Head Lice Symptoms
When we think of lice and other parasites, we tend to think of dogs, cats, and other pets. It is not only other animals that are susceptible to lice, however; people can catch them as well. One example of human lice is head lice, and they are fairly common, especially among children.
Head lice are often considered to be down to a lack of hygiene, but this is not necessarily the case. They are generally easy to treat and various products are available to kill the lice. They may be common, but head lice are not thankfully dangerous to us and are not considered to be a health risk.

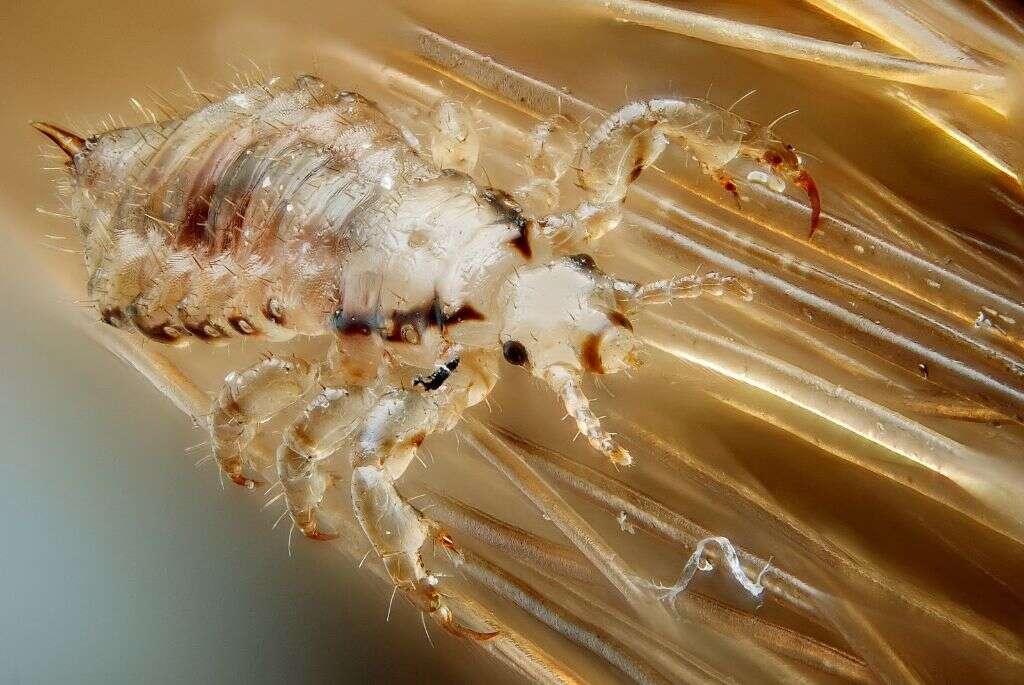
1. Head Lice
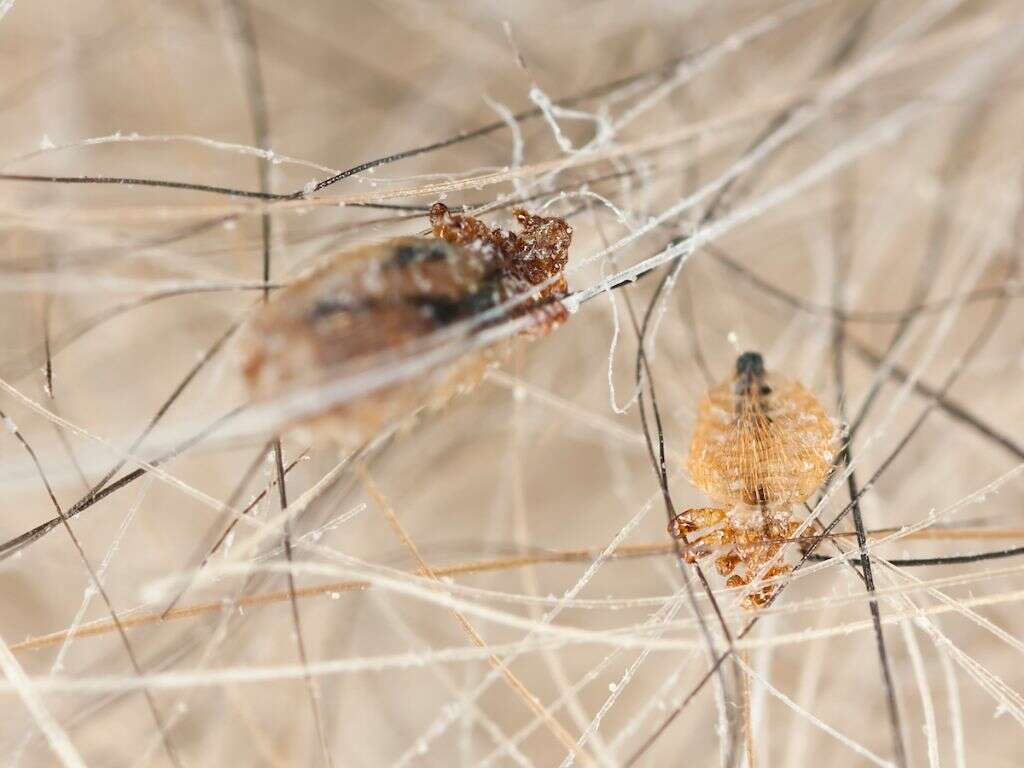
Perhaps the most common type of lice in people is head lice. As the name clearly suggests, these lice will live in the hair on our heads. They