What Is Hemorrhagic Fever?
There are a number of viral hemorrhagic fevers that are part of the same family of infectious diseases. While rare, these fevers range from minor discomfort to serious, life-threatening issues. Learn how to identify types, causes and symptoms of these viral infections today.
While a fever is the most obvious symptom of these viral infections, there are a number of other symptoms to consider. If left untreated, many cases can become serious. Find out how medical professionals can assist you by reducing the symptoms and preventing serious complications related to hemorrhagic fever.
1. What Are the Types of Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers?
Hemorrhagic fever is a category of viral diseases. While these diseases share similar characteristics, there are distinct differences. There are a wide range of viral fevers that fall in this category. It’s essential for medical professionals to identify the exact cause of a fever, but individuals should respond to all cases with the same precautions and by seeking immediate medical assistance.
The most common viral hemorrhagic fevers, or VHFs, are yellow fever, Lassa, Ebola and dengue. While there are differences, it’s important to explore the similarities to determine whether you or someone you know is dealing with a VHF. Many symptoms, causes, treatments and prevention strategies are shared between all VHFs, so it’s important to understand the general features of this family of viruses.

2. Is Ebola a Hemorrhagic Fever?
Ebola viral disease is a serious VHF. This particular viral fever has a high mortality rate. While extremely rare in the United States, this disease is an example of the life-threatening and highly contagious nature of many hemorrhagic fevers.
This virus appears to have originated in sub-Saharan Africa. The vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV has been approved to protect against the Zaire ebolavirus strain. Like other VHFs, Ebola originated in animals and subsequently spread to humans and primates. Some VHFs, like Ebola is passed between humans, while others aren’t contagious.

3. What Are Typical Causes?
Most hemorrhagic fevers are caused by viruses that live in animals and insects. Bats, ticks, mosquitoes and rodents are the most common animals and insects that pass these viruses to humans. Once transmitted, viral hemorrhagic fevers can become highly contagious and affect a number of individuals.
To prevent a VHF from becoming an epidemic, it’s important for individuals with the following symptoms to seek immediate medical treatment. Explore the common symptoms of most hemorrhagic fevers to learn more about causes and prevention strategies.

4. What Are the Symptoms?
While every virus can cause slightly different symptoms, all VHFs have a common set of typical symptoms. Most individuals experience a high fever, dizziness, weakness and fatigue. Some cause aches in muscles, bones and joints, as well. These symptoms can lead to more serious symptoms as the disease progresses.
The severity of these symptoms depends largely on the virus causing them. In some cases, hemorrhagic fevers are associated with bleeding in internal organs, under the skin and from the eyes, ears or mouth. If left untreated, the fever can escalate into delirium, internal organ failure, septic shock and death.
