10 Side Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers or calcium antagonists are a class of medication that disrupt the movement of calcium through the body’s calcium channels. They are primarily used in the treatment of hypertension as it helps decrease blood pressure. It is especially useful in hypertension caused by vessel stiffness, which is most commonly seen in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers can also be used in the prevention of cerebral vasospasm, alteration of heart rate, and to reduce chest pain in angina pectoris.
There are different classes of calcium channel blockers but generally, they are divided into Dihydropyridines such as amlodipine, nicardipine, and nifedipine to name a few. On the other hand, we have the Non-Dihydropyridine blockers such as verapamil and diltiazem.
While calcium channel blockers have been shown to be more effective than beta blockers in decreasing cardiovascular mortality, they also have more side effects.

Side Effect #1: Constipation
Constipation refers to the condition when there are hard or infrequent bowel movements. The stools can be dry and hard. Other associated symptoms include abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, and the feeling of incomplete evacuation.
Constipation can lead to complications such as anal fissure, hemorrhoids, and fecal impaction. Common causes of constipation include pelvic floor disorders, diabetes, hypothyroidism, colon cancer, celiac disease, and side effects of medications such as antacids, opioids, and calcium channel blockers. This side effect affects less than 10% of patients taking calcium channel blockers and it is usually associated with verapamil, diltiazem, and nifedipine but it can also be seen with other drugs.

Side Effect #2: Dizziness
Dizziness is the condition where there is impairment of stability and spatial perception. It is a term commonly used to describe disequilibrium, presyncope, and vertigo. There are many conditions that can cause dizziness as multiple body parts are required in the maintenance of balance. This includes the skeleton, muscles, inner ear, eyes, and nervous system.
Dizziness may occur when there is an inadequate blood supply to the brain, disorders of the inner ear, distortion or loss of visual cues, and side effects of medications such as proton pump inhibitors, warfarin, and calcium channel blockers. This is a common side effect associated with calcium channel blockers, especially in drugs like nifedipine where the incidence of this side effect ranges from 20 to 30% of the patients.

Side Effect #3: Headache
A headache is pain that is felt anywhere in the region of the head or neck. There are several types of headaches such as migraines, tension type headaches, and cluster headaches. Frequent headaches can result in depression and can affect school, employment, and relationships.
Headaches are very common and can be caused by dehydration, temporomandibular joint issues, sleep deprivation, stress, infections, fevers, head injury, and side effects of medications such as calcium channel blockers. Headaches that occur due to calcium channel blockers are due to vasodilation.

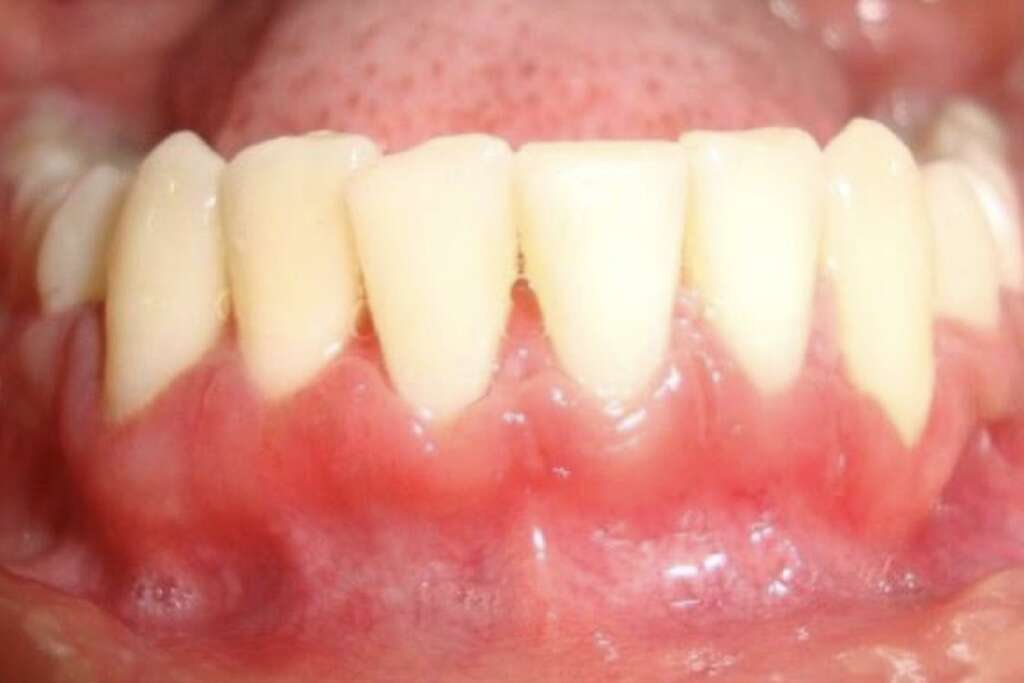
Side Effect #4: Gingival Overgrowth
Gingival overgrowth or gingival enlargement occurs when the size of the gums increases due to side effects of certain medications and inflammatory conditions. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Medications that can cause gingival overgrowth include anticonvulsants (phenytoin, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, vigabatrin, topiramate, ethosuximide, and primidone), cyclosporine (immunosuppressant), and calcium channel blockers.
Gingival overgrowth due to medications have been linked to genetic predisposition. In most patients, discontinuation of the medication usually resolves the enlargement of the gums.
Side Effect #5: Palpitations
Palpitations occur when there is a perceived abnormality of the heartbeat. They occur when the heartbeat is perceived to be excessively hard, fast, or irregular. Palpitations are also associated with anxiety and do not always mean that there is underlying disease or structural anomaly of the heart.
Some associated symptoms of palpitations include shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches, sweating, and chest pain. Palpitations can be seen in patients with hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, alcohol consumption, caffeine use, electrolyte imbalances, and side effects of medications such as calcium channel blockers and pseudoephedrine.