make their homes in between our hairs where they get to feed on the blood that is flowing just beneath our scalp. Head lice tend to transmit from person to person, and they usually crawl from the head of one person on the head of another.
They are often found in school children because children tend to stay close to each other. On some occasions, whole schools will experience outbreaks as one carrier can infect many other children in a short space of time.
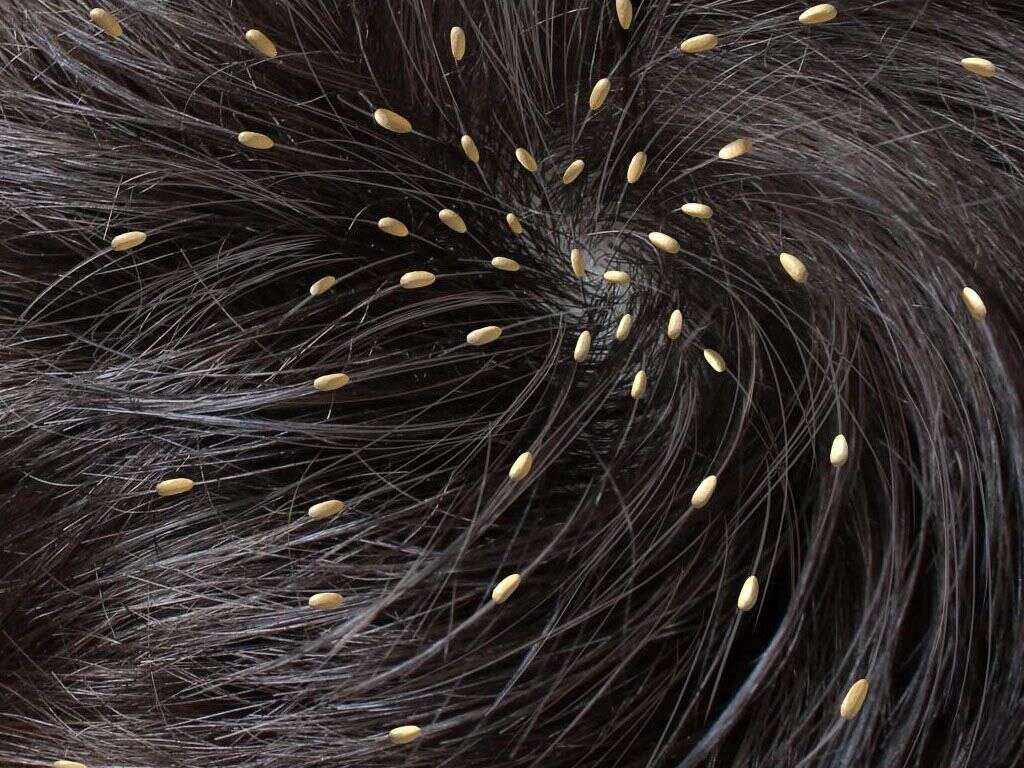
2. Body Lice
Because we are hairless, lice can find it harder to live on our bodies as they have less protection. Regardless, some people will still have problems with body lice. Instead of living on the body, they tend to live in our clothes and bedding instead, only to move to the body when they are in need of a meal of fresh, warm blood.
