10 Toxoplasmosis Symptoms
The cause of a toxoplasmosis infection is a protozoan called Toxoplasma gondii. The parasite affects both humans and animals such as cats and dogs. The parasite can have serious effects on unborn babies whose mothers get infected.
Toxoplasmosis is transmitted from animals to humans through the ingestion of contaminated meat, fruits, raw vegetables, water, and fecal particles, or from a mother to her unborn baby.
Over 200.000 cases of toxoplasmosis are reported in the US each year. It is important to know that 80% of patients with a toxoplasmosis infection will not have any symptoms. Here are 10 symptoms associated with toxoplasmosis.
Symptom #1: Flu-Like Symptoms
Getting flu-like symptoms can be a sign of a toxoplasmosis infection. While most people with the parasite in their bodies do not get any symptoms, they still show up in some people. Toxoplasmosis symptoms are usually more serious in people with a compromised immunity, including those with HIV and cancer. The symptoms may also occur in children who got the parasite from their mothers when pregnant with them.
The flu-like symptoms may include other signs such as headache, general body aches, and fever. If you get a mild form of flu, consider consulting a doctor about tests to determine its cause.

Symptom #2: Blurred Vision
While there are other causes, vision problems, especially blurred vision, may be a toxoplasmosis symptom. The presence of the Toxoplasma gondii parasites causes inflammation in different parts of the body. In the eyes, the inflammation mainly affects the retina, leading to blurred vision. The initial appearance of blurred vision may resolve. However, it may come back later and be more pronounced and accompanied by other symptoms like eye pain and permanent eye damage. Ocular toxoplasmosis can even cause blindness.
Like other symptoms of the infection, ocular toxoplasmosis can occur in adults and children who get the primary infection with the parasite. It can also occur in children who got the parasite when their mothers were pregnant with them.

Symptom #3: Headaches
According to some research studies, recurrent headaches are among the most common symptoms of a toxoplasmosis infection. Recurrent headaches occur as a result of the infection affecting the brain and the rest of the central nervous system.
As the immune system reacts against the invading parasites, inflammation occurs within the brain and other parts of the nervous system. A toxoplasmosis infection in the brain may also lead to other physical and psychiatric symptoms.

Symptom #4: Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck, is another common toxoplasmosis symptom. This may occur together with other symptoms such as fever, headaches, and general body pain.
Similar to other parts of the body, when the Toxoplasma gondii protozoa invade the body, they can cause inflammation in the lymph nodes. It is worth to note that the lymph system is part of the immune system and is therefore involved in trying to rid the body of the invading parasites. This leads to the swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck and elsewhere in the body. In some cases, the swollen lymph nodes may be painful, while in others they are painless.
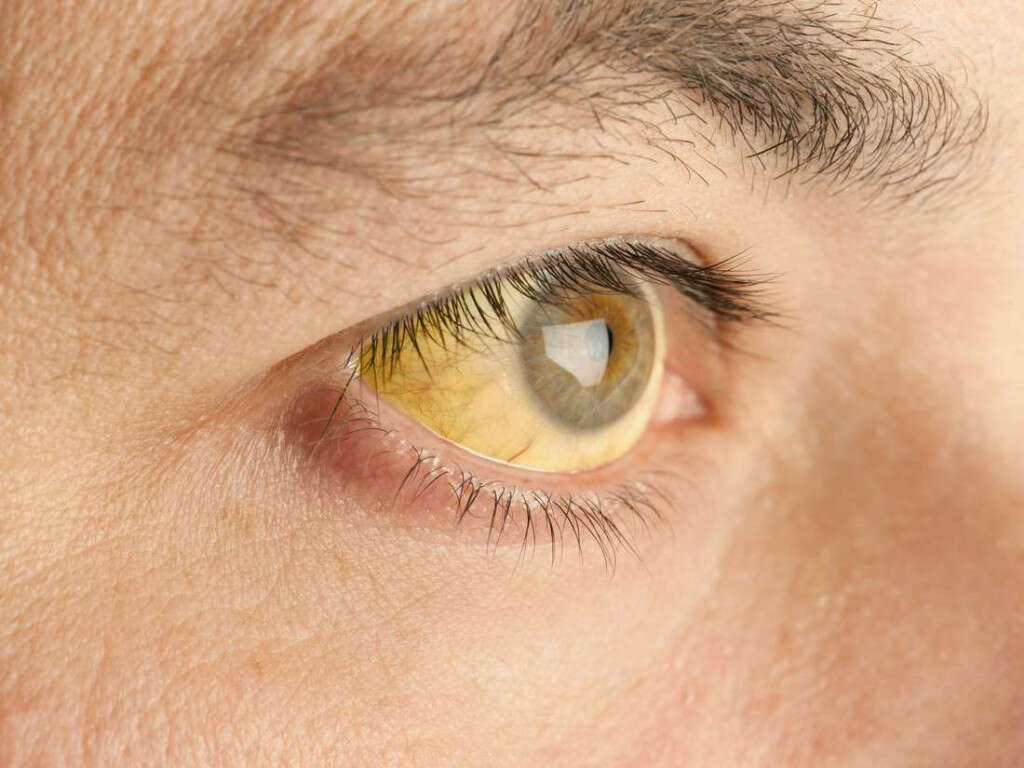
Symptom #5: Jaundice
Jaundice presents as yellowing of the skin and eyes. Most newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis will have no symptoms at all, but for the ones that do, this is one of the most common symptoms to appear.
In most cases, a congenital infection with the toxoplasma parasite does not lead to symptoms in the newborn. But one tenth of infected newborns will have symptoms that include jaundice, fever, rash, anemia, and an enlarged spleen or liver. In the rest of the babies with a congenital toxoplasma infection, if symptoms appear, they do so months or years after birth.

