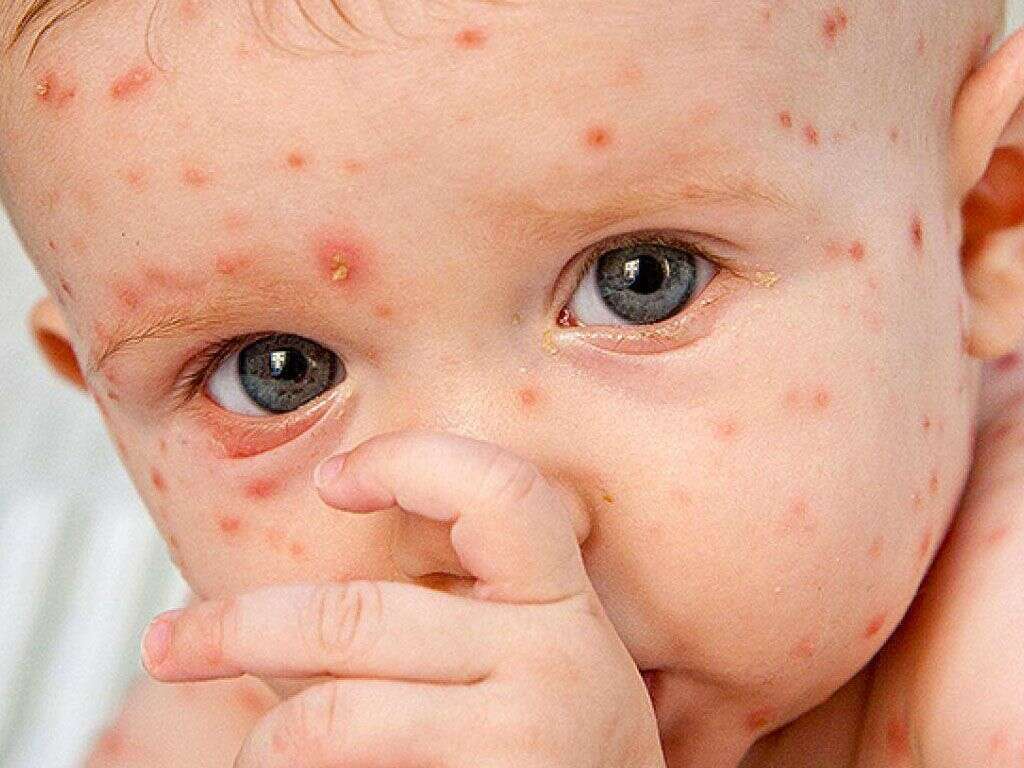
What Is Chicken Pox?
A lot of people over a certain age will be very familiar with chicken pox. It used to be a very common disease until a vaccine was developed and released in the mid-90s. Since then, instances of the disease have since plummeted in countries where the vaccine is common.
Despite being a fairly mild disease, chicken pox can still be dangerous in a small number of cases. Despite this, its high level of contagiousness meant that many individuals would develop serious problems. The disease has not completely disappeared, and it is a good idea to know what signs you should look out for.