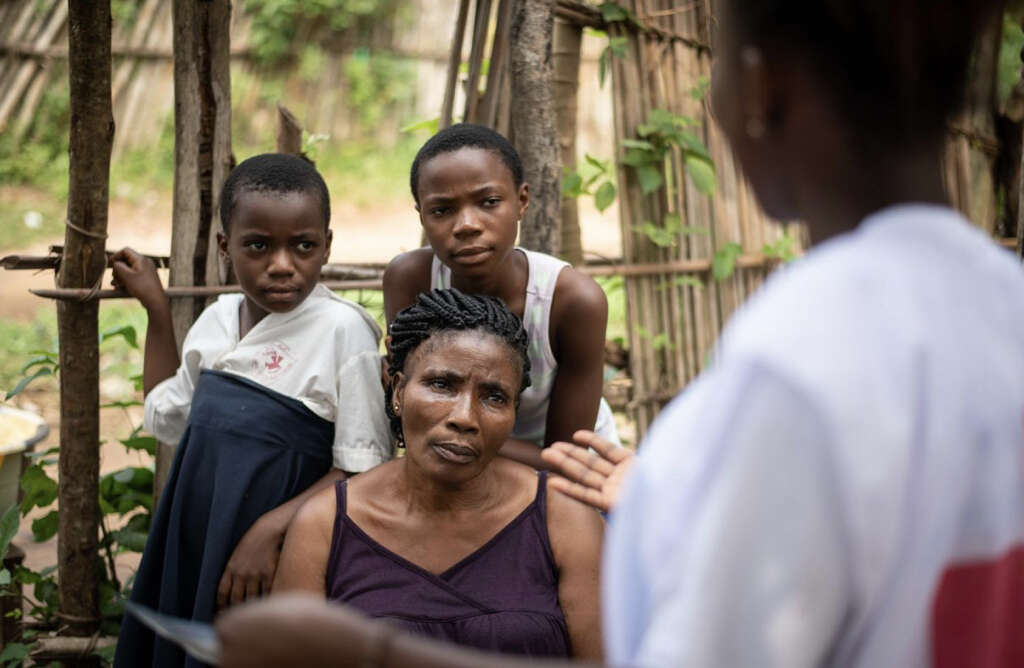
5. Is It Contagious?
Only some types of VHF can be spread from person to person. Most require a reservoir host to spread to humans. These hosts can include animals or insects. Ebola, Lassa, Marbug and other VHFs can be spread between humans and are considered contagious.
In contagious VHFs, the virus is spread through contact with bodily fluids or skin contact. It can take up to 21 days for symptoms to start to develop, so it can be difficult to find the source of many VHFs. Contagious hemorrhagic fevers are rare in the United States, with most cases originating in tropical regions of the world.

6. What Are Treatment Options?
Most hemorrhagic fevers have no specific treatments. However, there are a number of options available to reduce symptoms and decrease the risk of severe complications. Ribavirin is an antiviral drug that can reduce the risk of complications and lessen symptoms. Prevention strategies are important for reducing the need for treatment options, so be sure to follow proper precautions if you’re traveling to an area with known hemorrhagic fevers present.
Other options include vaccines for some VHFs, such as Ebola. Rest, hydration and proper nutrition are important treatment strategies. As symptoms progress, some cases are improved through kidney dialysis. This procedure removes wastes from the blood when kidneys start to fail.

7. How Common Is Hemorrhagic Fever?
