10 Tularemia Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
- 2. 'Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.' Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635
- 3. 'Tularemia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.' MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000856.htm
- 4. 'Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.' Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia
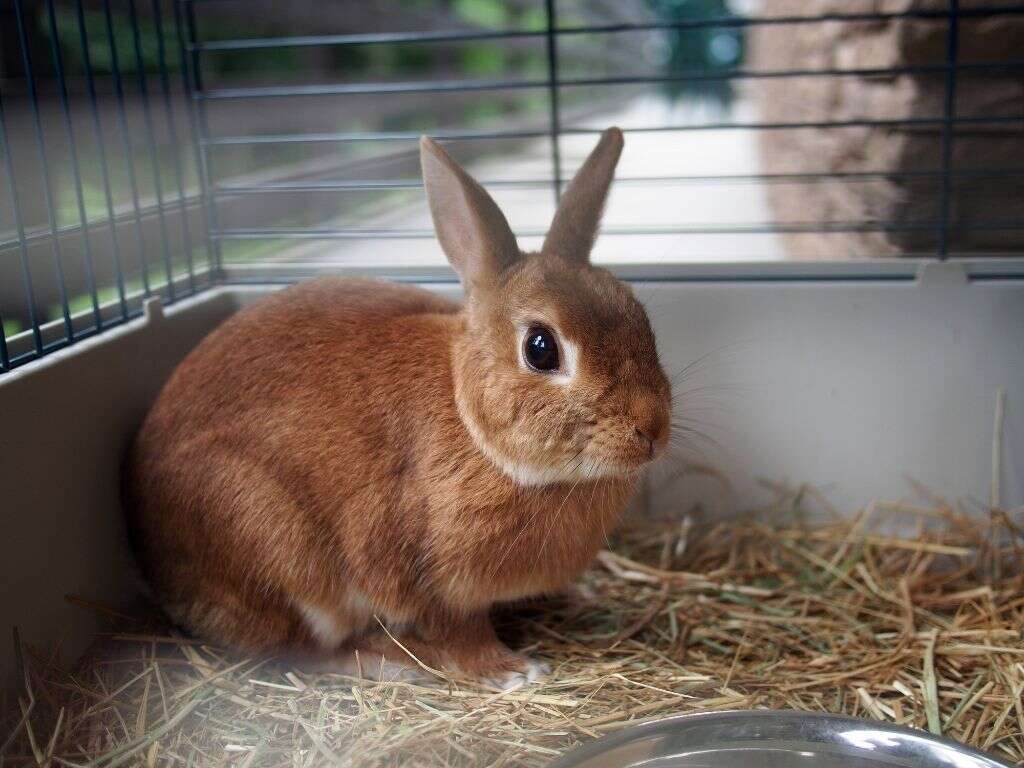
Tularemia is a rare but highly contagious disease. While it commonly affects rabbits and rodents, it can pass to humans through contact with infected animals, tick bites and breathing in or drinking liquid containing the bacteria.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
If even a few bacteria enter the body, they can make a person ill in days. The symptoms can range widely depending on how the infection enters the body and the type of tularemia the person has.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia The infection may be mild. However, if unaddressed, it can spread to the brain, heart or bones and lead to life-threatening complications such as meningitis or pneumonia.3‘Tularemia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.’ MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000856.htm

Skin Ulcers
Roughly 80% of people with tularemia have what's called the ulceroglandular type of infection.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia Commonly, a person with this type was bitten by a tick, or they were exposed to an infected animal. Sometimes, the bacteria can also enter through a scrape or wound.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635
A red spot may develop on the place on the skin where the bacteria entered the body. Over time, an ulcer forms on the skin. This sore may be painful and slow to heal. If a person who works outside or with animals develops skin ulcers, they should see a doctor to discuss a possible infection.3‘Tularemia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.’ MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000856.htm

Fever
Fever is also common with tularemia. Three to five days after the initial exposure, a person may begin to experience chills, unusual sweating and feeling overheated. They should discuss this with their doctor, who may recommend over-the-counter fever reducers along with antibiotics.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635
It's common for the illness to come on suddenly, and symptoms may last for several weeks. Although some symptoms can be managed at home, it's recommended to see a doctor. Untreated tularemia can be fatal or lead to serious illness.3‘Tularemia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.’ MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000856.htm