Body lice are not as common as head lice are and they tend to be found only in people that are unable to keep themselves and their clothing clean. This includes the elderly, the sick, the homeless, and people with certain mental health conditions.
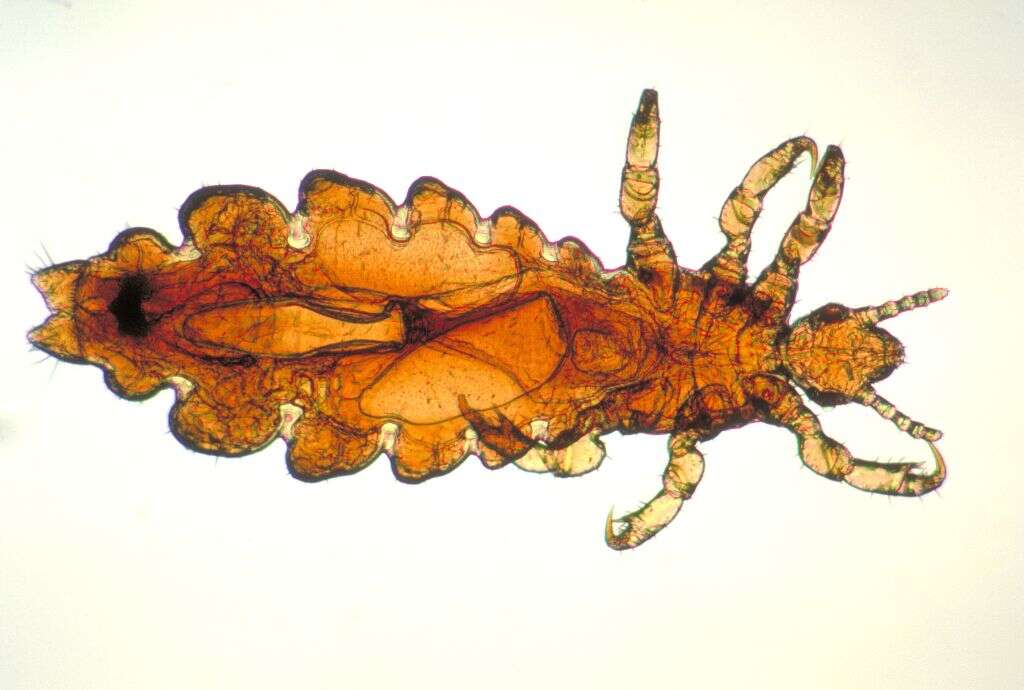

3. Pubic Lice
If you have an itch down below, it might be down to pubic lice. As with head lice, pubic lice make their home among your pubic hair, feeding on the ready supply of blood just beneath the surface of the skin. In most cases, the lice are transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person.
It is also possible to catch pubic lice without sexual contact, however. The lice can remain in a person’s bedding, clothing, or on a towel or similar. Shaving the pubic area will help to deal with infestations, as well as helping to prevent the spread of pubic lice to others. Pubic lice are commonly known as ‘crabs’.

