10 Strep Throat Symptoms
Streptococcal pharyngitis is also known as strep throat. It is an infection of the throat and tonsils caused by group A streptococcus. The symptoms of strep throat usually begin one to three days after the individual is exposed to the pathogen. It spreads through respiratory droplets from an infected individual and contact with contaminated objects. Carriers (people who carry the bacteria without exhibiting symptoms) can also spread the disease. Severe or advanced cases can lead to complications, such as peritonsillar abscess and rheumatic fever.
Diagnosis of strep throat is achieved via a throat culture or a rapid antigen test. The disease can be prevented with proper handwashing and if you do not share eating utensils. Infected individuals should avoid mingling with others for a minimum of twenty-four hours after starting treatment. Strep throat is a bacterial infection and is therefore treated with antibiotics. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, and acetaminophen (or paracetamol) can also help treat the symptoms.
Strep throat is a common bacterial infection among children. Fifteen to 40 percent of children and 5 to 15 percent of adults are affected. It is more likely to occur during early spring and late winter.
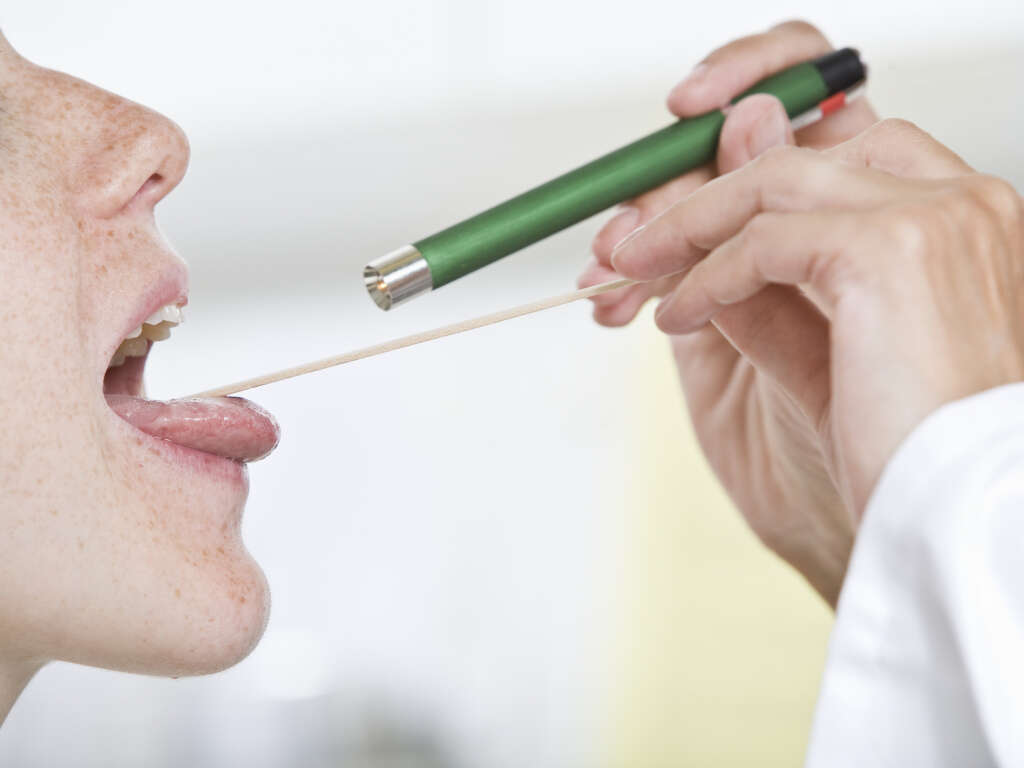

Symptom #1: Sore Throat
A sore throat is pain, discomfort, or irritation of the throat. Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and trauma are common causes of sore throats. It is a common and nonspecific symptom mostly seen in viral infections, tumors, and acid reflux disease.
A sore throat can be managed using pain medications, such as paracetamol or acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Antibiotics may be prescribed. Home remedies include gargling with warm salt water and resting the voice.