Side Effect #6: Rash
A rash refers to changes on the skin in terms of texture, color, and appearance. A rash can be generalized or localized to one part of the body. A rash can be itchy, dry, painful, swollen, dry, and chapped.
There are many causes of rash such as measles, food allergy, friction, poor personal hygiene, scarlet fever, infection, and side effects of medications. Studies have found that calcium channel blockers can cause cutaneous adverse reactions such as a maculopapular rash, urticaria, and pruritus.

Side Effect #7: Nausea
Nausea is an uncomfortable and unpleasant sensation where affected individuals experience an urge to vomit. While it may not be painful, it can be debilitating especially if there is prolonged nausea as it places discomfort at the back of the throat, upper abdomen, and chest.
Nausea is a common and nonspecific symptom that can be seen in motion sickness, food poisoning, gastritis, and gastroenteritis. Some medications can also cause nausea. Examples include calcium channel blockers such as nifedipine, chemotherapeutic agents, and ergotamine.

Side Effect #8: Drowsiness
Drowsiness or somnolence describes the strong desire to sleep. It can be due to circadian rhythm disorders or an underlying disease. Drowsiness may be accompanied by weakness, lack of mental agility, and lethargy.
Drowsiness can cause excessive daytime sleepiness that can have a negative impact on school, work, and daily routines. When fatigued due to drowsiness, microsleeps can occur. This can be dangerous when the individual is performing tasks such as driving a vehicle. Drowsiness can also be due to side effects of medications such as analgesics, anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, antihistamines, and antipsychotics.

Side Effect #9: Hypotension
Hypotension or low blood pressure occurs when the systolic blood pressure drops below 90 mmHg or if the diastolic blood pressure is less than 60 mmHg. While this is the definition, in practice, hypotension only occurs when there are noticeable symptoms.
Patients with hypotension may experience dyspnea, chest pain, dizziness, and fainting. Since calcium channel blockers are used to reduce blood pressure, hypotension may occur if the dosage prescribed is not optimal. Patients who are taking calcium channel blockers and experience symptoms of hypotension should inform their doctor.

Side Effect #10: Edema
Edema occurs when there is abnormal fluid accumulation in the interstitium. Edema usually manifests as swelling. Edema can be localized or generalized. In calcium channel blockers, peripheral edema is a common side effect and is believed to be due to arteriolar dilation, which leads to fluid extravasation and intracapillary hypertension.
A study concluded that the incidence of peripheral edema increases with the duration of calcium channel blocker therapy. Throughout the study, researchers observed that more than 5 percent of patients stopped using calcium channel blockers due to edema.