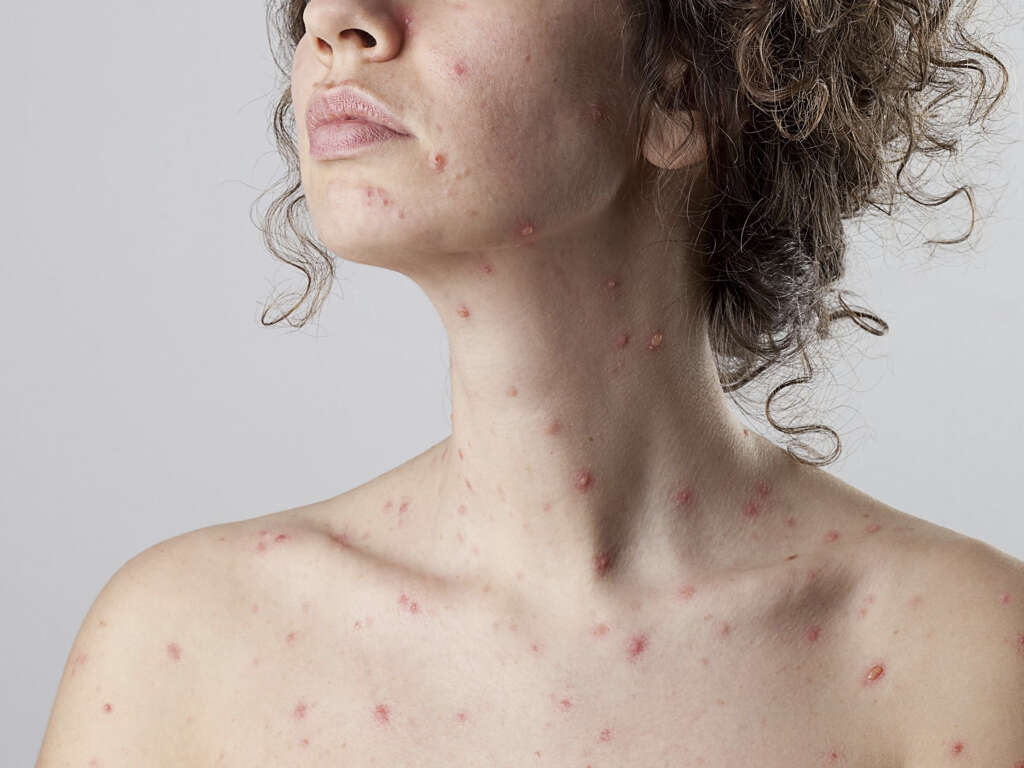
1. Chickenpox
Chicken pox is an infection that is caused by the varicella zoster virus. The disease is also sometimes called varicella. It is a highly contagious disease that most often occurs in children, although some adults will also catch it. It used to be far more common than it is now, thanks largely due to the introduction of a vaccine.
Such was the prevalence of chicken pox that it was considered almost inevitable that children would get it. Indeed, some parents even threw ‘chicken pox parties’. When a child was infected, other parents were invited to bring their children over. The idea was to help get the disease out of the way so the child would not catch it at a later age.
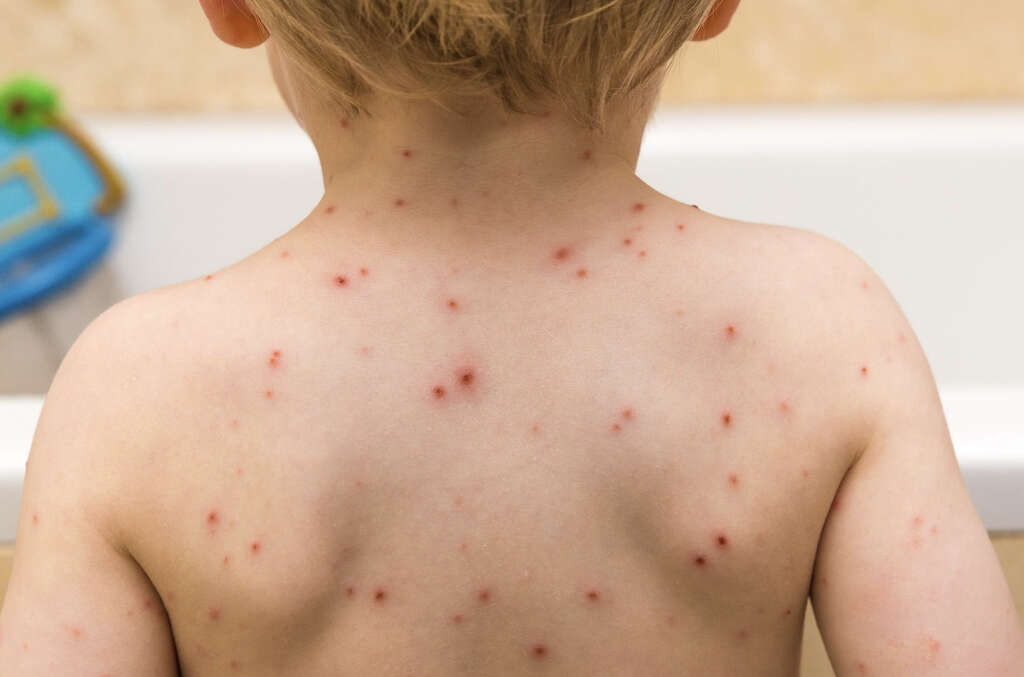
2. Transmission
Chicken pox is a very contagious disease, and it is spread from person to person. The disease causes blisters and the fluid from these is especially contagious. The disease is also contagious for a day or two before the blisters arise. It tends to occur more so in children because they tend to stay closer together in groups.