4. Itchiness
An itchy scalp is the most common symptom that head lice will cause. They feed by biting through the thin scalp to access blood from the blood vessels just below. When they bite, the bite can result in an allergic reaction, and this results in the itching sensation that we experience.
It will often take around 6 weeks before we feel any itchiness as just a few lice will have little impact. As the lice begin to grow in numbers, however, the effects of their bites gradually become more intense. The lice can still infect other people even before symptoms appear, and this means that a carrier can infect a lot of other people without being aware.

5. Tickling Sensation
House lice are quite active little creatures and will often be moving around between the hairs on our head. As with the itchiness, we are unlikely to feel anything to begin with, but we will begin to notice as the lice breed and proliferate.
When they do move around, we are likely to feel their movements as a tickling sensation.
This tickling can be almost as irritating as the itchiness for some people, and it can contribute to some of the other symptoms that the patient will be feeling. The tickling should stop once the lice have been dealt with.

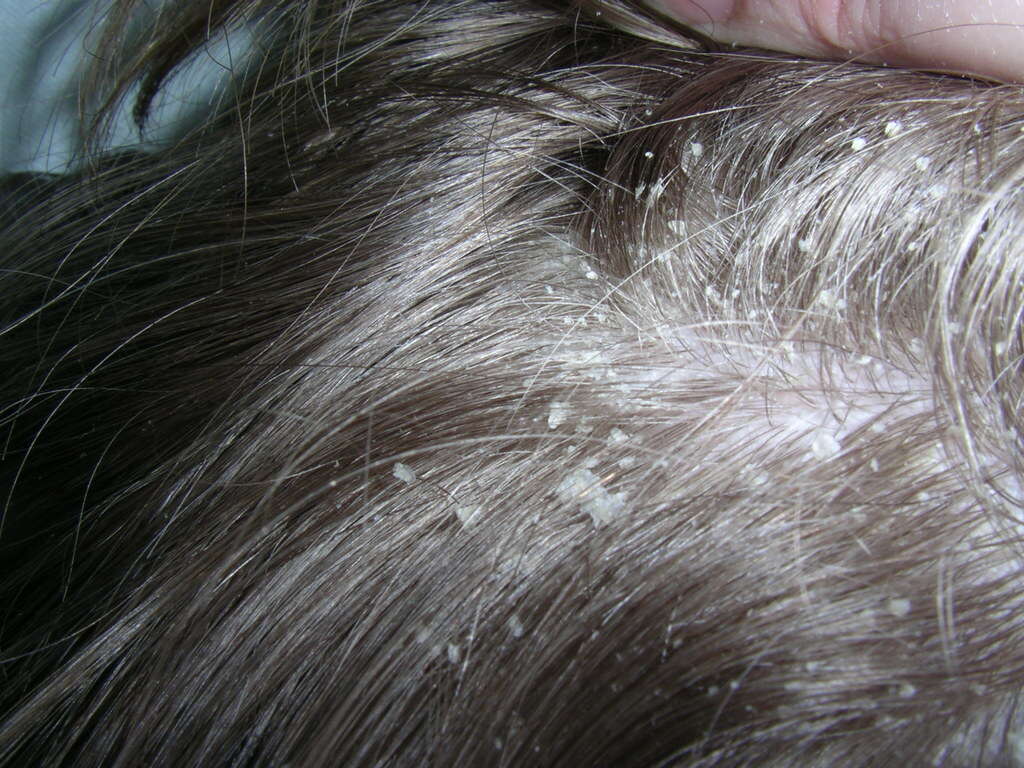
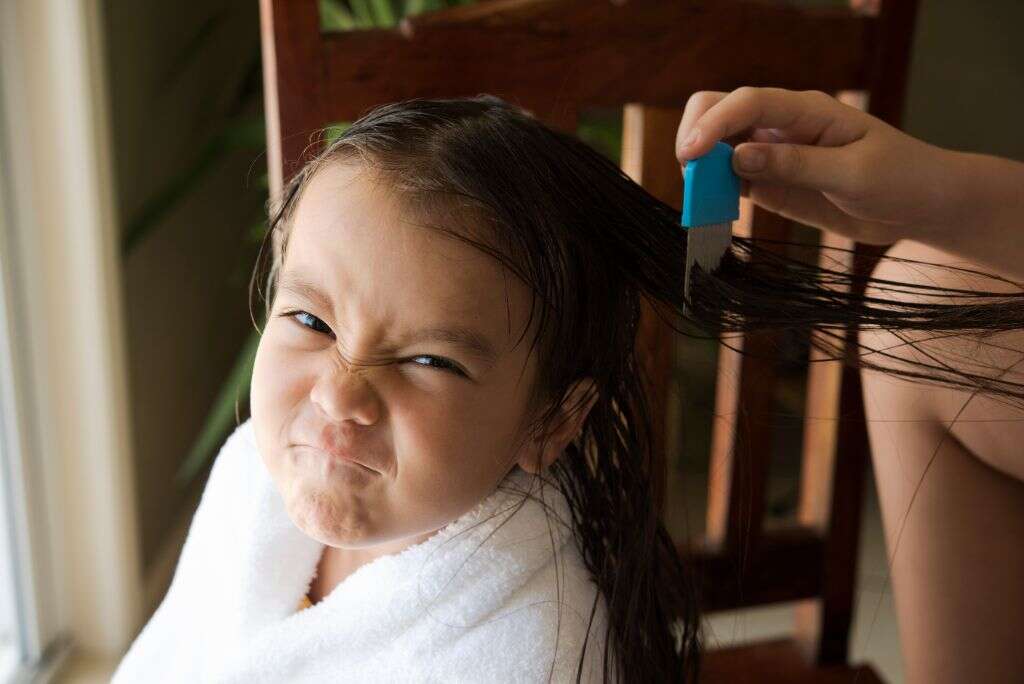
6. White Particles In Hair
When they breed, hair lice lay eggs. They lay these eggs at the base of individual hairs and are attached firmly with an adhesive. Here they will stay until they hatch. Although very small, these eggs are visible to the naked eye and are a sure sign of infestation. The lice themselves are also visible with the naked eye.
Many lice and eggs can be removed using a fine comb. When the lice or eggs are found, they can be killed by squeezing them between your nails. This will help to ensure that infestations cannot come back again after successful treatment.
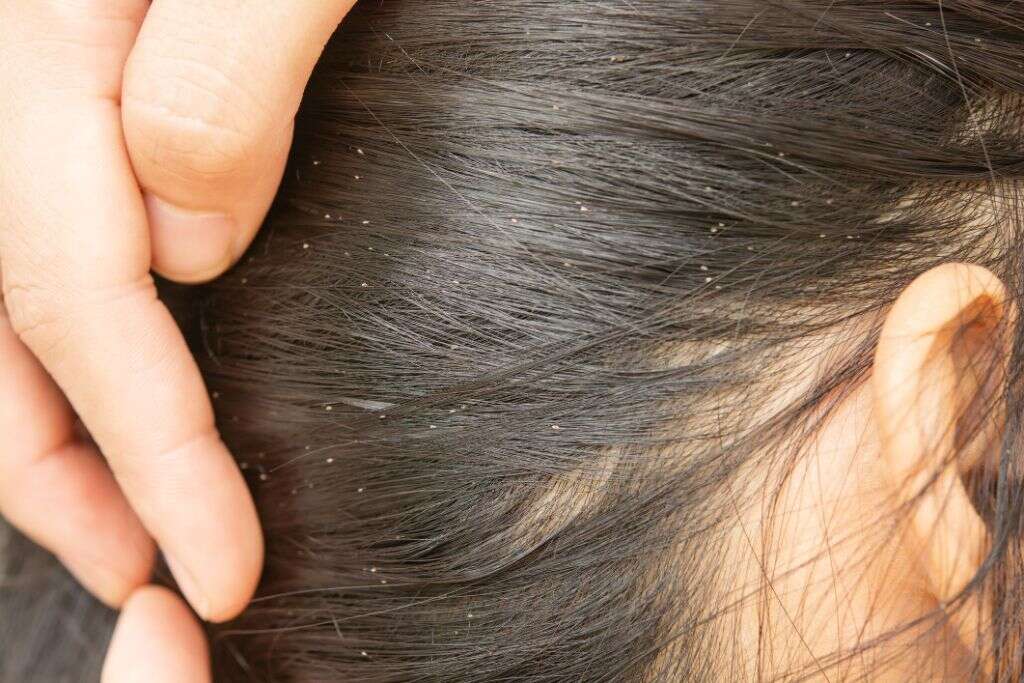
