10 Histoplasmosis Symptoms
Histoplasmosis is a disease with many names. It can be known as “caver’s disease”, “spelunker’s lung”, “cave disease”, “Darling’s disease”, “reticuloendotheliosis”, or “Ohio Valley disease”. It can cause a variation of symptoms due to an infection by the fungus, Histoplasma capsulatum. When other organs besides the lungs are affected, it is known as disseminated histoplasmosis. If left untreated, this can be fatal. It is a common disease seen among patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. In normal individuals who are not immunosuppressed or immunocompromised, a past infection can lead to partial protection.
Histoplasma capsulatum is often found in soil where there is decaying bird droppings or guano. It has been found in caves, bird roosts (especially starlings), poultry house litter, and areas harboring bats. The disruption of soil due to construction or excavation may release the infectious elements into the air which are then inhaled and settle into the lungs causing pathology. The disease is not contagious and is only contracted through the inhalation of spores. Since there is a wide spectrum of symptoms, the diagnosis can be difficult.
Tests include the identification of the fungus from blood, organs, or sputum; detection of antigens in the urine samples or blood; detection of Histoplasma antibodies in the blood; and Histoplasma skin tests. The disease resolves without treatment in most immunocompetent individuals.

Symptom #1: Fever
Fever is also known as a febrile response or pyrexia. It can be defined as an excessive increase in body temperature due to a new higher set point of body temperature.
This leads to a feeling of coldness (chills) and muscle contractions (rigors) in an effort to produce more heat. It can be caused by various conditions such as parasitic, bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Non-infectious causes include deep vein thrombosis, cancer, side effect of medication, and vasculitis.

Symptom #2: Chills
Chills refer to a feeling of coldness when one has a fever. However, in some cases, it can also be a symptom that occurs alone. In fever, it is due to the release of prostaglandins and cytokines as part of an inflammatory response. This response increases the set point of body temperature, which leads to the feeling of coldness until a new point is reached.
During chills, shivering may also occur as this helps produce heat and increase the body temperature. Chills are seen in inflammatory diseases such as malaria and flu.

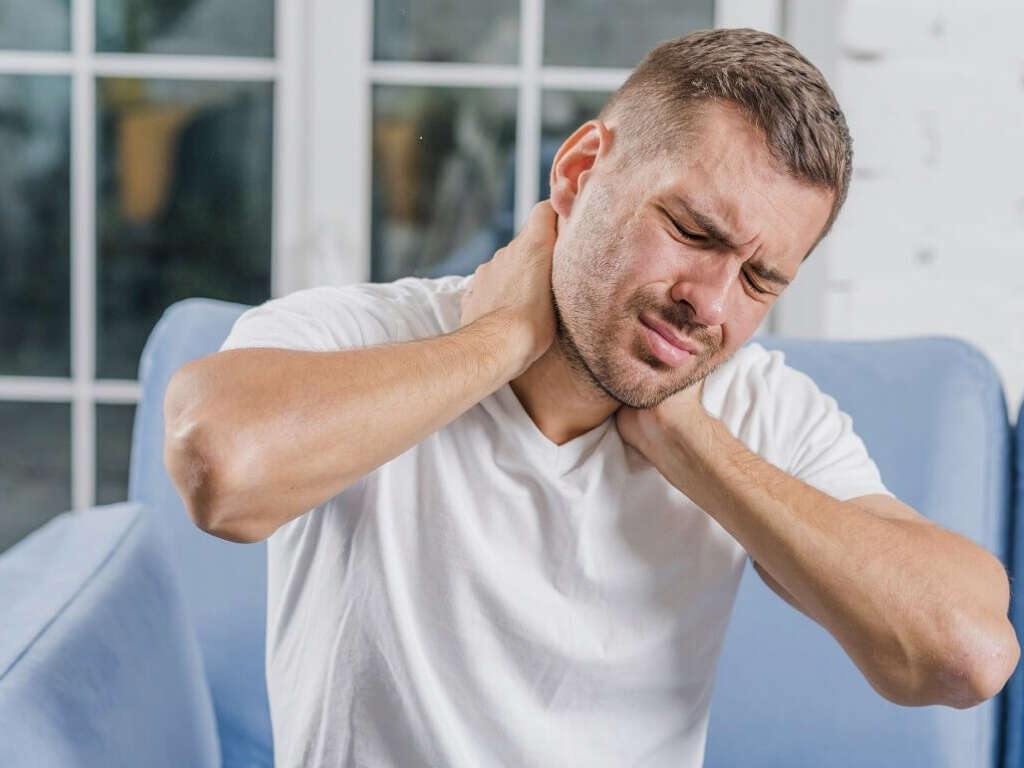
Symptom #3: Myalgia
Myalgia is a term that describes muscle pain. It is a symptom that is commonly seen in many situations or disorders such as overuse of muscles, overstretching, viral infections, compression injury, potassium deficiency, fibromyalgia, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and withdrawal from some drugs.