In addition to the blisters’ fluids, the disease can also be spread in other ways. This includes coughing, sneezing, and through the patient’s saliva. The patient will remain contagious until all of their blisters have burst and developed a dry crust over them.
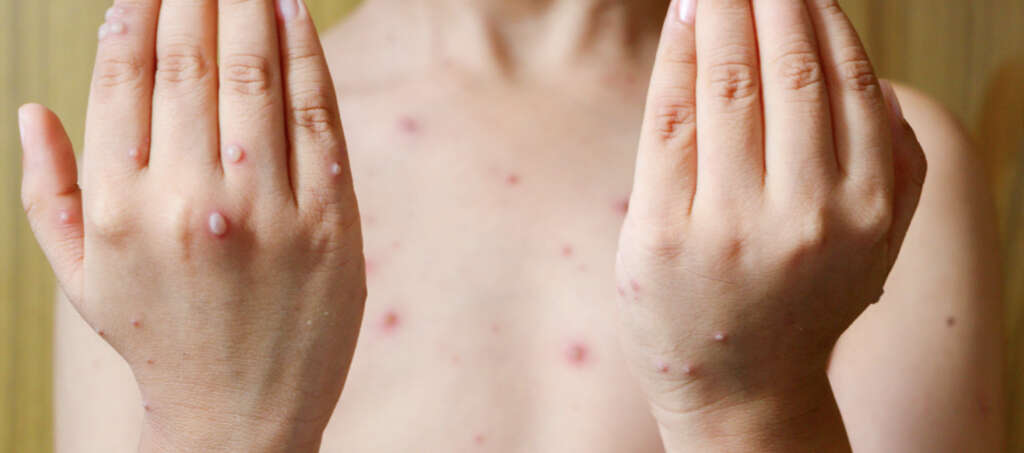
3. Incubation Period
If you catch chicken pox then it will be around 7 to 21 days before you know anything about it. During most of this time you will not be contagious to others. The patient will become contagious, however, around 48 hours before the rash begins to occur.
This allows a window of time when the patient is contagious with the disease, but the patient and/or their parents are not aware. This makes it more likely that the disease will be spread to other people. Even though the rash may not have developed yet, however, there are some other symptoms that can draw people’s attention to a potential problem.