7. Sleeplessness
The itchiness caused by head louse can be very difficult to bear. They are also nocturnal animals, meaning they are more active at night, and this can become a problem for people when it comes to bedtime. Unable to relax due to the itchiness, people with a head lice infestation will sometimes find that they cannot sleep.
Not being able to sleep can cause a number of other problems for the patient. They can struggle to perform in their job, and they can also struggle in social situations. If you are having difficulty sleeping then you should speak with a professional about it.

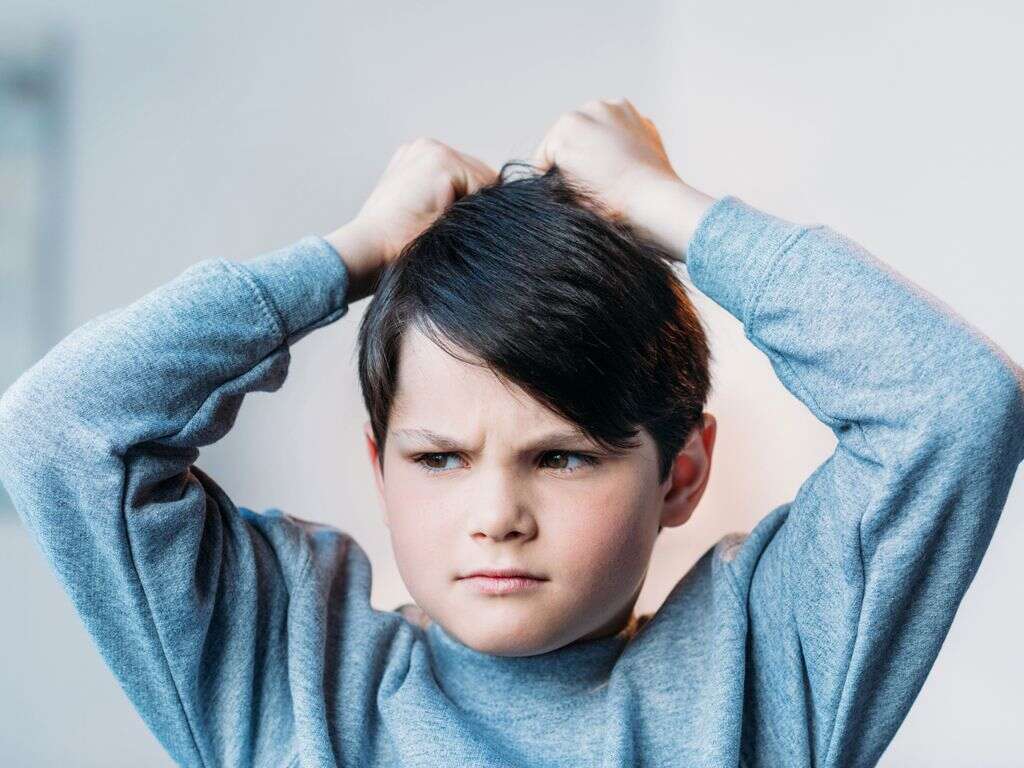
8. Irritability
The near constant itching caused by head lice can be tormenting for a lot of people. This can be very difficult for people to deal with as it can provide little to no respite. This can cause the patient to become very irritable. This is especially the case where young children are involved.