Hemorrhagic fevers are extremely rare. Even travelers visiting countries where these viruses are present face a low risk of infection. Most cases are caused by rural travel in countries in sub-Saharan Africa, central Asia, central Europe or southern Africa.
A few precautions are typically all that are necessary for reducing the risk of hemorrhagic fever. While these fevers come with a high mortality rate and other serious risks, the number of cases remain rare. Some cases have been present in the United States in past epidemics, but VHFs aren’t generally present.
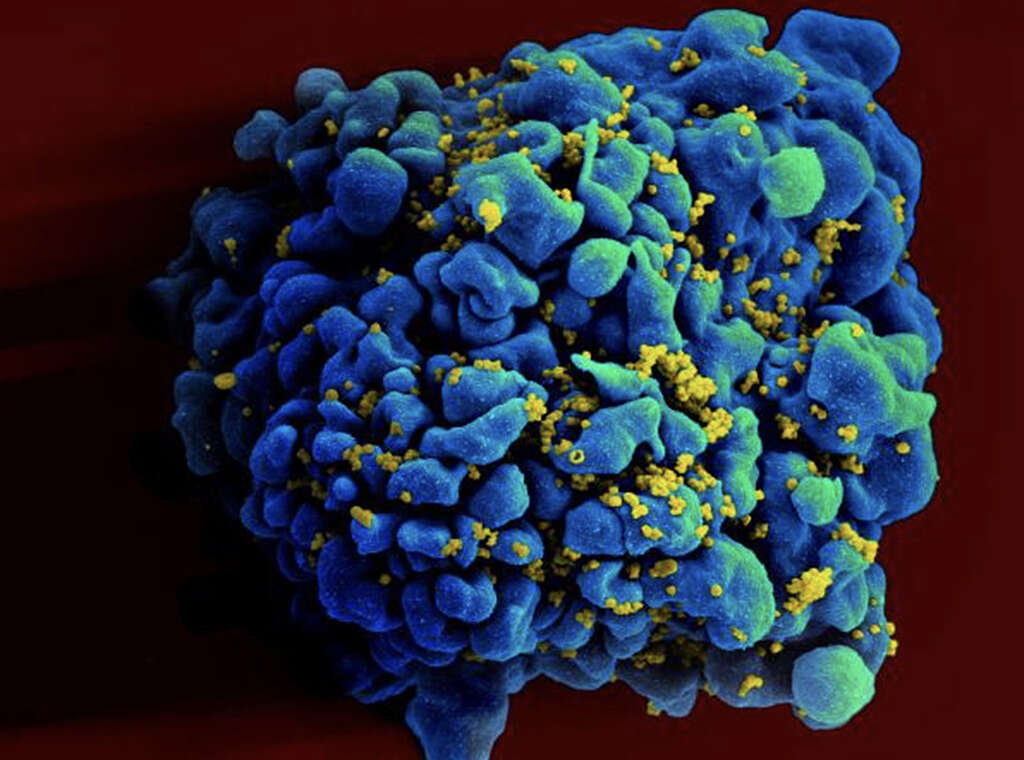
8. Are There Any Risk Factors?
Although these viral diseases are rare, there are a few risk factors that may increase your risk of contracting a hemorrhagic fever. Working with sick individuals in areas of known VHF presence can increase your risk of contracting a fever.
Other risk factors include being exposed to blood or body fluids of infected individuals, eating bush meat from countries with known viruses or traveling in rural jungle areas in these regions. Unprotected sex, intravenous drug use and other practices can spread these viruses, so these activities in tropical regions are also risk factors.
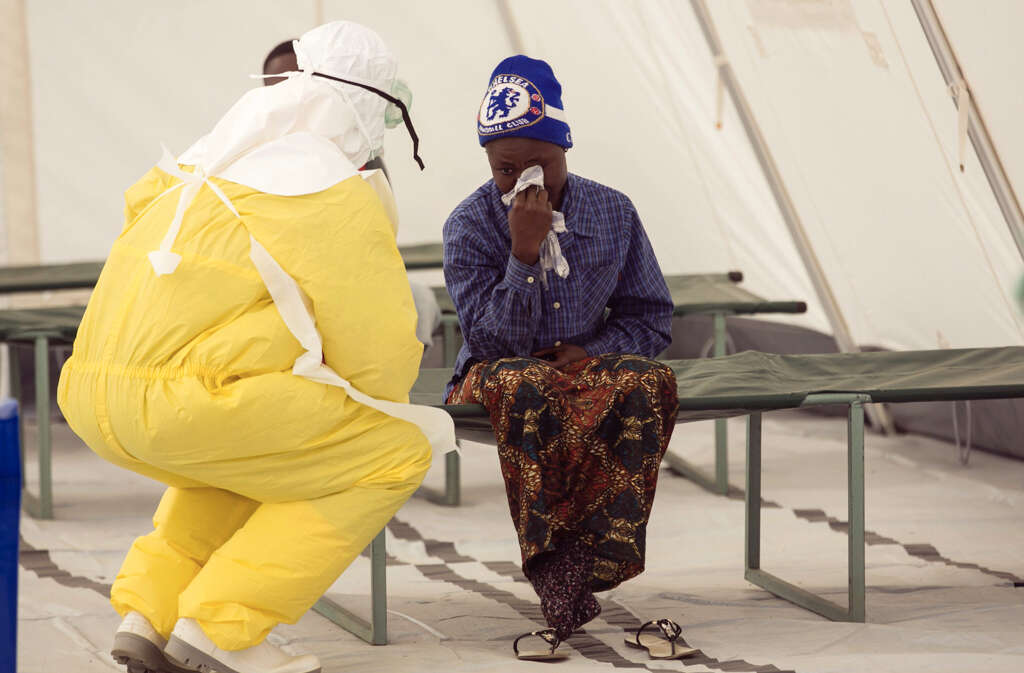

9. What Are the Long-Term Complications?
Even with prompt diagnosis, hemorrhagic fever can result in long-term complications. Because no cures are known, there are many complications that can lead to long-term issues. Brain damage, kidney failure, a coma or even death can be caused by many VHFs.