Without knowing the cause of myalgia, it can be managed symptomatically using paracetamol (acetaminophen), NSAIDs, rest, heat packs, and muscle relaxants.

Symptom #4: Headache
A headache can be defined as any pain that is felt anywhere in the region of the neck or head. Headaches can be divided into tension type headaches, migraines, cluster headaches, and secondary headaches. Headaches are a very common occurrence with as many as 21.8 percent of the population being affected.
They can occur in dehydration, loud noises, fatigue, sleep deprivation, hunger, stress, viral infections, common colds, sinus issues, dental problems, and head injuries. They can be managed symptomatically using pain killers such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) and NSAIDs.

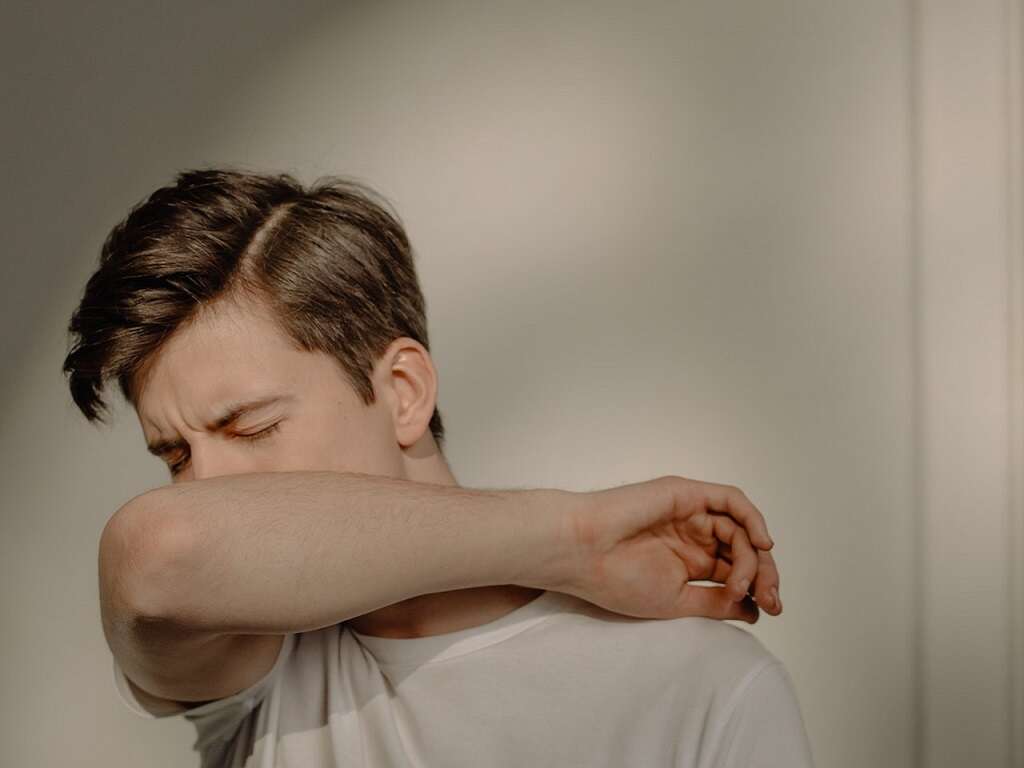
Symptom #5: Dry Cough
Cough refers to the repetitive and sudden protective reflex which functions to clear the airways from microbes, foreign particles, fluids, and irritants. There are three phases to the cough reflex: inhalation, forced exhalation, and release of air from lungs which makes a distinctive sound. When there is frequent coughing, it may indicate the presence of a disease.
