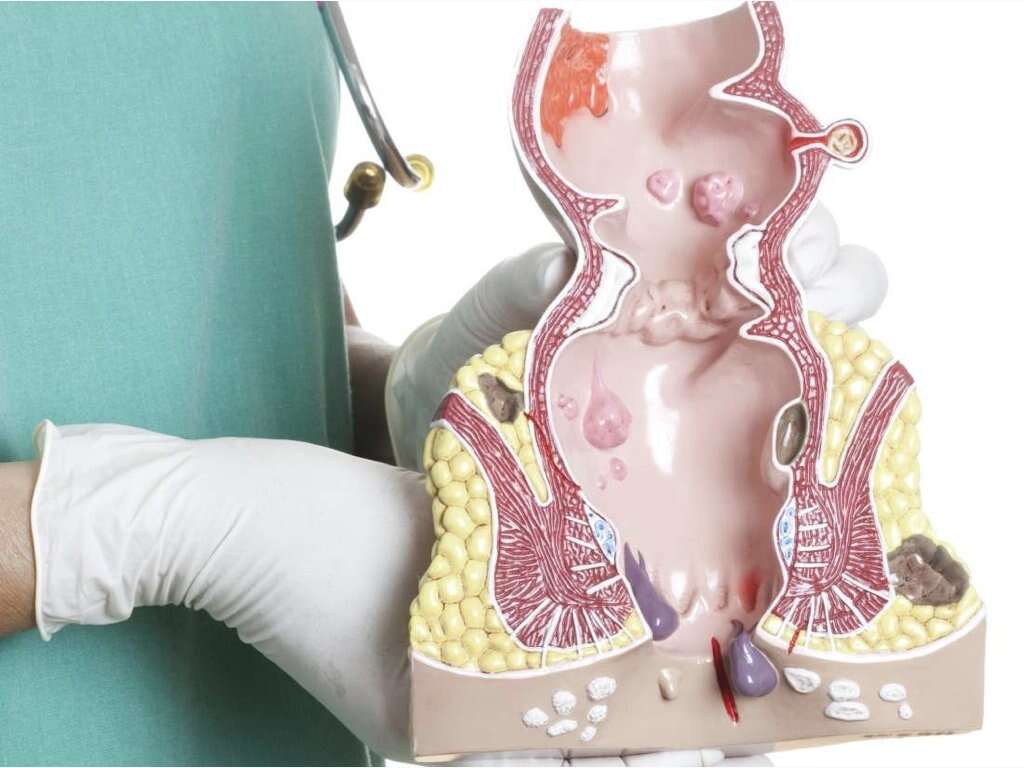
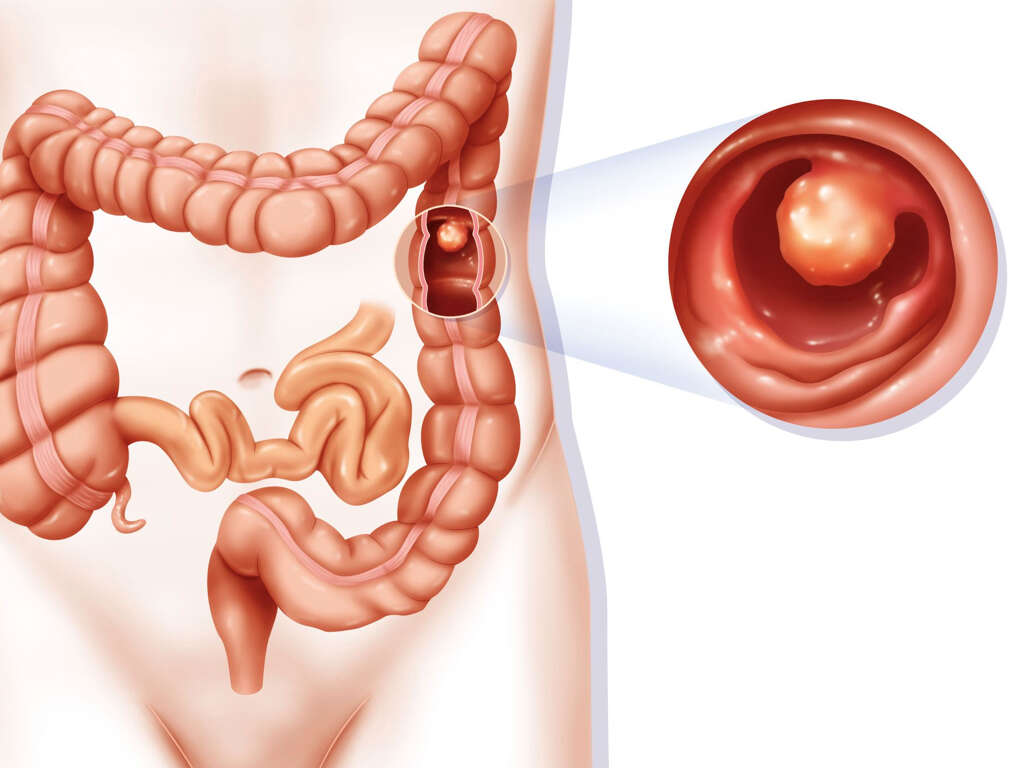
What Is Colon Cancer?
Cancer is a disease marked by abnormal cells that destroy body tissues and divide in an uncontrollable manner. Cancer has many different names, depending on where it originates.
Colon cancer is one of the more common types of cancer. In fact, if skin cancers are excluded, colon cancer is the third most common type of diagnosed cancer among both women and men in the U.S.