The best solution to avoid long-term complications is to prevent being infected. Explore common prevention strategies to avoid complications, particularly if you’re living in or planning to visit areas where these viruses are present.
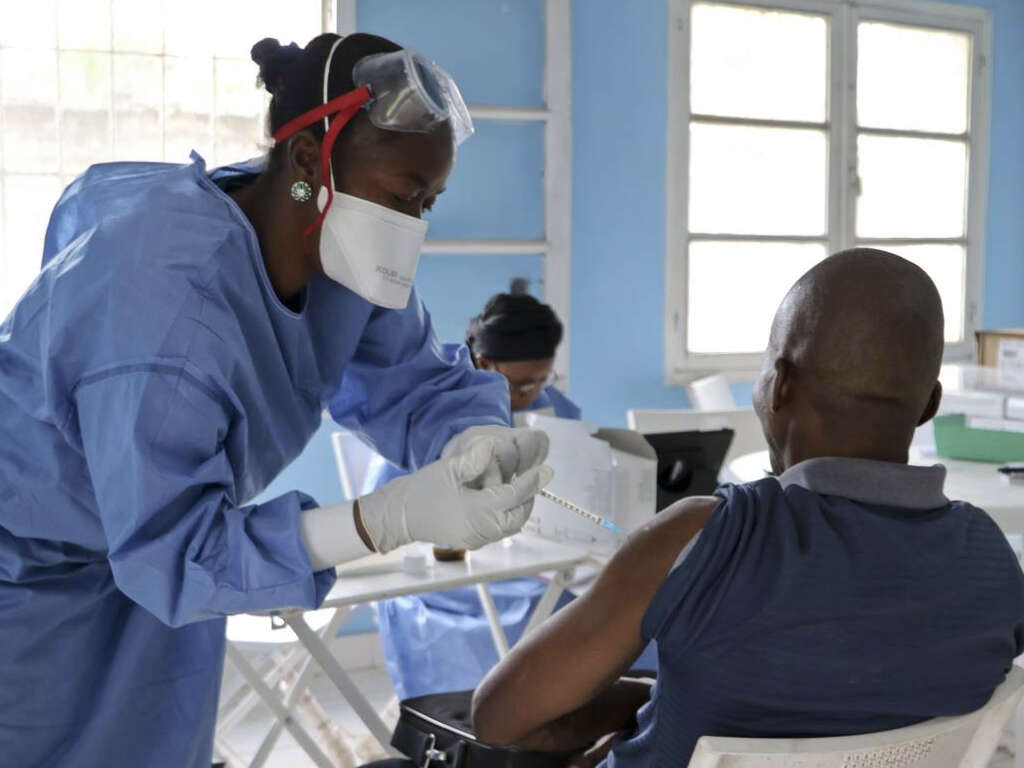
10. Can Hemorrhagic Fever Be Prevented?
Yellow fever, dengue and Ebola have known vaccines, which are the best prevention measures for VHFs. If you are in an area with a VHF with no known vaccine, take the necessary precautions to prevent the spread from animals, insects or humans.
Avoid tick and mosquito bites in areas where VHFs are present. Protect yourself and your home from rodents by removing trash and storing food and trash in rodent-proof containers. Avoid contact with body fluids of individuals known to have a hemorrhagic fever. Due to the lack of a cure for many VHFs, prevention is the best strategy to stay safe while traveling or living in tropical areas.