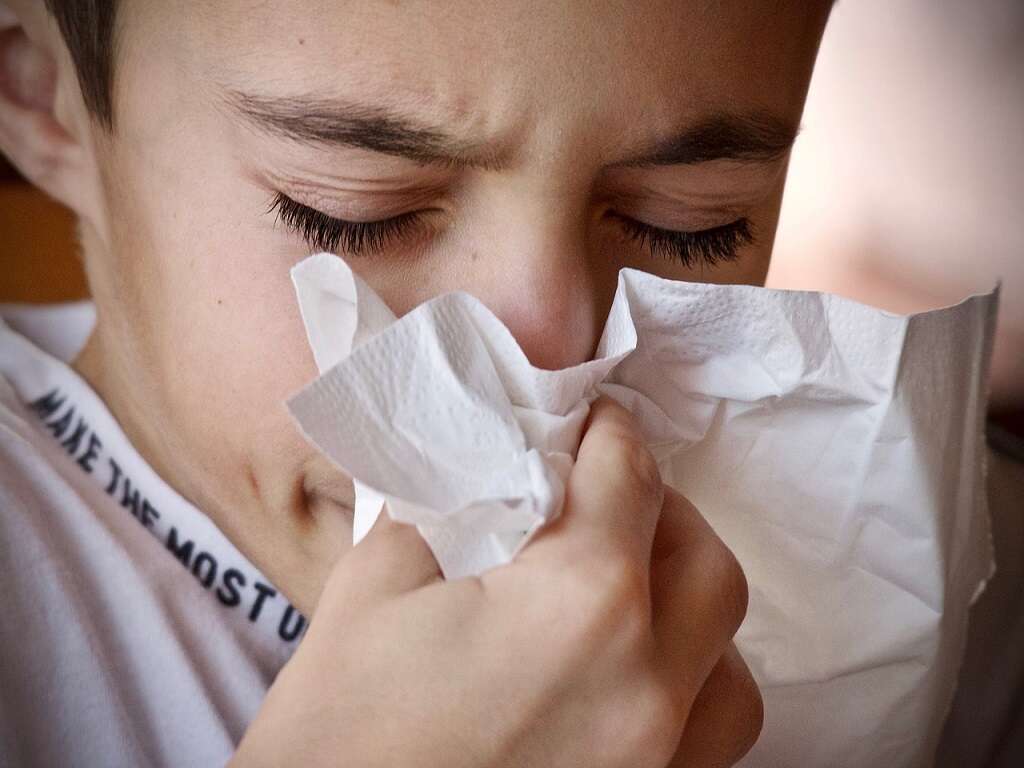
Early Flu Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Boktor SW, Hafner JW. Influenza. [Updated 2020 May 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459363/
- 2. “Cold Versus Flu.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 30 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/coldflu.htm.
- 3. Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X
- 4. Evans, Sharon S et al. “Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat.” Nature reviews. Immunology vol. 15,6 (2015): 335-49. doi:10.1038/nri3843
- 5. “Flu Symptoms & Complications.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Sept. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/symptoms.htm.
- 6. 6 North County Health Services, 18 June 2020, www.nchs-health.org/the-meaning-behind-different-types-of-coughs/.
The flu is a virus that affects the respiratory system and can be passed between people via respiratory fluids. Sometimes it can be passed between species such as with the Avian Flu. The flu is contagious before symptoms show up until about a week after contracting it. The flu vaccine is created to avoid or limit the symptoms of the anticipated viral type and strain of that season.1Boktor SW, Hafner JW. Influenza. [Updated 2020 May 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459363/
Lab tests and perhaps a chest x-ray will be used to help make a diagnosis. Severity of symptoms, risk factors, and how the individual is responding will guide what kind of treatment is used and can range from none at all to hospital level care.1Boktor SW, Hafner JW. Influenza. [Updated 2020 May 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459363/ Typically flu symptoms will come on quite abruptly and can range from mild to severe.2“Cold Versus Flu.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 30 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/coldflu.htm. Visit a doctor if you have some or all of the following symptoms.