From an evolutionary perspective, coughing is beneficial to bacteria and viruses as it helps to spread the disease to new hosts. Causes of coughing include air pollution, choking, asthma, smoking, post nasal drip, heart failure, and lung tumors. In histoplasmosis, the cough is often dry.

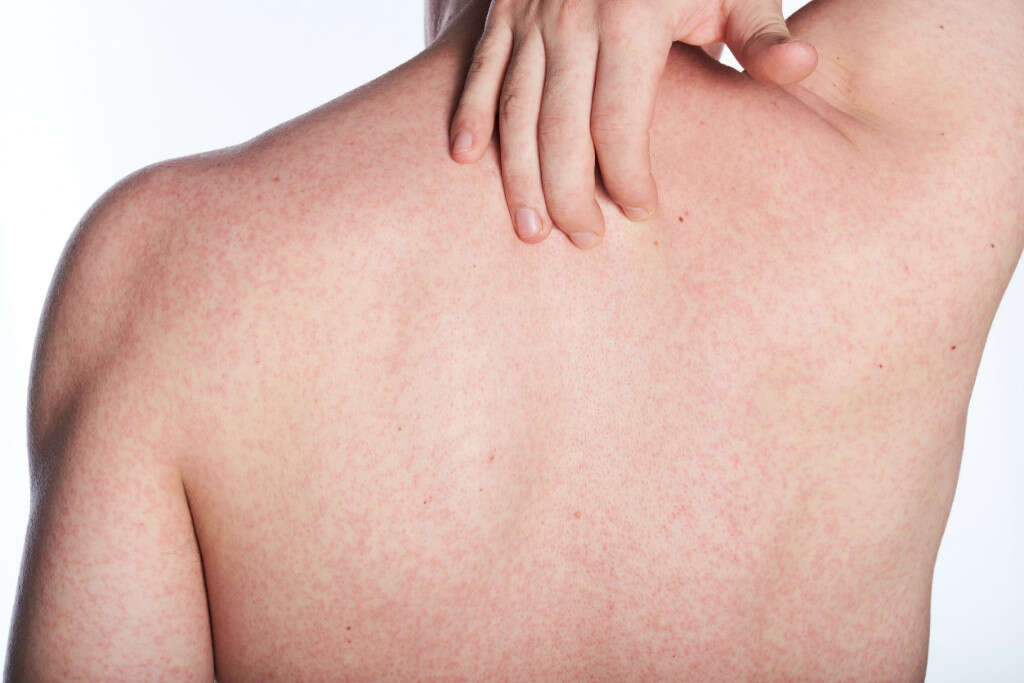
Symptom #6: Rash
A rash is defined as the change of human skin in terms of texture, color, or appearance. It can be localized or affect the entire body. Rashes can lead to itching, bumps, dry, cracked, warm, and blistered skin. There are many causes of rash with varying types of treatment.
Examples of conditions that can cause a rash include measles, food allergy, side effect of medications, skin contact with an irritant, eczema, psoriasis, and pregnancy. In histoplasmosis, the rash may be scattered with erythematous pustules and papules.
