is obesity, with obese people being more prone to the condition than non-obese people are. High levels of triglycerides and other types of fat in the blood are another potential contributing factor.
Other potential factors include hyperglycemia, which is a high blood sugar level. This means that diabetes is often associated with fatty liver disease. In many cases it is a combination of these and other conditions that make a person more prone to developing fatty liver disease.
4. Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
Fatty liver disease will often cause no noticeable symptoms at all. This is not necessarily a positive thing because it can mean the condition will go unnoticed for a long time. During this period, and without treatment, the condition can be gradually getting worse until more serious problems develop.
When symptoms do show they will typically include fatigue. This can mean the patient is lacking energy regardless of how well they are eating and sleeping. The condition will also sometimes cause pain in the abdomen, and this will be located in the upper right section where the liver is located.

5. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Symptoms
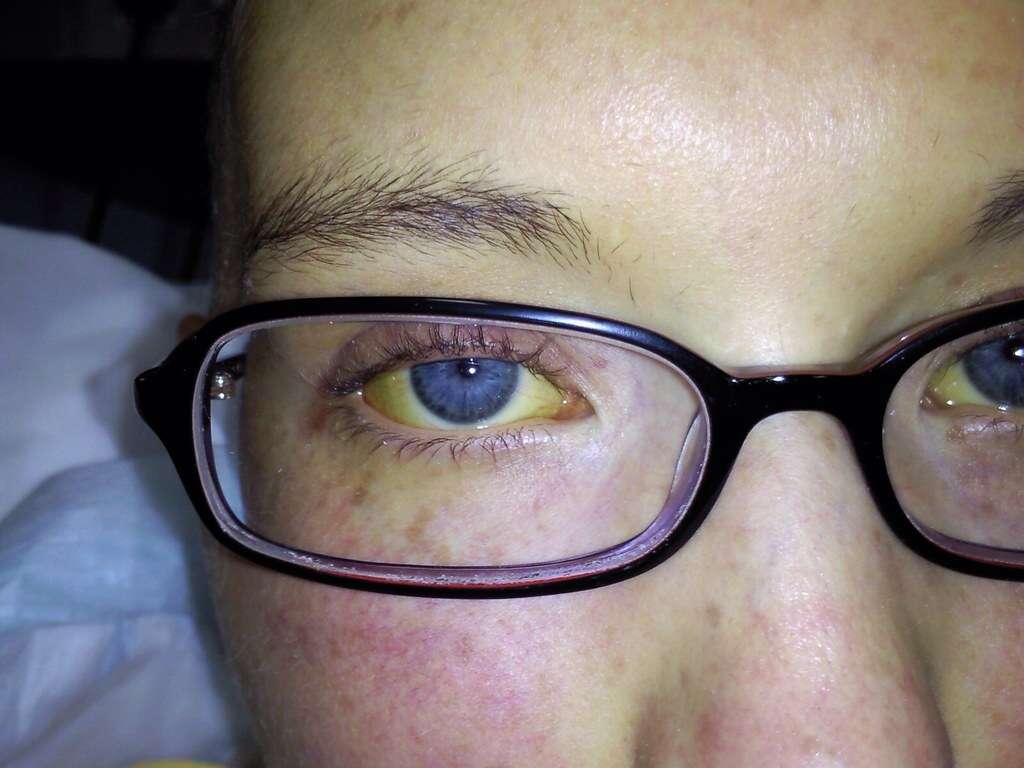
If fatty liver disease progresses to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis then symptoms are likely to become rather more noticeable. One of these is jaundice as the liver struggles to remove bilirubin from the blood as well as it usually would. This causes yellow skin and other symptoms like itchy skin.
Other potential symptoms include ascites, which is a swollen abdomen. An enlarged spleen is another potential symptom. Blood vessels just below the skin can also become enlarged, and the patient will also sometimes develop red palms. Anybody showing these symptoms should speak with a doctor if they have not done so already.

6. Risk Factors
As mentioned, obesity and diet are contributing factors to fatty liver disease, but there are other factors that increase a person’s risk. This includes older people, and people who have metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a combination of conditions that result in symptoms like excess body fat, and high blood sugar levels.
An underactive pituitary gland is another potential factor, as is an underactive thyroid. This is because these glands produce hormones that affect the metabolism, which is why polycystic ovary syndrome is another potential factor. Patients with a condition known as sleep apnea are also in a higher risk category.