To make matters worse, sleepless nights are also likely to contribute to the patient’s irritability. The irritability alone is reason enough to get the condition seen to as early as possible, while there are also potential health problems. The good news is that head lice are relatively easy to treat.

9. Red Bumps
In instances of head lice infestations, the bites caused by the lice will sometimes result in small red bumps. A lot of the time, these bumps will remain hidden under the hair meaning they don’t get noticed. The lice will also sometimes feed on other areas on the body, though, particularly the neck and shoulders.
Other types of lice can also cause these small red bumps, meaning they might also be found on the body, including in the pubic region. Humans can also be bitten by fleas and some other insects and parasites. As such, it is a good idea to get these red bumps checked out if they occur regularly.
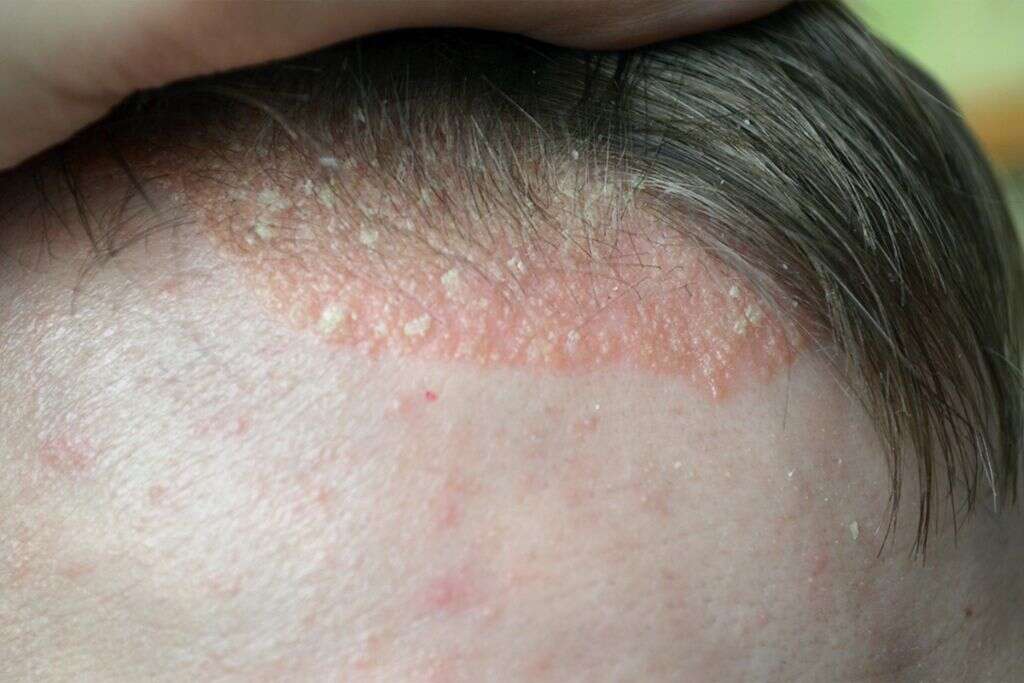
10. Sores
When you have an itch, the most obvious response is to scratch it. This can provide temporary relief from the itch, but the relief is likely to be very short-lived and will often resume as soon as the scratching stops. In some cases, scratching an itch can even make the situation worse.
Sharp nails can quite easily break the skin during scratching and can also irritate the wound, causing it to become inflamed. This can result in painful sores that are prone to becoming infected. It is always a good idea to do what you can to prevent itching, no matter how tempting it might be.