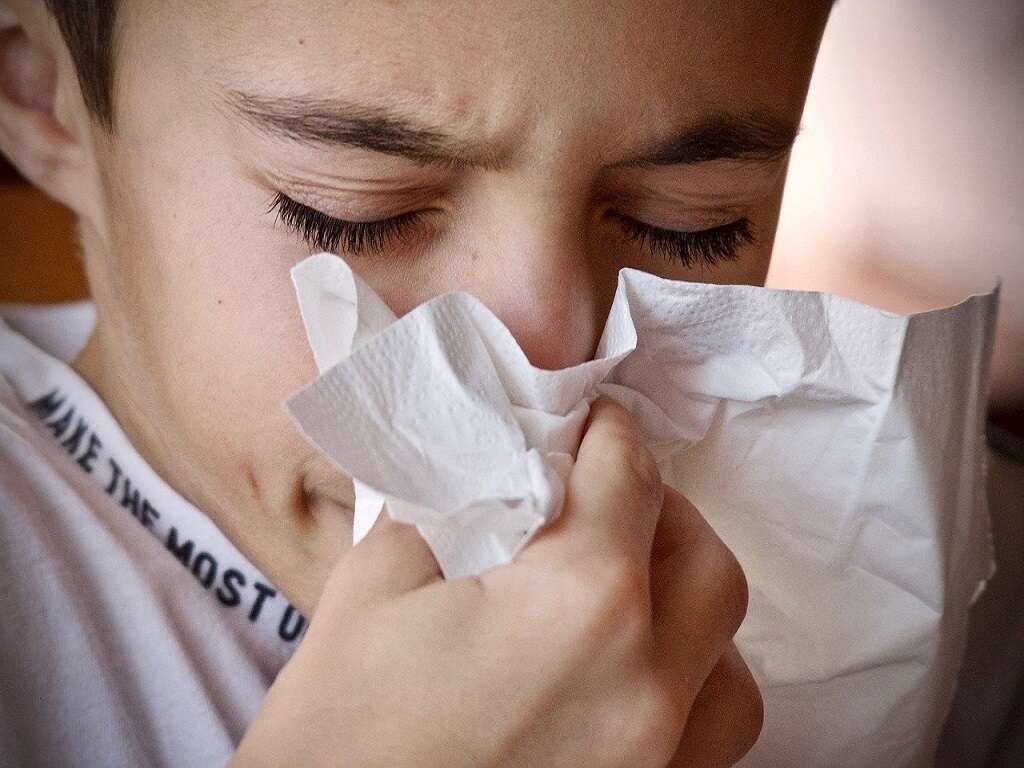
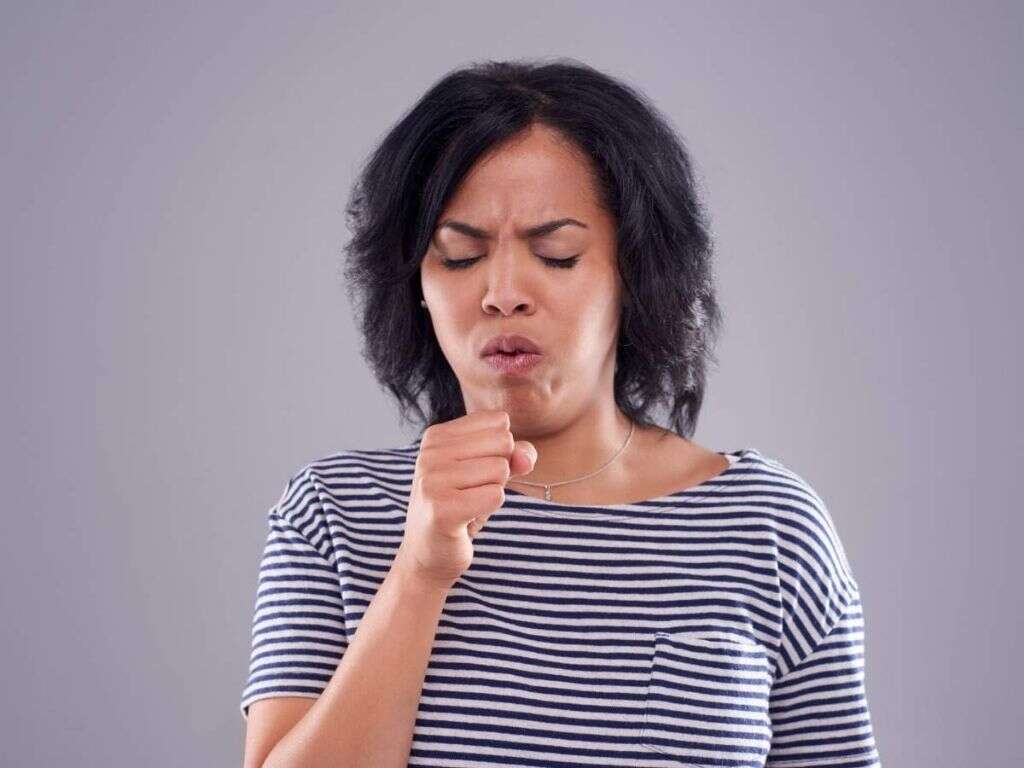
1. Cough
A cough is an action meant to remove some sort of an obstruction from the pulmonary system. The pulmonary, or respiratory, system includes the trachea, bronchioles, lungs, alveoli, etc. and is our airway in and out of the body.
A cough can indicate a number of illnesses affecting the pulmonary system such as allergies, asthma, the flu, cancer, pleuritis, COPD, a pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension, etc. A cough alone is typically not enough to make a diagnosis and so other symptoms and tests will be taken into account. That being said, the type of cough (dry vs wet vs croup vs whooping vs uncontrollable) can help indicate what may be going on.66 North County Health Services, 18 June 2020, www.nchs-health.org/the-meaning-behind-different-types-of-coughs/.