4. Symptoms
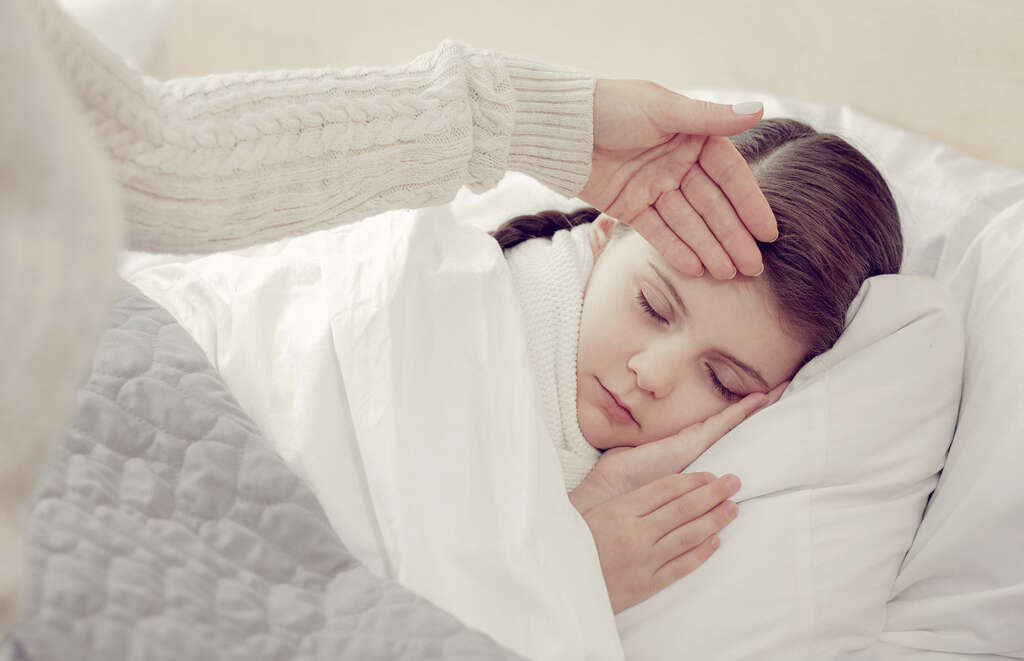
Before the patient develops a rash, they can begin showing other symptoms a day or two beforehand. One of these is a fever. A headache can also occur, and these symptoms can make a young child irritable. These symptoms can be quite mild at first and the disease will often be overlooked as something else at this point.
