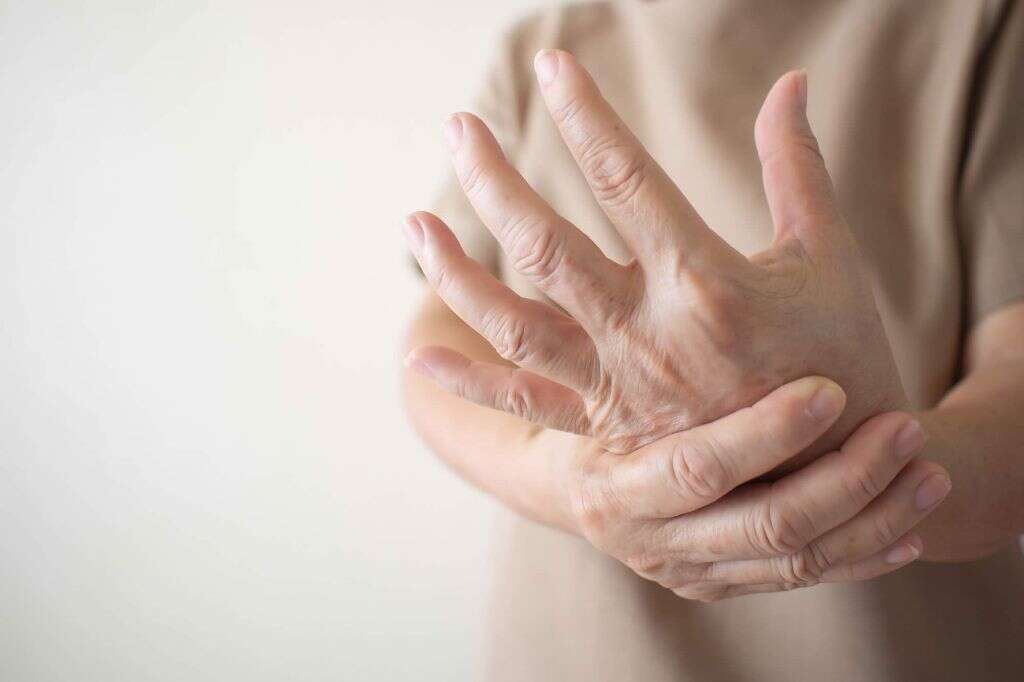
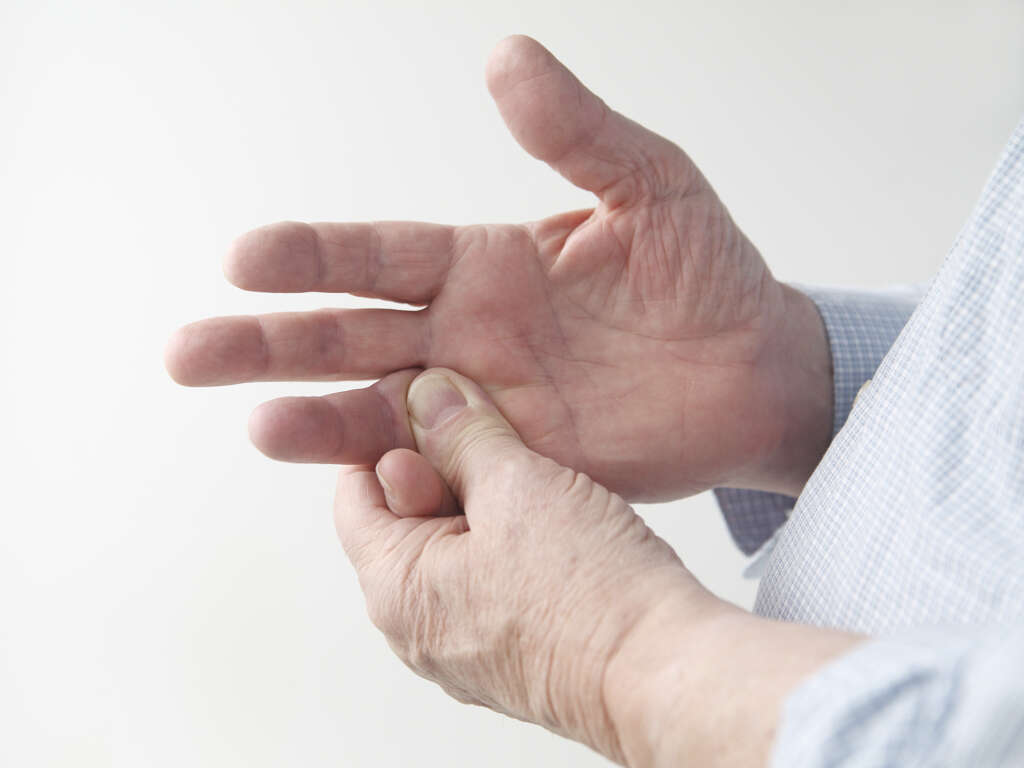
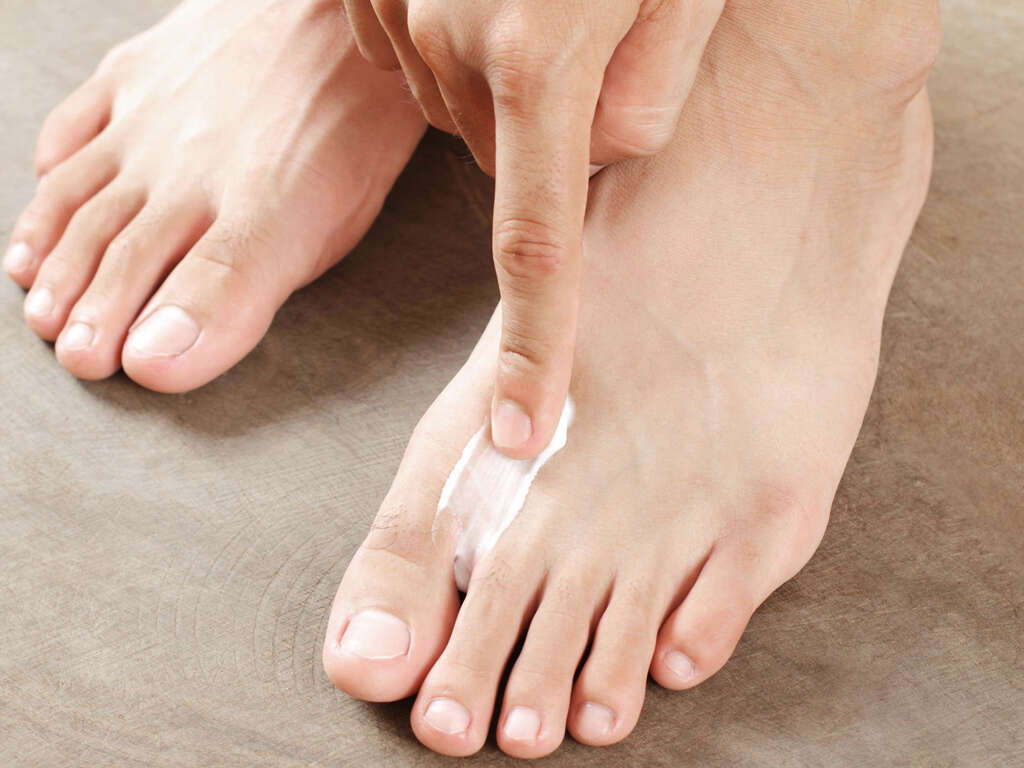
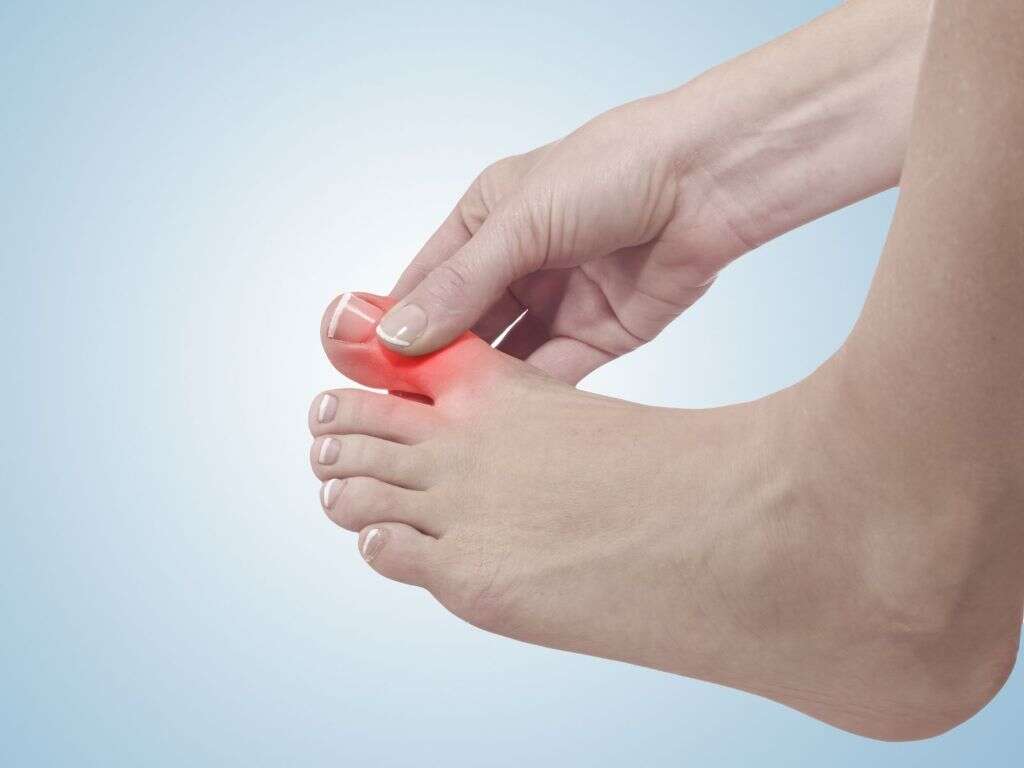
What Is Raynaud's Disease?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Fava, A., & Boin, F. (1970, January 01). Historical Perspective of Raynaud's Phenomenon. Retrieved September 02, 2020, from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4939-1526-2_1
- 2. Hansen-Dispenza, H., MD. (2019, November 02). Raynaud Phenomenon: Practice Essentials,Pathophysiology, Etiology. Retrieved 2020, from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/331197-overview#a5
- 3. Goudry, B., Bell, L., Langtree, M., & Moorthy, A. (2012). Diagnosis and management of Raynaud’s phenomenon. BMJ, 344, 37-42. doi:10.1136/bmj.e289
9. Management
The first step in the management of uncomplicated Raynaud’s phenomenon is educating the affected person about their condition. This can include recommendations on certain lifestyle changes. The warming of the affected region can also help with the acute symptoms. Lifestyle modifications can be very effective for people with primary Raynaud’s phenomenon. These include avoidance of environmental factors that trigger episodes (i.e. contact with frozen objects), the use of gloves or thick socks, and cessation of smoking. Patients can also be advised to discontinue drugs that provoke episodes. If these recommendations are insufficient, certain topical medications (that cause the widening of blood vessels), can be prescribed by the doctor.
If an underlying disease is suspected, referral to a specialist (i.e. rheumatology) is warranted. Treatment for a secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon varies according to the associated disease. Also, if a specific occupation is the cause of the condition, the patient can be advised to avoid triggers at work if possible. Certain medications can help to decrease the frequency and severity of the attacks in secondary disease. Most of them will act by relaxing and opening small blood vessels in your extremities to improve blood circulation. Finally, severe complications may warrant hospitalization and immediate medical or surgical treatment.
Advertisement