2. Fever or Feeling Feverish
Fevers are a sign of infection or inflammation. Fevers occur when our immune system triggers a part of our brain to increase our internal temperature in order to reduce the chances of a pathogen being able to survive within the body, among other complex immunity responses. In some cases, a 1-4 Fahrenheit degree increase can actually improve chances of survival of the person, particularly with the flu.
That being said, an uncontrolled fever is not beneficial especially if the person has high levels of inflammation, an injury to their nervous system, or sepsis. Fevers that are too high can cause tissue damage or seizures. Fevers are an amazing adaptation that help to keep us safe from pathogens but when uncontrolled can cause serious harm.

3. Sore Throat
As mentioned above, the flu is a viral infection of the respiratory tract. Since the throat is a part of the respiratory tract it makes sense that a sore throat would be a symptom of the flu. A sore throat could also be caused by Strep throat, different infections of the upper respiratory system, allergies, smoke inhalation, etc.
It can be tough to tell if a sore throat is from a bacterial infection or a viral infection which can sometimes make treatment a challenge. A doctor will likely review why a sore throat may be bothering a patient and combine this with other symptoms and some lab tests in order to come to the correct diagnosis and course of treatment.

4. Myalgia and Body Aches
Myalgia, or muscle pain, is a pretty vague symptom. Myalgia can be caused by a strenuous workout or injury to a muscle; however, this type of muscle pain will only be in the areas that were overworked or injured. In the case of myalgia from dehydration or by something more sinister such as disease or a side effect of a medication, pain symptoms will be more spread out throughout the body.
Myalgia and body aches are a common symptom of the flu. This pain occurs due to increased inflammation and chemicals from the immune system working hard to fight off the harmful germs. This explains why the aches and pains seem to be all over the body as opposed to just one spot.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X

5. Headache
It is currently unclear as to why headaches occur with the flu. It has been thought that headaches can be caused by the chemical reaction that occurs in an immune response. As mentioned before, an immune response is when the immune system works hard to ward off a harmful pathogen within the body.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X
Headaches can also be caused by dehydration or lack of nutrients. When an infection occurs, and especially if a fever accompanies it, the body is working very hard to combat the harmful virus or bacteria thus using more of the body’s resources even while resting.