People with the condition will also often lose their appetite. It is important that the patient is still given all the food they need to help them keep up their strength. This can be particularly difficult where young children are concerned, however.

5. Rash
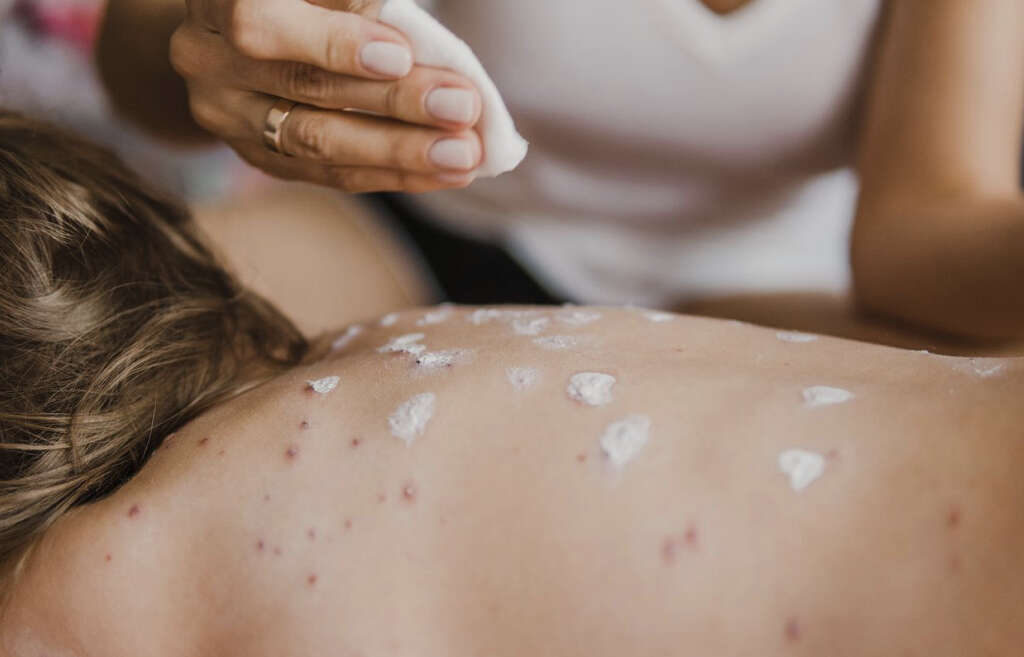
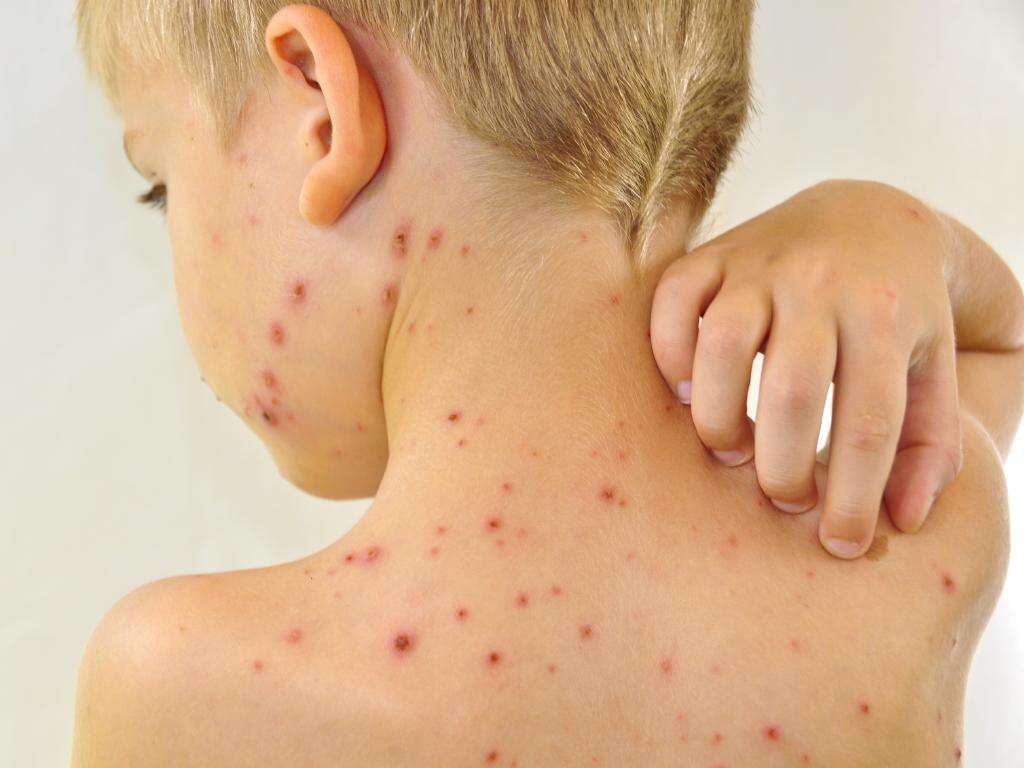
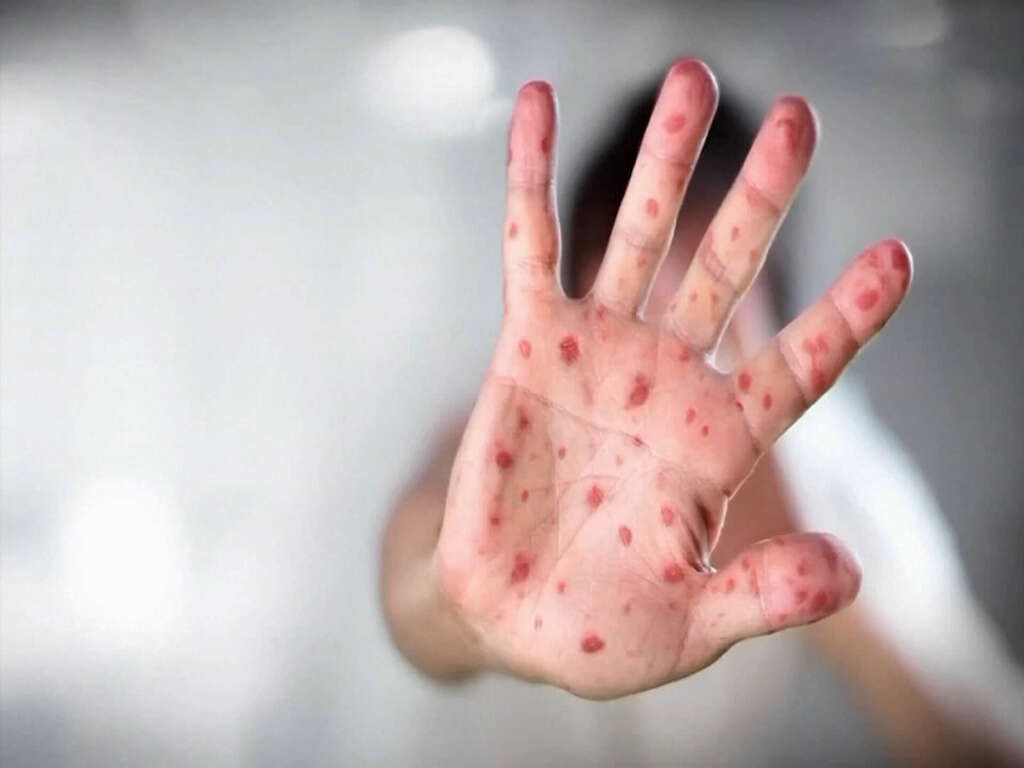
