What Is a Bone Infection?
Our bones need to be strong enough to help support our bodies, and anything we are carrying. They are also located within the body, relatively safe from external dangerous such as pathogens. This does not mean to say that our bones are completely safe from becoming infected, however.
Our bones can become infected and, when they do, it has the potential to be very serious. Thanks to modern medicine, however, such infections are treatable, but treatment should be found as soon as possible. If appropriate medical assistance is not found soon enough then the patient might end up losing parts of their body.
1. Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is the medical term for a bone infection. In the past, it was a condition that was considered to be incurable and, ultimately, fatal if the infected bone is not amputated in time. With new medicine, however, the condition can be treated successfully in most cases. Regardless, surgery is still usually required.
There are a number of potential ways that osteomyelitis can occur. In some cases, an injury can mean that the bone will be infected directly. In other cases, an infection elsewhere in the body can spread to the body. Regardless, it can be very dangerous if not treated so the patient should be found treatment as soon as possible.
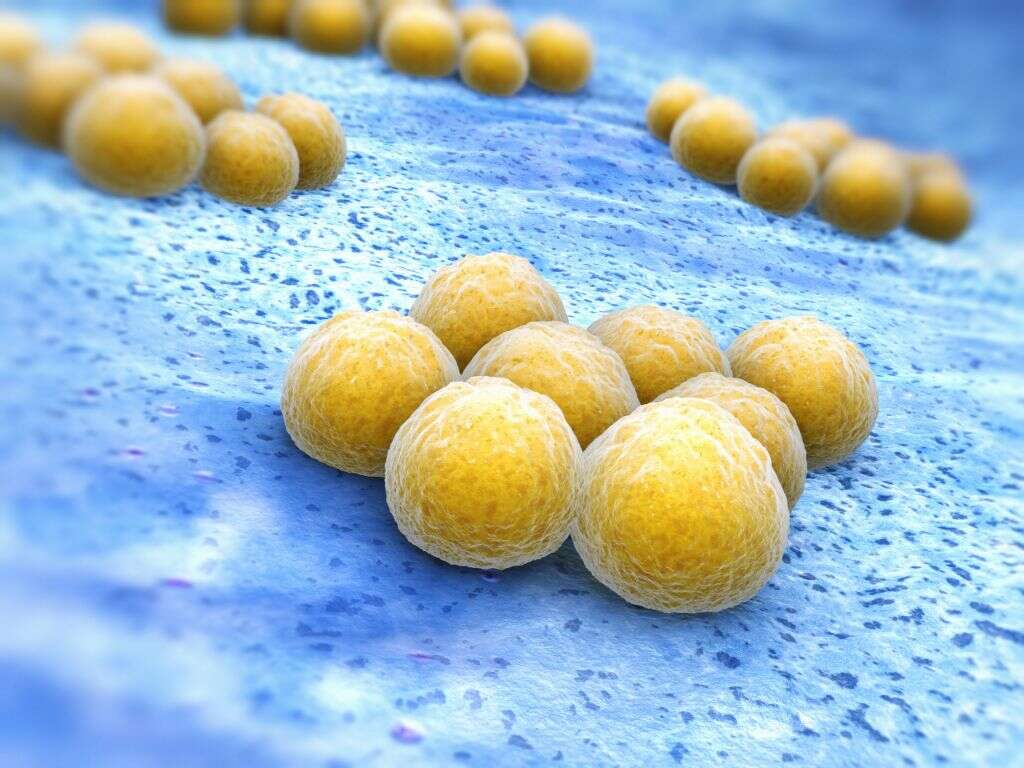
2. Causes
As mentioned, a bone infection can be caused in a number of ways, but it will nearly always be caused by the bacterium staphylococcus. If an injury was to cause the bone to penetrate through the skin, for example, then the bacteria may be able to infect the bone directly. Infections can also sometimes occur after surgery.
Bacteria from infections elsewhere in the body can also travel to the bone in the bloodstream. If they were to find a point where they can access the bone, an infection can form. This can happen in cases of infections like urinary tracts infections and pneumonia, to name just a couple.

