10 Alcohol Poisoning Symptoms
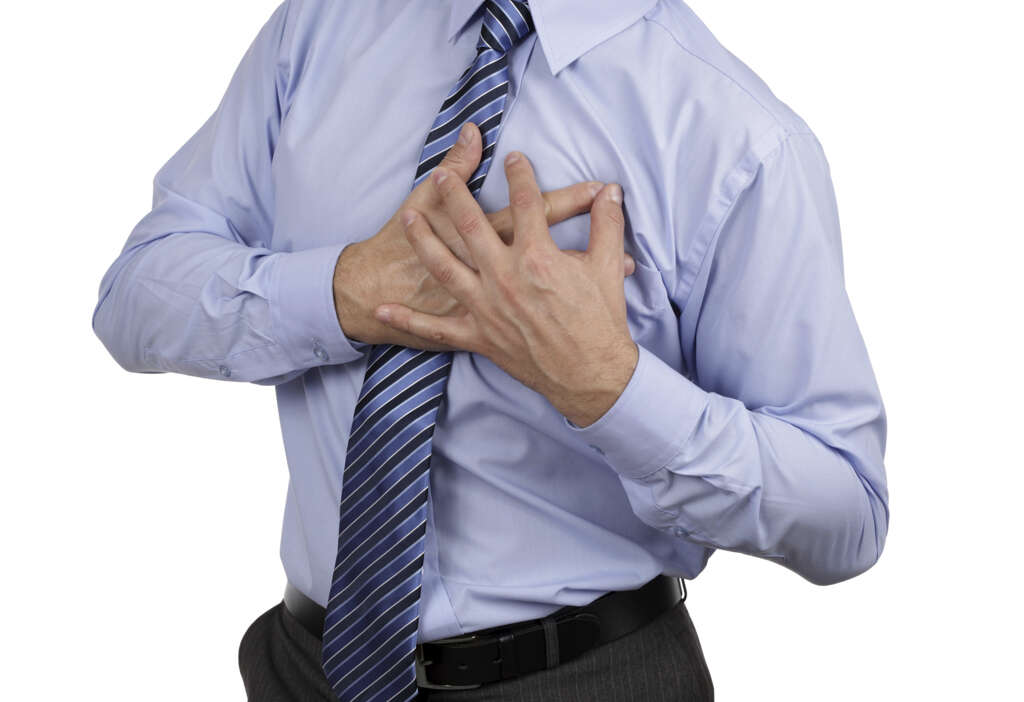
4. Palpitations
Palpitations can be defined as the sensation of a rapid or irregular heartbeat. It is a non-specific symptom that is commonly associated with certain lifestyle factors, such as the consumption of stimulants (coffee, nicotine, stress, exercise), drugs, and several medical conditions. For example, fever, anemia, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), anxiety disorders, heart conditions, and thyroid disorders can trigger palpitations. Alcohol can also cause palpitations due to various reasons. Ethanol poisoning can cause excessive fluid loss through vomiting and urination, which can result in hypotension. In compensation for this low blood pressure, the heart rate will increase (compensatory tachycardia) and the affected individual may experience palpitations.
Chronic and acute alcohol consumption can have a toxic effect over the heart, directly on its muscular tissue (myocardium). It can even induce high blood pressure in some people. These aspects, in conjunction with other factors, can alter the cardiac function and trigger cardiac complications during alcohol poisoning. Cardiac arrhythmia is a cardiac complication that can cause palpitations in alcohol poisoning. It can be loosely defined as a disorder where the heart beats with an irregular rhythm. Interestingly, there is a condition known as “Holiday heart syndrome”, where heart arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation) occur after bouts of binge drinking, even in healthy people.
Advertisement