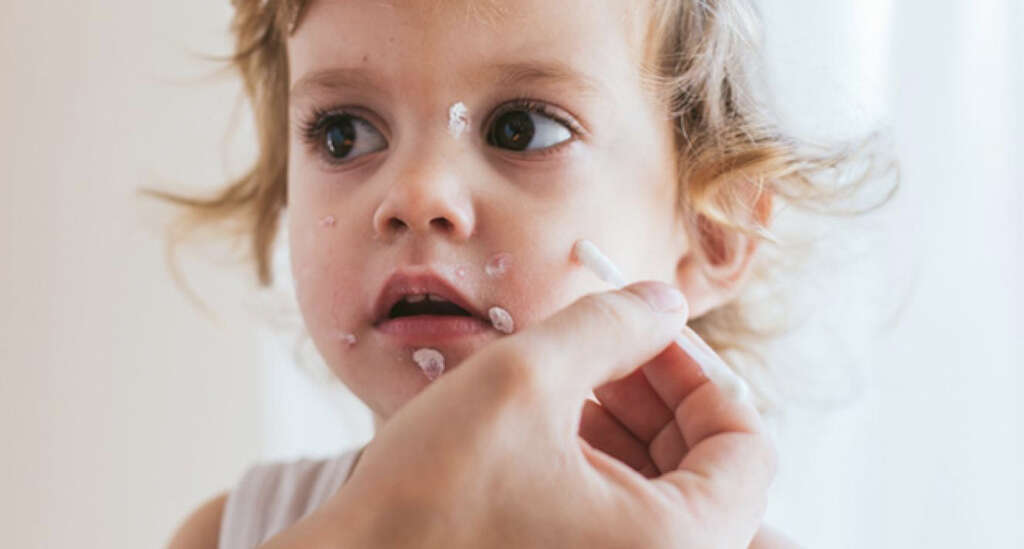
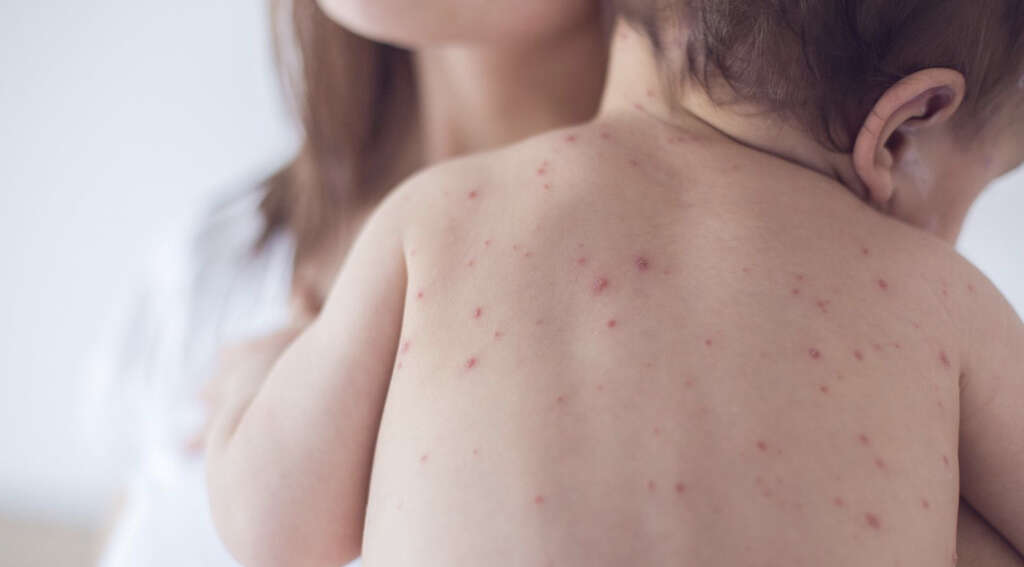
Perhaps the most characteristic symptom of chicken pox is the rash. The rash will tend to start showing a day or two after the other symptoms have appeared. The rash will be very itchy and will go through 3 main phases. Different spots of the rash will be at different phases at different times.