Headache
Many people with tularemia report a headache and exhaustion. Depending on the type of tularemia, they may also experience sensitivity to light.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
A person may experience headache, fever, chills, exhaustion and swollen glands but not have an ulcer on their skin. This may still be tularemia. Glandular tularemia is similar to the ulceroglandular type, but doesn't cause ulcers. This type is also usually caught through a tick bite or by handling infected animals.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635

Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes are another symptom of tularemia. This can result in painful lumps under the skin as the lymph nodes swell and become tender.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html Where swollen lymph nodes develop can point to the type of tularemia a person has.
It's common for ulceroglandular or glandular tularemia to affect lymph nodes in the armpit or groin. Tularemia infecting the throat commonly affects lymph nodes in the neck, and swollen lymph nodes in front of the ear may indicate an eye infection.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635

Eye Pain
Sometimes a person gets tularemia from rubbing their eyes after butchering, skinning or handling an infected animal.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635 This type, called oculoglandular tularemia, affects the eyes. A person may develop a painful ulcer beneath their eyelid or simply experience redness and pain. The eye may swell or leak discharge.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
Oculoglandular tularemia commonly affects one eye and is relatively rare. Only one to two percent of people with tularemia get this type, and the symptoms may be mistaken for pink eye.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia

Throat Pain
A sore throat and the presence of ulcers in the mouth can indicate a type of tularemia that affects the throat. Oropharyngeal tularemia can come from eating infected meat that hasn't been cooked properly or drinking infected water.
Once it gets into the throat, this infection causes inflammation of the tonsils and nearby lymph nodes. The symptoms include swollen, painful lumps in the neck and inflamed tonsils. It can be painful to swallow, and a person may lose their appetite.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html

Upset Stomach
Along with a sore throat, tularemia can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting. Swallowing may be painful, but it's important to continue to drink water and clear fluids to remain hydrated and aid recovery.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
Oropharyngeal tularemia is commonly caught by eating undercooked rabbit. Wild meat can carry many foodborne illnesses and should be handled carefully. Wearing gloves while butchering or handling wild meat and cooking the meat thoroughly can help prevent tularemia and other infections.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia

Muscle Pain
If a person who's recently been bitten by a tick or handled wild animals develops tularemia symptoms and muscle pain throughout the body, they may have typhoidal tularemia.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635
This variant is relatively rare, affecting only 10-15 percent of people with tularemia.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia This form can also be more severe, affecting many parts of the body. High temperature, chills, vomiting, weight loss and muscle pain are among the common symptoms. It's important to see a doctor as this form can progress to pneumonia.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html

Dry Cough
Pneumonic tularemia infects the lungs and can be highly dangerous. It can be caught through breathing in the bacteria or from untreated forms of the tularemia spreading to the lungs via the bloodstream.2‘Tularemia - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 29 Aug. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tularemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378635 A dry cough and chest pain are common symptoms.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html
Early treatment of other tularemia types may help prevent this more serious variant from developing. A doctor will prescribe antibiotics and other medications to manage the symptoms. It's important to take all antibiotics prescribed even after the symptoms go away.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia

Difficulty Breathing
If a person with tularemia doesn't take antibiotics to manage the illness, it can progress to pneumonic tularemia. Untreated pneumonic tularemia can be especially dangerous. Over time, the infection may cause a person could to go into respiratory distress or even stop breathing.4‘Tularaemia. Understand About Tularaemia Zoonosis Infection.’ Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient, 19 Oct. 2016, patient.info/doctor/tularaemia
If a person is short of breath, breathing too quickly or not able to breathe deeply, they should go to a hospital. They may need extra oxygen or mechanical ventilation along with antibiotics to manage the infection.1‘Signs and Symptoms of Tularemia | CDC.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 18 Dec. 2019, www.cdc.gov/tularemia/signssymptoms/index.html