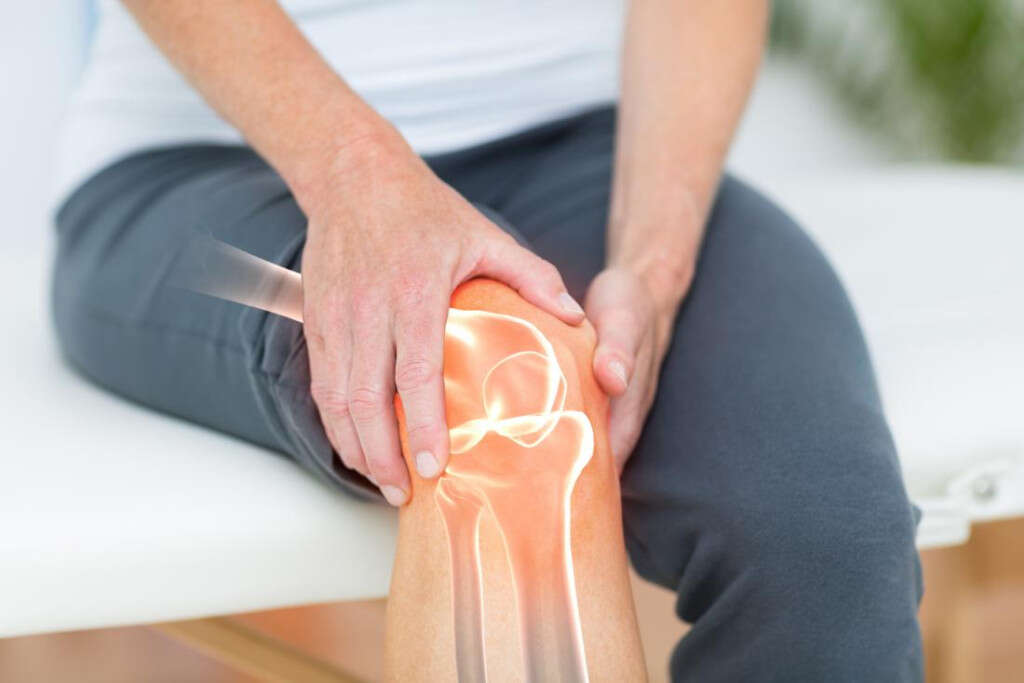
Symptom #7: Joint Pain
Joint pain or arthralgia is a common symptom that is seen in conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout attack, septic arthritis, reactive arthritis, gonococcal arthritis, and hemarthrosis.
The treatment of joint pain depends on the specific cause where it may involve the use of immunosuppressants, antibiotics, discontinuation of medicine, or joint replacement surgery.
Symptom #8: Weight Loss
Weight loss refers to a decrease of total body mass due to the loss of adipose tissue, fluid, tendon, muscle, bone mineral deposits, and other connective tissue. Divided into intentional and unintentional weight loss, unintentional weight loss may be due to impaired digestion, impaired intake of food, excessive nutrient loss, and altered metabolic demands.
Weight loss can be seen in cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, infection, renal disease, gastrointestinal disorders, neurologic disease, and cardiac disease. There are also some medications that can indirectly or directly lead to weight loss.

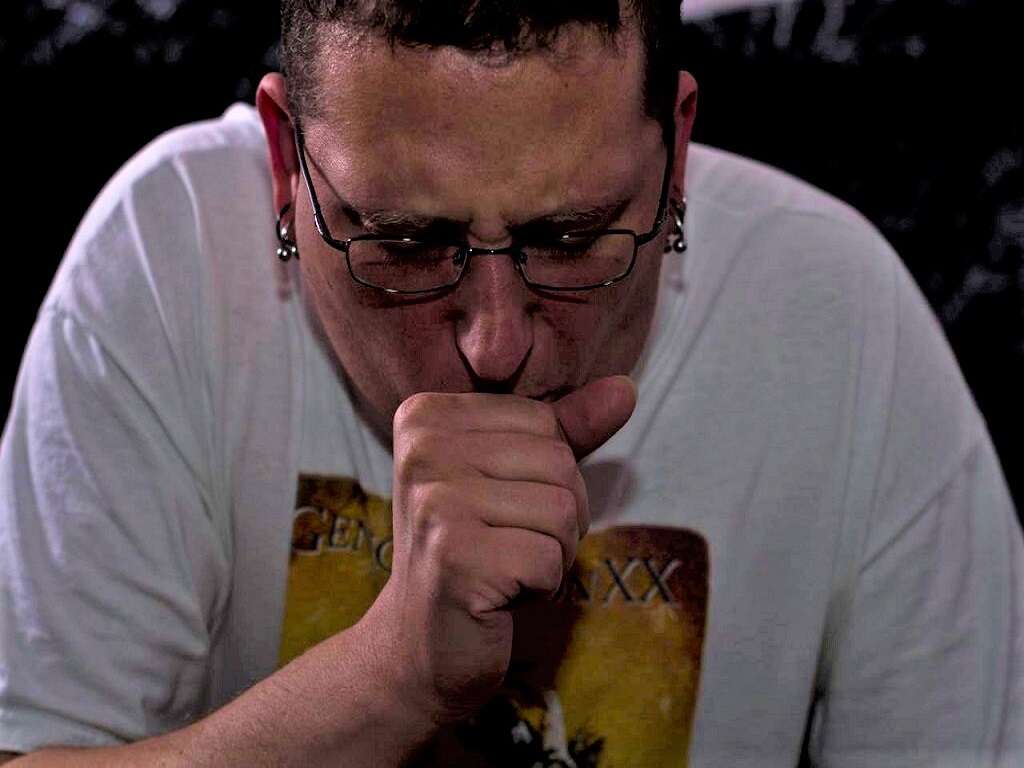
Symptom #9: Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is a term describing the coughing up of blood where it may be present in mucus from the trachea, larynx, bronchi, or lungs. Hemoptysis can be seen in tuberculosis, pneumonia, bronchitis, lung cancer, aspergilloma, pulmonary embolism, cardiovascular conditions, or when there is a foreign body in the airway.