Symptom #6: General Body Aches
Although there are many causes of general body aches, they can also occur as a result of a toxoplasmosis infection. Inflammation is a common cause of pain wherever it occurs. Because infection with toxoplasma can affect different parts of the body, it can lead to pain in all these parts.
General body aches may be accompanied by other toxoplasmosis symptoms such as fever, headache, seizures, and blurred vision. In case you experience generalized pain that does not go away, seek medical care.

Symptom #7: Seizures
If the toxoplasmosis infection reaches the central nervous system, it can cause seizures. This symptom is often associated with immunocompromised patients and congenital toxoplasmosis as well.
Research studies have found that the parasites cause lesions due to inflammation in the brain besides other parts of the body. They also interfere with the production of some chemical compounds in the brain. Researchers think that these effects could be responsible for the neurological changes associated with toxoplasmosis.

Symptom #8: Eye Pain
Toxoplasmosis can affect the eye in many ways. Some patients may experience damage to their retina in a condition known as retinochroiditis. These patients will have an impaired vision that can be sudden or gradual.
One of the most common symptoms associated with retinal damage due to toxoplasmosis is the appearance of eye pain. It can be accompanied by light sensitivity (photophobia) as well.

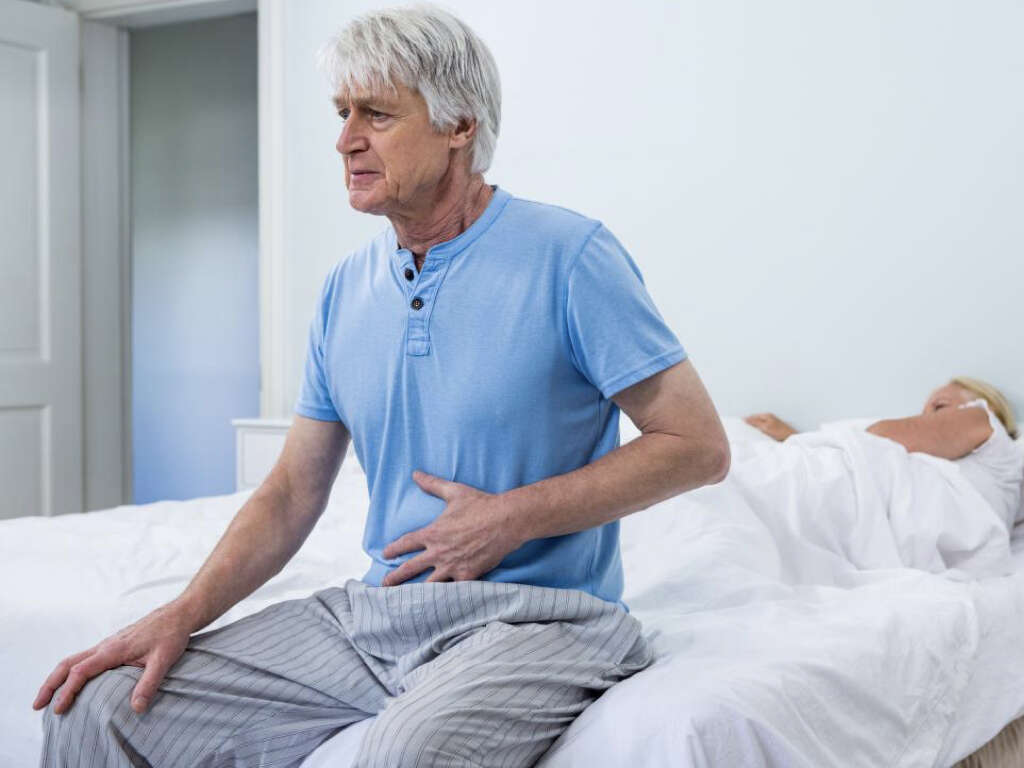
Symptom #9: Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
Patients with toxoplasmosis may suffer from enlarged lymph nodes in their abdomen. If this occurs, abdominal pain may appear, but this is not always the case. Patients may experience diffuse abdominal pain which can be mild to moderate depending on the affected lymph nodes.

Symptom #10: Altered Mental Status
Patients with a compromised immune system are more susceptible to neurological manifestations of toxoplasmosis. This is often the case for patients with HIV and cancer patients as well.
If toxoplasmosis reaches the central nervous system, many symptoms may appear. One of the most common ones is confusion and fogginess. It is not common for these changes in mental status to reach a state of a coma but depending on the inflammation of the structures in the brain, it may happen.