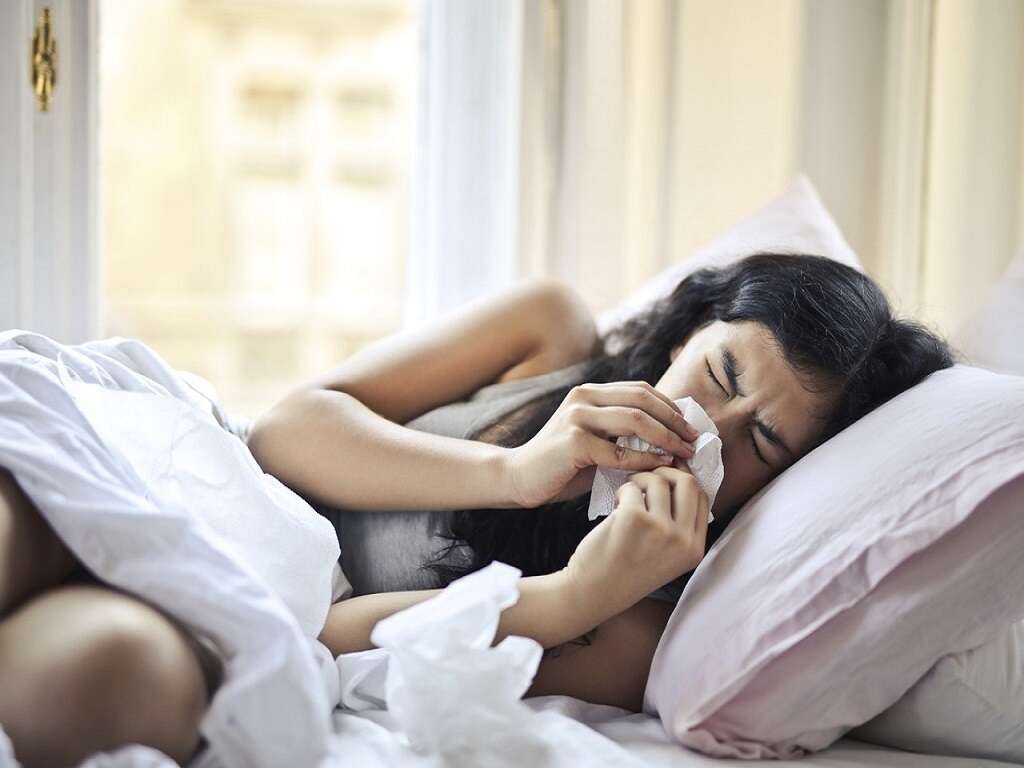
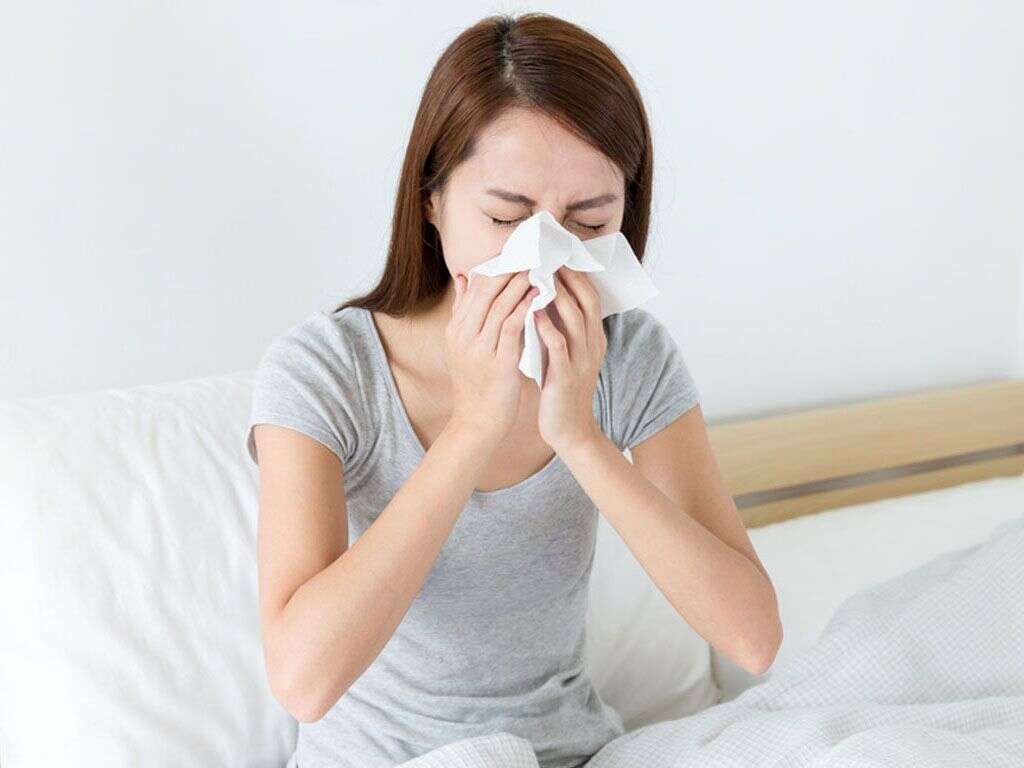
6. Runny Nose
Runny nose is a classic early sign of the flu. It occurs as a reflex, much like sneezing, and is a part of the immune system’s response to an illness such as the flu. The color of the mucus helps to indicate whether or not the infection is a virus or bacteria which can help healthcare providers to narrow down their diagnosis and treatment plan.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X
Nasal congestion is typically a symptom that will occur later in illness like the flu. Sinus pain may also be a symptom of the flu and is due to pressure changes within the sinuses and also pressure changes of the blood vessels associated with the sinuses.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X