While treatment is dependent on the underlying cause, it may involve the use of iced saline, selective bronchial intubation, topical vasoconstrictors, laser photocoagulation, endobronchial tamponade, or removal of the lung lobe. It is also a symptom seen in histoplasmosis, which is a common cause for the misdiagnosis of tuberculosis.

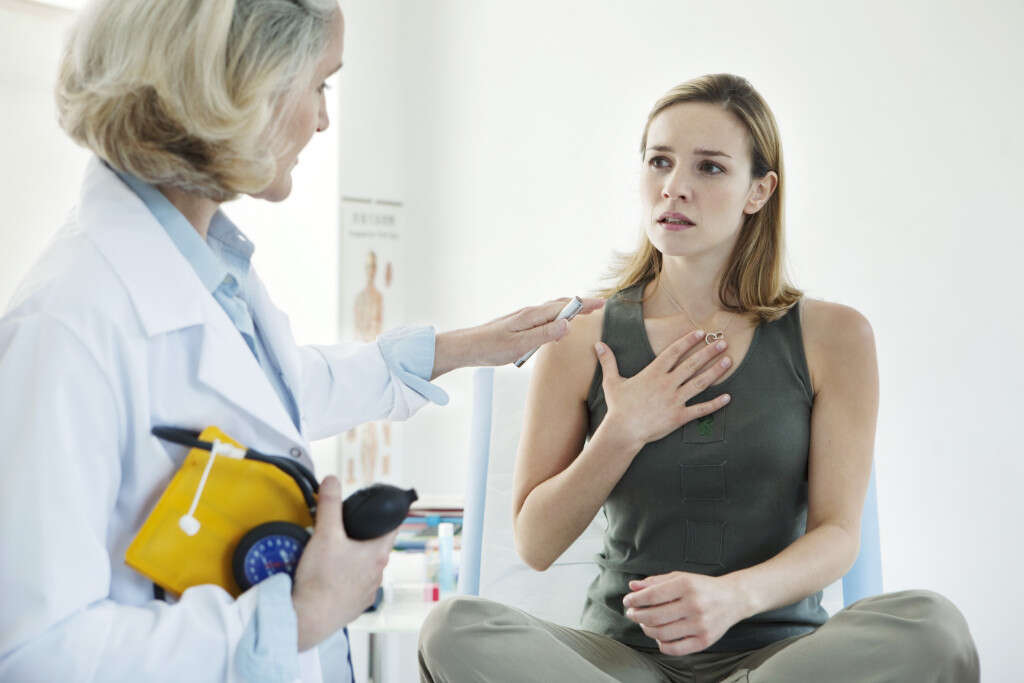
Symptom #10: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea refers to the sensation where one is unable to breathe well due to air hunger, chest tightness, or the requirement for extra effort to breathe. It is a symptom that can be seen in interstitial lung disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiac ischemia, asthma, pneumonia, psychogenic causes, and heart failure.
In histoplasmosis, the acute phase of the infection is characterized by cough and flu-like symptoms. Shortness of breath is a common symptom experienced in histoplasmosis infection and usually resolves itself once the infection is over.