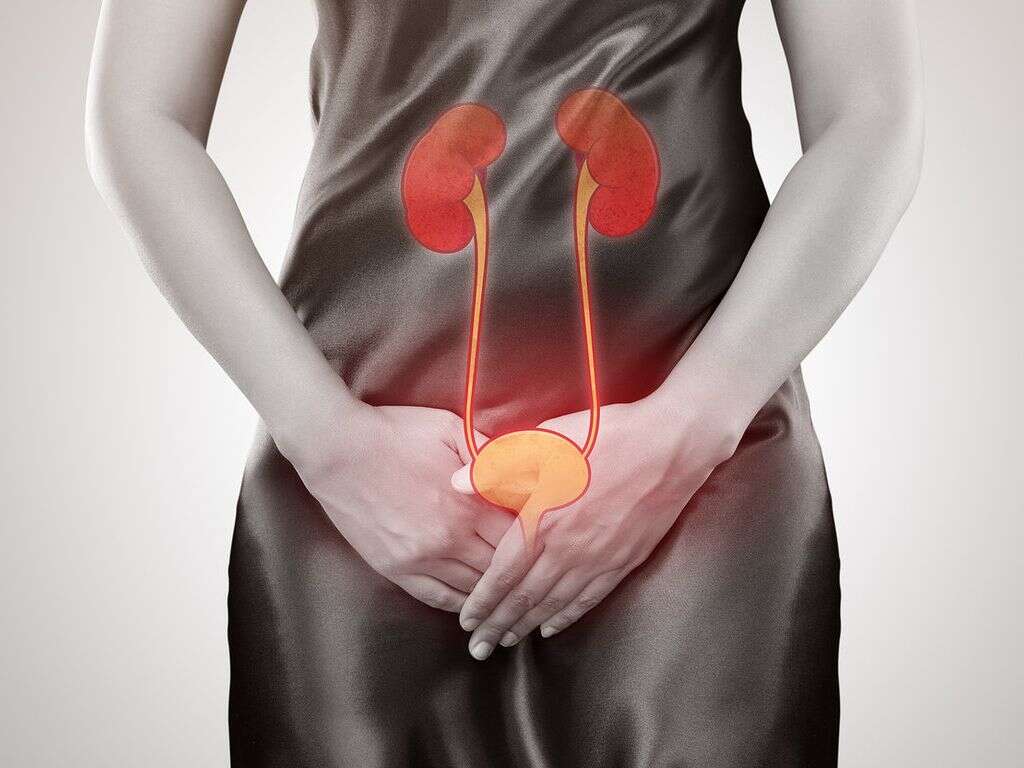
Overactive Bladder Symptoms
An overactive bladder causes a person to constantly want to go to the bathroom. It is the main cause of incontinence, or involuntary loss of urine. The condition is more common in women than men, and is quite common. Moreover, the condition is unpredictable and can be quite embarrassing for the victim.
An overactive bladder can cause some people to give up on social activities, and avoid people. This subsequently decreases their quality of life, and after a while, can lead to emotional stress, depression, and isolation. The good thing is that the condition is treatable, and you can have full control of your bladder. But what causes it, and what are the symptoms of an overactive bladder?

1. Overactive Bladder Causes
Your kidneys are responsible for the production of urine. Once urine is produced, it is transported to the urinary bladder where it accumulates before excretion through urination. Your brain gives your pelvic muscles signals to relax so that you can urinate. If your bladder is overactive, it will contract involuntarily even if it is not full. The condition can be brought about by the intake of too much fluid, taking medications that hasten the process of producing urine, urinary tract infections, excessive intake of coffee, tea, or caffeine in general, incomplete bladder evacuation, and bladder problems such as bladder stones.

2. Urinary Urgency
This is a sudden, powerful sensation of the urge to go to the bathroom and urinate. Its main cause is the sudden involuntarily contraction of the urinary bladder muscular wall.
The urgency is usually accompanied by incontinence, increased frequency of urination also called polyuria, excessive urination at night, known as nocturia, urinary incontinence, and interstitial cystitis. This urgency increases as the person gets older. The condition is controllable. However, if uncontrolled, it is called urge incontinence.

3. Polyuria
Polyuria, or frequent urination, is the need to go to the bathroom and urinate more than usual. There are many causes of polyuria; the most common cause in children and women is having a urinary tract infection (UTI). In older men, the most common cause of polyuria is an enlarged prostate. Polyuria is usually associated with urinary urgency and sometimes with urinary incontinence.
The frequency of urination per day differs between people, and changes with age. In children, it reaches 8 to 14 times. The number decreases to 6 to 12 in older children, and 4 to 6 in adults and teenagers.

4. Nocturia
Nocturia, also called nocturnal polyuria, describes excessive urination at night. While sleeping, the body produces a reduced amount of urine compared to in the daytime. However, this little amount is more concentrated.
This is why most people do not have to wake up to urinate at night, and can sleep for 8 hours without interruption from the bladder. You may have an overactive bladder if you have to wake up from your sleep to urinate.

5. Urinary Incontinence
This happens when you lose control of the urinary bladder. It is more common than many people can imagine, and it can put a person in a very awkward situation. There is a range of severity from leakages when coughing or sneezing to having an urgency to urinate immediately.
Urinary incontinence is common in old people. If you have been in this kind of awkward situation many times, it is reasonable to see a doctor for assistance.

6. Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence, or stress urinary incontinence or effort incontinence, is a special type of urinary incontinence due to the inability of the urinary bladder to close its sphincter. The condition is associated with coughing, laughing, sneezing, and doing physical activities.
All these acts lead to an increase in the intra-abdominal pressure, which subsequently increases the pressure on the urinary bladder, leading to incontinence.
7. Bladder Pain
Bladder pain syndrome, or interstitial cystitis, is a chronic pain condition affecting the urinary bladder. It is associated with urinary urgency, frequent urination, and painful sexual intercourse. Bladder pain alone can lead to severe depression and interfere significantly with the quality of life.
It is usually associated with irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia. Overactive bladder leads to bladder pain. Some patients even visit their doctors because they have bladder pain; not because they have urgency or increased urination frequency.

8. Painful Sexual Intercourse
Womens sexual health is affected negatively by an overactive bladder, whether the condition is associated with urinary incontinence or not. Sexual intercourse becomes painful and women find difficulty in achieving orgasms. Due to the pain and lack of orgasm, women’s sexual desire decreases further.
Overactive bladder can be the main cause behind the painful intercourse. Lack of sex in sexually active women can lead to depression and low quality of life, besides other problems.

9. Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are associated with an overactive bladder. An infection in the urinary tract makes the muscles of the urinary bladder more active. This increases the urgency and frequency of urination. An overactive bladder and UTIs can be associated with a burning sensation during urination.
Sometimes, overactive bladder symptoms are similar to urinary tract infection symptoms. Either way, you should pay your doctor a visit to assess the condition and confirm the diagnosis.

10. Dysuria
Dysuria means a burning sensation during urination. The condition is usually associated with urinary tract infections and an overactive bladder. Bladder overactivity alone does not usually cause a burning sensation when urinating. The burning sensation is also associated with hematuria.
The burning sensation is a dangerous sign, for which reason, you should pay your doctor a visit immediately for diagnosis and treatment. Dysuria, changes in urine odor and color, and overactive bladder suggest having a urinary tract infection.