7. Congested Eyes and Eye Pain
Eye congestion is typically a response to inflammation within the nose and sinuses.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X This type of inflammation is common with the flu and other respiratory illnesses. Eye congestion or watery eyes may also be due to another type of infection, allergies, or exposure to a pollutant.
Eye pain, specifically pain behind the eyes, is another symptom of certain strains of the flu.5“Flu Symptoms & Complications.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Sept. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/symptoms.htm. This pain can actually be due to the increased pressure of the congestion sign that is so common with the flu. This may also be another reason for headaches that often occur with the flu.

8. Fatigue, Malaise, and Mood Changes
When people become sick it will not only be apparent in their physical symptoms but also in their behavior as well. It is well documented that fatigue, malaise, and mood changes are indicators of sickness. Other behavior changes include reduced alertness, depression, irritability, lack of motivation, etc. A sudden onset may indicate an acute infection.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X
It is thought that these changes in behavior are due to responding to the discomforts of the physical symptoms of illness. There is also evidence that the actual chemical changes that occur with an immunity response can cause “sickness behavior” as well.3Eccles, Ron. “Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza.” The Lancet. Infectious diseases vol. 5,11 (2005): 718-25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X

9. Asymptomatic
When first contracting the flu people will often not have any symptoms at all. It takes about 1-4 days after being infected for symptoms to appear. During this asymptomatic time the flu can still be passed between people. In fact, the flu tends to be most contagious in the first 3-4 days and can last 7+ days after becoming sick.
If you encounter someone who you think may have the flu it may be wise to limit your contact with others for a couple of days. This will help to avoid further spread of the virus. Also, give your immune system an extra boost by getting plenty of sleep and eating good, nutritious food. Vitamin C is also well known for its immune boosting function.
10. Emergent Symptoms
The flu is potentially deadly and so it is worth noting the emergent symptoms that can occur. Medical help should be sought out right away if these signs are present.5“Flu Symptoms & Complications.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Sept. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/symptoms.htm.
In children these symptoms include the following: fast or trouble breathing, blue lips or face, ribs that pull in with breathing, chest pain, refusing to move due to pain, dehydration, not alert or interactive, seizures, fevers more than 104 degrees, a fever in an infant less than 12 weeks, fever or cough that returns after going away, or worsening of another medical condition.5“Flu Symptoms & Complications.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Sept. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/symptoms.htm. Emergent symptoms in an adult include: shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, pain or pressure in the chest or stomach area, dizziness, confusion, difficult to arouse, seizures, not urinating, severe muscle pain, severe weakness, fever or cough that returns after going away, or worsening of another medical condition.5“Flu Symptoms & Complications.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Sept. 2019, www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/symptoms.htm.