3. Symptoms
Many patients with a bone infection will experience no symptoms; at least not until serious complications develop. When symptoms do show, they will often be mistaken for something less serious. This is especially the case in people with a weakened immune system, and both young and older people.
When symptoms do shows, they will typically include a fever. The infected area can be painful, and the area is also likely to be red and warm to the touch. A bone infection will also often cause the patient to feel fatigued. Infections always have the potential to be dangerous, so symptoms of an infection should prompt anybody to see a doctor.

4. Skin Cancer
As well as the symptoms mentioned, a bone infection can cause some potentially serious complications. One of these is skin cancer. The condition has been known to cause squamous cell cancer in particular. Squamous cells are cells that help to make up the outermost part of your skin.
This can occur if a bone infection is releasing pus into the nearby skin, causing the cells to become damaged. Squamous cell cancer is thankfully treatable in most cases, but the patient should still find medical attention as soon as the condition is detected. In many cases, the cancerous cells will simply be removed surgically.
5. Osteonecrosis
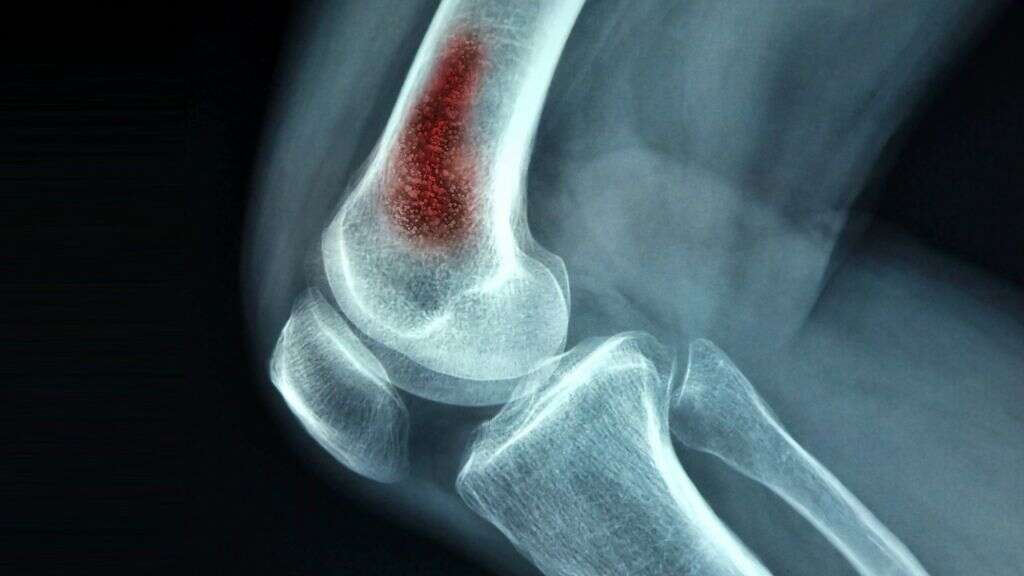
It might not look like it, but our bones are made from living tissues. Just like all of our other tissues, they need to have a constant supply of fresh blood. If this blood supply was to be cut off somehow, then the tissues could literally die. This is a condition known as osteonecrosis.
Osteonecrosis can occur when an infection of the bones disrupts the flow of blood to the bone. There is no way to reverse this bone death and the dead bone tissue will need to be removed surgically. Antibiotics will also be necessary to help fight any bacteria that are still remaining.

6. Impaired Growth
Growth plates are located at the end of the long bones in adolescents and children. They are made of cartilage and allow for the bones to grow as people grow and develop. These growth plates will disappear and turn into solid bone once the patient has stopped growing.
If osteomyelitis is in the area of the growth plates then it can result in impaired growth of the bones. This impairment will be permanent and the patient is likely to have shorter limbs than other people. Having the condition treated quickly will help to ensure that the patient doesn’t experience any growth impairment.