The first stage of the rash is the pink/red bumps will appear on the patient’s skin. The bumps will then develop into fluid filled blisters and the fluid will leak out from them. In time, the blisters will develop a crust and begin to scab over. Once this stage is over, the scabs will heal and the disease will be gone.
6. Shingles
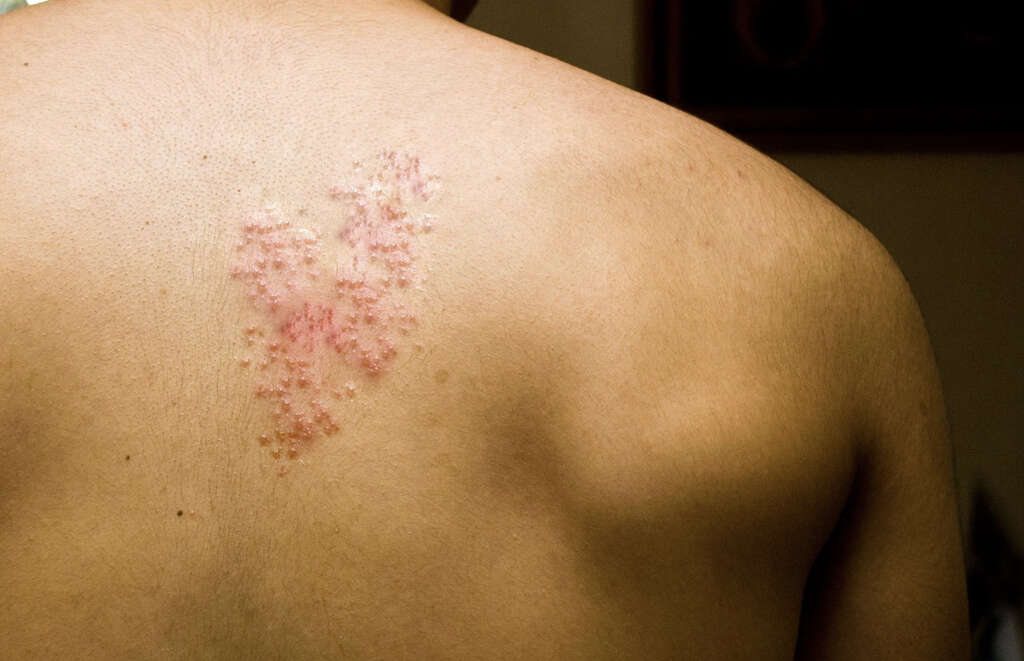
While the disease itself may be over, the virus will remain in the patient’s body. Here, it will remain dormant and, in the majority of cases, it will remain dormant. For a small percentage of people, however, the virus will become reactivated. When this happens, it can result in a disease known as shingles.
Shingles is a whole lot more unpleasant than the chicken pox, causing considerable pain on the patient’s skin. It is also contagious and people with shingles can transmit chicken pox to other people. They cannot transmit shingles directly, however. Shingles tends to affect older people, and it can result in some very serious complications.