1. What Is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer (also commonly known as colorectal cancer), is a type of cancer that develops in the colon or rectum. This type of cancer is usually slow-growing and takes many years to develop.
Most colon cancers start as non-cancerous polyps that eventually change into cancer. A polyp is a type of tissue growth that occurs in the rectum or colon lining. It’s important to note that not all polyps will turn into cancer.
However, if you receive a colonoscopy and your doctor detects one or more adenomas or non-cancerous polyps, he or she will likely suggest that you receive cancer screenings regularly.
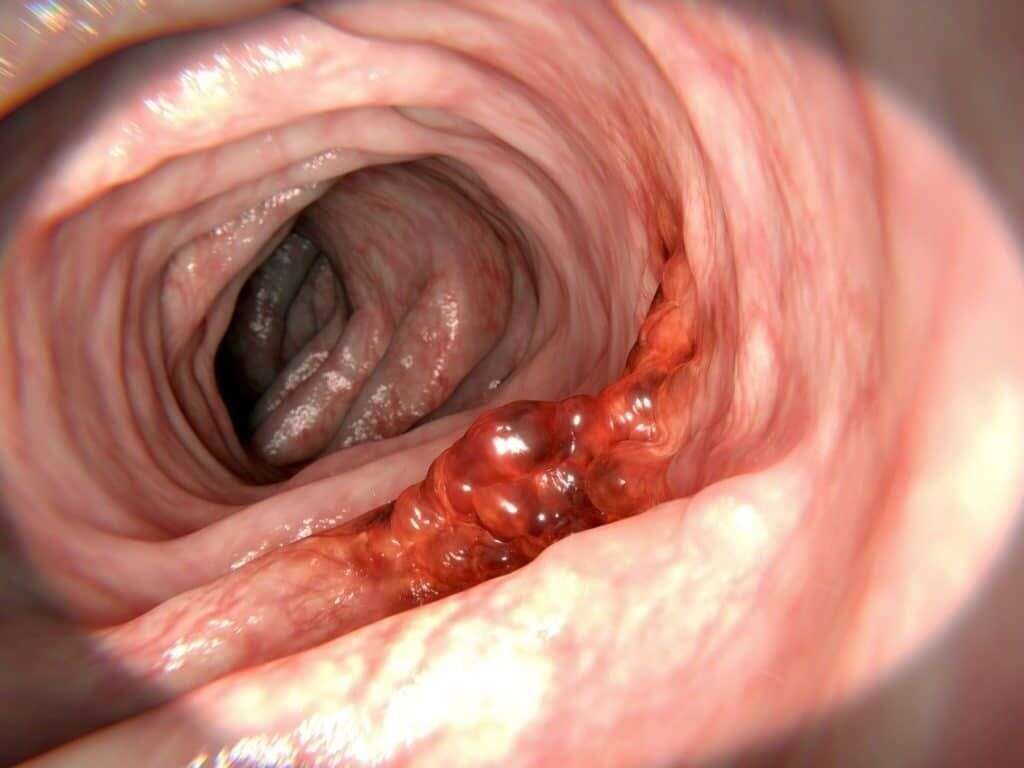
2. What Are the Symptoms of Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer is one of the quieter types of cancer because it often doesn’t cause any symptoms as it develops. For this reason, many people fail to have colon cancer diagnosed during its early stages. As the cancer develops and becomes more serious, it may begin to exhibit detectable symptoms.
Some common symptoms associated with colon cancer include stools that are long and narrow, unexplained changes in bowel habits, blood in the stools, and unexplained weight loss. Some people also experience frequent abdominal pain and anemia.