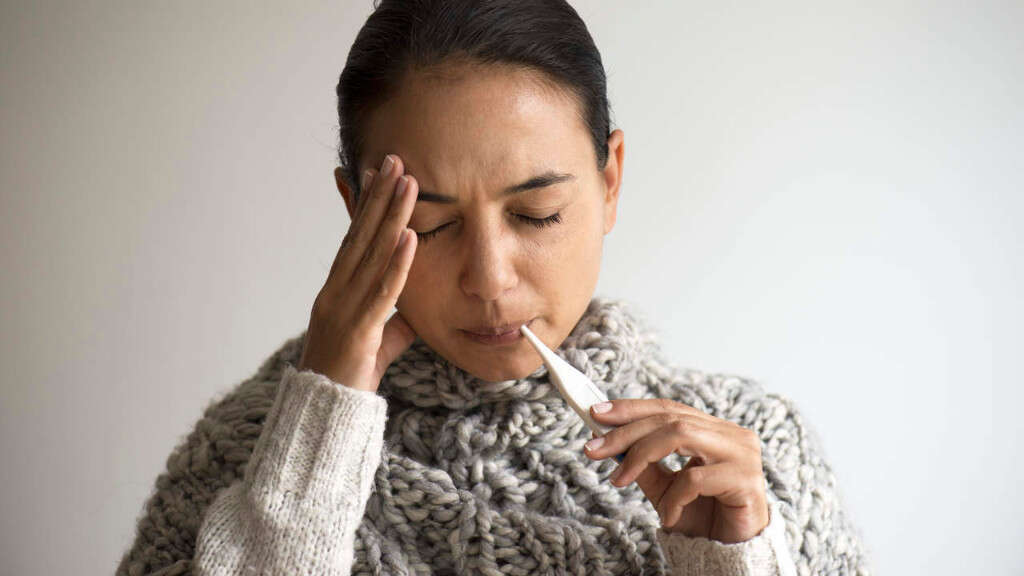
Symptom #2: Fever
A fever is the elevation above normal of the set point of body temperature. It is the body’s natural way of helping the immune system fight an infection. When the set point of body temperature increases, the body tries to reach the higher temperature.
A feeling of coldness, or chills, often accompanies a fever. The repeated muscle contractions caused by shivering help increase body temperature as the body continuously tries to produce and conserve more heat. In strep throat, the fever is usually greater than 38 degrees Celsius or 100 degrees Fahrenheit.

Symptom #3: Tonsillar Exudates
The tonsils are a collection of lymphoid tissues. A set of lymphatic tissues called Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring includes two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsil, and the adenoid tonsil.
However, the term tonsils often only refers to the palatine tonsils located on either side at the back of the throat. In strep throat, whitish-yellow or yellowish-brown pus (called tonsillar exudates) may appear on the palatine tonsils due to the bacterial infection.

Symptom #4: Enlarged Cervical Lymph Nodes
The lymph nodes are the part of the body’s immune system that helps fight off infections and filters foreign pathogens and cancer cells. There are about eight hundred lymph nodes in the human body, with approximately three hundred in the neck.
Cervical lymph nodes or lymph nodes in the neck are often affected in various conditions, such as tumors, inflammation, and infection. In viral infections, the lymph nodes can enlarge, a condition known as lymphadenopathy. When affected, the lymph nodes can become inflamed, swollen, hard, and tender. In strep throat, the lymph nodes will return to normal once the infection is treated.

Symptom #5: Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort anywhere in the neck or head. Types of headache include migraines, tension headaches, and cluster headaches. It is a common and nonspecific symptom that can be either mild or serious.
Causes of headaches include high blood pressure, dehydration, sleep deprivation, stress, fatigue, side effects of medication, brain tumor, brain bleed, and pituitary apoplexy. Most headaches can be managed using a painkiller but definitive treatment depends on the underlying cause.

Symptom #6: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a sensation of unease and discomfort that often includes an urge to vomit. Vomiting is the involuntary and forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth and sometimes the nose. It is also known as barfing, puking, throwing up, or emesis. Both are common and nonspecific symptoms that are observed in various conditions, such as pregnancy, gastroenteritis, food poisoning, chemotherapy, and viral infections.
Nausea and vomiting can be managed using antiemetics, such as metoclopramide and ondansetron. Definitive treatment will depend on the underlying cause.

Symptom #7: Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain (or stomachache) is pain or discomfort felt in the abdomen. It is a nonspecific symptom observed in many conditions, such as gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, and appendicitis.
It is also a symptom of strep throat infection. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the abdominal pain.

Symptom #8: Myalgia
Myalgia, or muscle pain, is a nonspecific symptom seen in many diseases and conditions, such as viral infections, metabolic myopathy, nutritional deficiency, and chronic fatigue syndrome. The commonest causes of myalgia are overuse of the muscles, injury, or strain.
Myalgia is distinct from arthralgia (joint pain). Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include rest, heat, paracetamol or acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and muscle relaxants.

Symptom #9: Scarlatiniform Rash
A scarlatiniform rash is characteristically seen in scarlet fever. In strep throat, the rash starts one to two days after a sore throat, fatigue, or a fever. With a scarlatiniform rash, there is diffuse redness of the skin with small bumps and papules that resemble goose bumps. These bumps give the rash its characteristic sandpaper texture. The reddened skin also blanches if pressure is applied, and the rash may be itchy.
It first appears on the trunk and eventually spreads to the arms and legs, but it spares the face, palms, and soles. After the rash spreads, it becomes increasingly pronounced in skin creases and folds, such as in the armpit or groin. After one week, the rash fades and the skin desquamates, leaving a sunburned appearance.

Symptom #10: Palatal Petechiae
Petechiae are small reddish or purplish spots on the skin that are caused by a minor break or bleed in a capillary blood vessel. The spots are less than 3 mm in size. Petechia is one of the three descriptive types of bleeding, which are differentiated by size. (The other types are purpura and ecchymosis.)
Although it is a nonspecific symptom seen in many conditions, in strep throat, the petechiae specifically appear on the palate. It is a rare but highly specific finding.