7. Who’s At Risk
Our immune systems are usually strong enough to prevent our bones from becoming infected. However, people that are older are likely to have less resistance to the bacteria. The same goes for people that have a weakened immune system due to medication and/or other medical conditions.
People that have recently experienced a deep injury are also at a higher risk, as are people that have recently undergone surgery. People with certain circulation disorders are also at a higher risk of developing a bone infection. This is because it is harder for white blood cells and other resources to get to the area to help fight bacteria. People that have sickle cell disease are also at a higher risk, as are people that smoke.
8. Prevention
Any infection has the potential to develop into something serious, no matter how small it might be. This means that you should take precautions when you pick up cuts and scratches. To help prevent infections from developing, any wound should be kept clean and covered. If the wound does become infected then speak with a doctor as soon as you can.
People that have recently undergone surgery are also at a higher risk, and antibiotics will often be prescribed to help prevent any infections occurring. People that have had an organ transplant are at particular risk because they are likely to be given medication that will suppress their immune system.
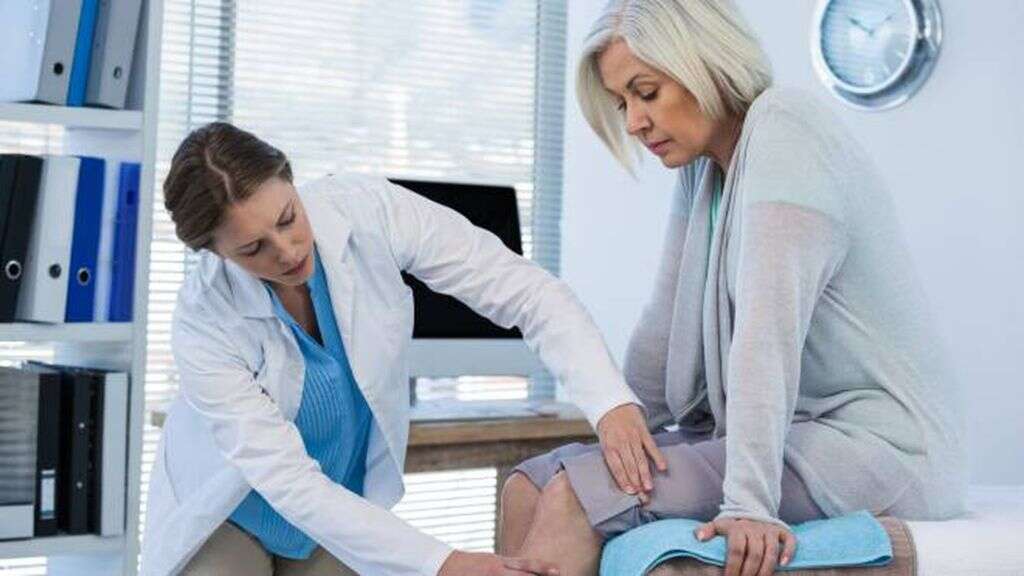
9. Diagnosis
Your doctor is likely to ask about your medical history, and about your symptoms. They are also likely to perform a brief physical exam to help look for signs of an infection. If a bone infection is suspected then the doctor is likely to request more tests. One of these will be a blood test that will help the experts look for signs of an infection.
X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans may also be used to get an image of the patient’s bone. If tests do confirm the presence of an infection then it may be deemed necessary to perform a biopsy of the bone. This is to help determine the exact nature of the infection so that the appropriate medication can be prescribed.

10. Treatment
Treatment of a bone infection will typically involve antibiotics that will help to kill the bacteria. Surgery is also often considered necessary. Surgery is required when some of the bone tissue has died, meaning it will need to be removed. The most common treatment for osteomyelitis is surgery to remove the parts of bone that are dead or infected.
Antibiotics will then be given intravenously to help kill remaining bacteria. Surgery is also sometimes needed to drain any fluids or pus that has built up. If the flow of blood has been affected then surgery may be necessary to help restore the flow. In the more severe cases, a complete amputation might be deemed necessary.