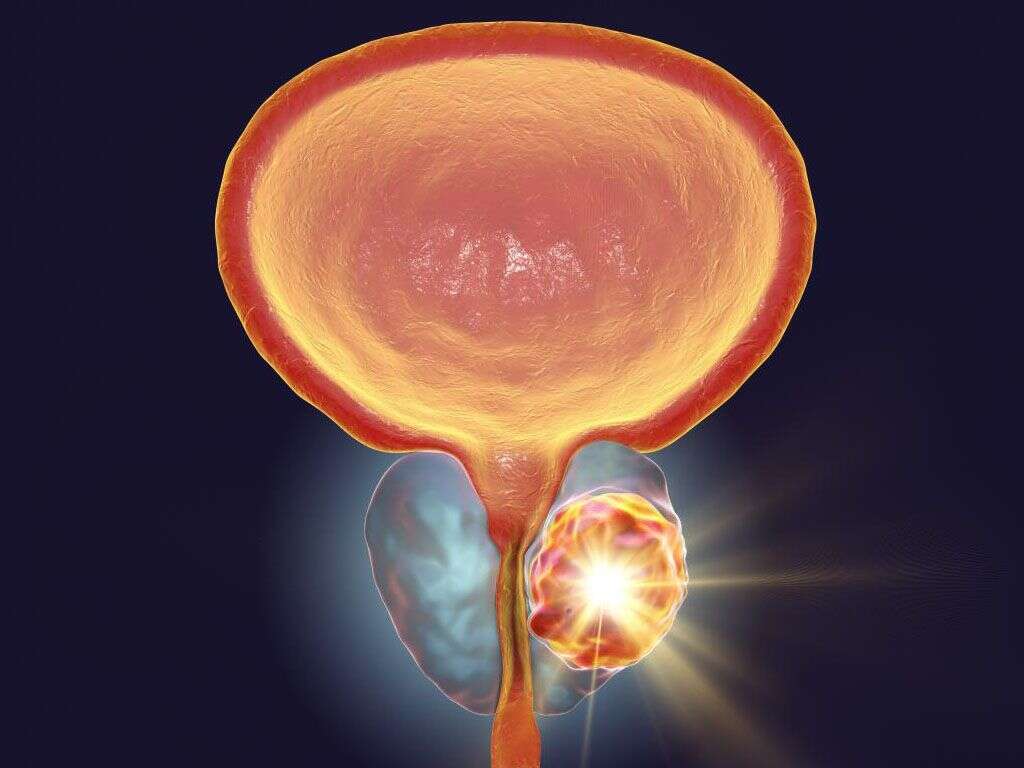
What Causes Prostate Cancer?
6. Investigations
Most cases of prostate cancer are identified through prostate specific antigen (PSA) screening and digital rectal examination (DRE) in asymptomatic men. When the PSA levels are elevated or if DRE findings are abnormal, a needle biopsy of the prostate is recommended. The evaluation from the biopsy is important as it allows the Gleason score to be calculated so prognosis can be determined.
Those with advanced disease may benefit from electrolytes, serum creatinine, and liver function tests. A urinalysis should be performed before cancer therapy is planned. A computed tomography (CT) scan may be helpful for those with a high risk of metastasis to the lymph nodes. Genetic tests for those with a family history of mutations (BRCA 1, BRCA2, and so on) may be recommended.
Advertisement