7. Complications
As mentioned, fatty liver disease can cause cirrhosis of the liver, and this can cause some potentially serious problem for the patient. These problems include hepatic encephalopathy, which causes the patient to become drowsy and confused with slurred speech. This happens when a build-up of toxins in the blood begin to affect the functioning of the brain.
Another potential complication is esophageal varices, which causes veins in the esophagus to become swollen. Cirrhosis will also increase the likelihood that liver cancer will develop. There is also the possibility of end stage liver failure, which means that the liver has stopped working altogether.

8. Prevention
Although there is no sure way to prevent fatty liver disease, we can at least significantly reduce the chances of being affected by it. This largely means trying to live a fairly healthy lifestyle and maintaining a healthy weight. It is especially important to lose some weight if you are overweight.
This largely means getting at least a reasonable amount of exercise, and just a little exercise can make a big difference in some people. It also means trying to eat a healthy diet. This means foods that are relatively low in fat content, low in carbohydrates, and high in fiber.

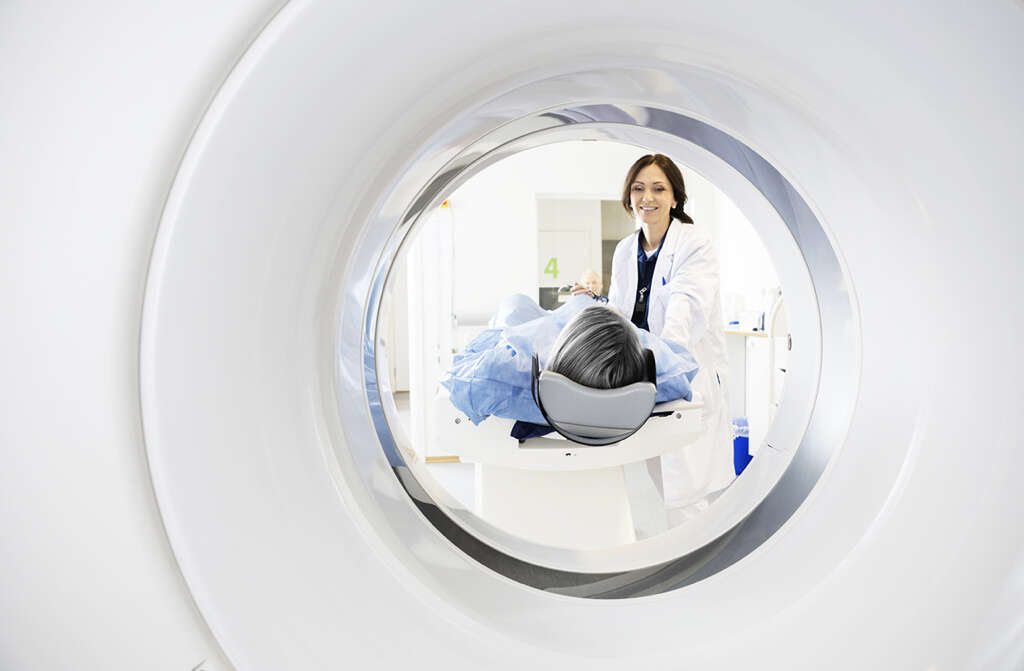
9. Diagnosis
Your doctor will need to ask you about your symptoms, about your lifestyle, and about your medical history. They will also need to request tests in order to confirm what is causing the patient’s symptoms. This will often include blood tests that will allow experts to look for signs of the disease.
Imaging technologies may also be used to look for signs of the condition. This includes ultrasound that uses sound waves to create images. MRI scans and CT scans can also be used to help look for signs of the disease. A biopsy will also sometimes be performed so the patient’s liver tissue can be examined.

10. Treatment
As things stand, there is no medical treatment for fatty liver disease. If the disease does progress then the patient may need treatment for their complications. In some cases, this might even mean the patient having to have a complete liver transplant.
Fatty liver disease can still be treated, however, even though no medication is available. This is achievable by making lifestyle changes that will help to reduce the build-up of fat in the organ. As mentioned, this means eating healthily and being active. In the more severe cases, surgery to help the patient to lose weight might be considered.