3. What Are Risk Factors of Colon Cancer?
Anyone can potentially get colon cancer at some point. The exact cause of this type of cancer are largely unknown. However, some studies indicate that the following risk factors may increase a person’s chance of developing colon cancer: polyps, a diet high in fact and calories, age (people older than 50 are more likely to get the disease), a family medical history of colon cancer, ulcerative colitis, and a history of other types of cancer.
If you have one or more of these risk factors, it doesn’t mean you’re guaranteed to get colon cancer. However, your chance of developing the disease is higher than someone who doesn’t have any of the associated risk factors.

4. How Common Is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. It’s also the third most commonly diagnosed type of cancer each year. This year alone, it’s estimated that over 140,000 adults will be diagnosed with colon cancer in the United States.
The lifetime risk of developing this type of cancer is about 4.1% for women and 4.4% for men. Colon cancer is very rare in young adults, teenagers and children.
5. Do Only Older Men Get Colon Cancer?
There are many myths surrounding colon cancer. One of those myths is that only older men get the disease. Unfortunately, this myth can cause younger people and women to disregard their symptoms as something else.
It’s important to understand that colon cancer can potentially affect anyone. Though it is most common in men older than 50, women are not far behind.

6. Is Colon Cancer Deadly?
Colon cancer is second only to lung cancer in terms of cancer-related deaths. It’s also one of the easiest forms of cancer to detect. Like many other types of cancer, colon cancer is most curable if it is detected and treated in its earliest stages.
Regular colonoscopies are recommended by most doctors for people over age 45. If you have risk factors for the disease, you may want to receive a colonoscopy even earlier. If your initial colonoscopy shows no signs of cancer, you may not need to get another one for 10 years. However, once you each age 75, you should talk to your doctor about the need for more frequent screenings. Your doctor will help you set up a colonoscopy schedule based on your unique situation and health history.

7. What Does It Mean if Colon Cancer Has Metastasized?
If your doctor tells you that your colon cancer has metastasized, it means that it has traveled to other body parts. Usually, metastatic colon cancer spreads to the liver. However, it can also spread to the central nervous system, bones, lungs and lymph nodes.
Once colon cancer metastasizes, it must be treated aggressively for the best outcome. Talk to your doctor about recommended treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy and other options.
8. How Is Colon Cancer Diagnosed and Treated?
If a suspected colon cancer is detected during a diagnostic test or screening, your doctor will most likely perform a biopsy. This involves using a special instrument to remove a small piece of tissue in the affected area. In rare cases, part of the colon may need to be taken out surgically in order to diagnose colon cancer. Once a biopsy is taken, it’s sent to a lab to be looked at under a microscope. If the lab results positively identify cancer, additional tests may be done to classify the cancer with accuracy.
The type of treatment recommended for colon cancer depends on a variety of factors, including the location, size and stage of the cancer. Common treatment types include surgery, medications and chemotherapy or radiation treatments. Each of these treatment types is associated with various benefits and potential risks. Before deciding what type of treatment to receive for yourself, it’s important to make sure you understand all of your available options in detail.
9. What Are the Stages of Colon Cancer?
There are four stages of colon cancer. Stage I Colon Cancer refers to cancer that has invaded the submucosa and mucosa. Stage II happens when the cancer spreads beyond the colon wall but hasn’t spread to nearby lymph nodes. Stage III colon cancer has spread to lymph nodes but hasn’t yet affected other bodily organs. Stage IV colon cancer refers to cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs.
It is important to note that each stage can be further divided into substages. Talk to your doctor for further details about your cancer stage.

10. What Is the Outlook for Colon Cancer?
The overall 5-year survival rate for people with colon cancer is 63%. If diagnosed in its earliest, localized stages, the survival rate is very good. However, if it is diagnosed in stage IV, the 5-year survival rate drops to approximately 14%.
When it comes to the outlook for colon cancer, it’s important to remember that you’re not a number or a statistic.
Maintaining a positive attitude may help your outlook after a colon cancer diagnosis. A growing number of people with advanced colon cancer live longer than two years after diagnosis. With treatment, you can still have a good outcome.