7. Risk Factors
The risk of catching chicken pox is massively reduced if you have had it in the past, or if you have had a vaccination. Other than that, it is usually children under the age of 12 that will develop the disease. This is because children tend to be closer together, making it easier for the virus to spread.
Adults that have not had the virus or the vaccination are also at a higher risk of catching chicken pox. People that have a weakened immune condition are also more likely to catch the disease. As mentioned, older people that have had chicken pox in the past are more likely to get shingles.
8. Complications
Chicken pox can be very uncomfortable, especially for young children, but it is not usually a dangerous condition. The disease will usually pass before too long with no permanent damage done. It can be serious in a small number of cases, however, so it is a good idea to look out for warning signs.
If the rash is particularly tender and warm to the touch then it might be a sign that it’s become infected. You should also seek medical attention if the patient appears to be having difficulty breathing. Also get help if the rash spreads to the patient’s eyes. Chicken pox can cause birth defects if pregnant women are infected.

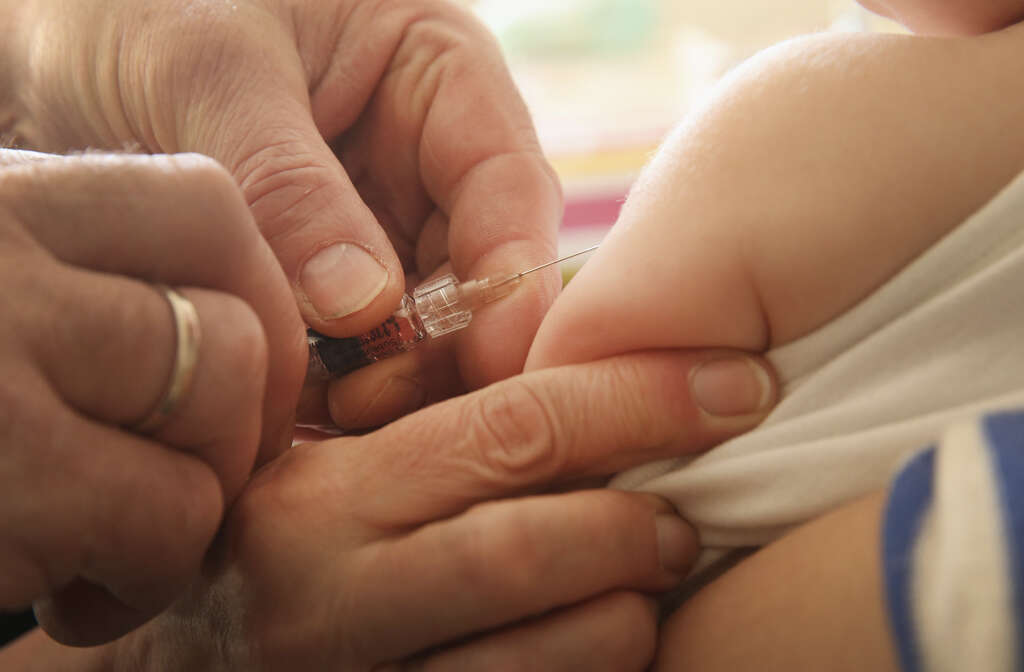
9. Prevention
The vaccine for chicken pox drastically increases a person’s protection against the disease, although it doesn’t make us completely safe. Many adults over a certain age will not have been vaccinated but they are still able to do so to keep them protected.
Should you or somebody else catch the disease then you should take care to avoid spreading it further. Not everybody is able to be vaccinated, and vaccines don’t give 100% protection, so it is still possible to transmit the disease. If you are infected then you should stay as isolated as possible until the disease has passed.
10. Treatment
Treatment for chicken pox usually involves treating the symptoms while the patient rides the disease out. This will tend to involve ointments and antihistamines that can help to relieve the patient of their itching. It is important to try and minimize scratching to help prevent the blisters and skin from becoming infected.
If the symptoms do appear to be worse than usual, then antiviral drugs may be recommended. These will not be able to cure the condition themselves but they will be able to help slow it down. If serious complications do arise then you should seek medical assistance as soon as you can.