10 Jaundice Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Jaundice.' NHS.uk, 30 Jan. 2018, www.nhs.uk/conditions/jaundice
- 2. Gillott, Caroline. 'Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.' Medical and Health Information, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165749#symptoms
- 3. 'Jaundice.' Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/jaundice
- 4. 'Stools - Pale or Clay-colored.' MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003129.htm
- 5. 'Common Characteristics of Liver Disease.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/common-characteristics-of-liver-disease
- 6. Bassari, Ramez, and Johnathan B. Koea. 'Jaundice Associated Pruritis: A Review of Pathophysiology and Treatment.' PubMed Central (PMC), Feb. 7, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4316083/
- 7. Suely Falcão de Oliveira Melo, Norma, et al. 'Green Teeth Resulting from Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Report of a Case.' ScienceDirect.com | Science, Health and Medical Journals, Full Text Articles and Books, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031393914003199
Nausea and Vomiting
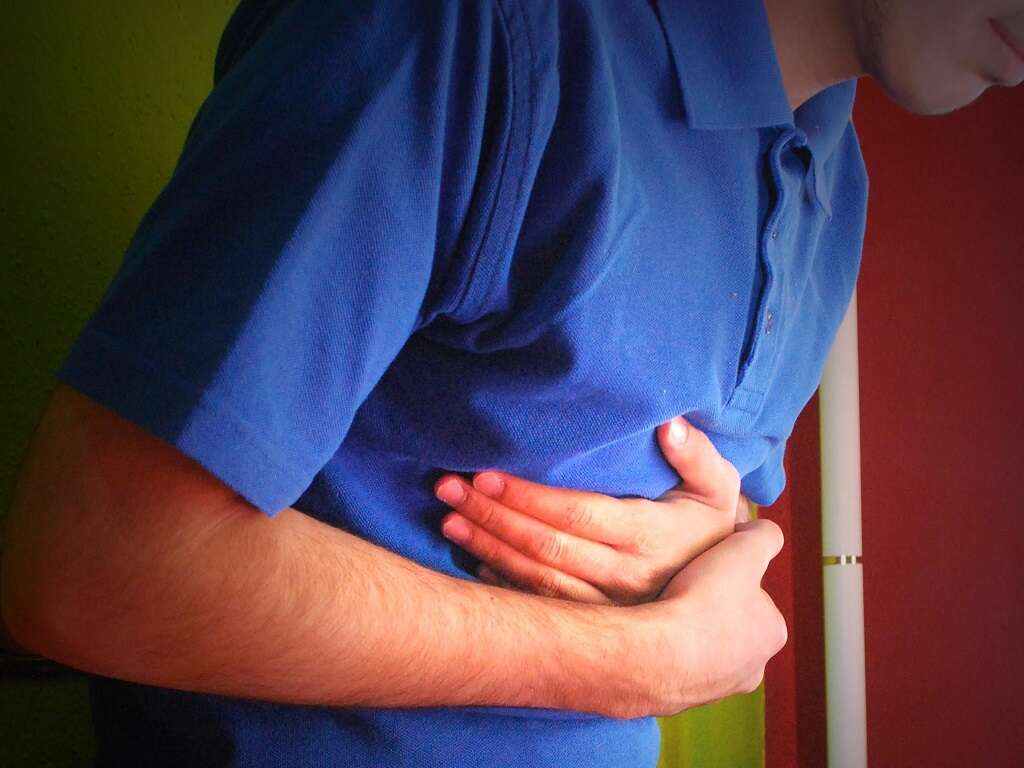
Nausea and vomiting may occur with jaundice. As with other symptoms, whether a person experiences nausea or vomiting depends on the underlying cause of the jaundice. Severe liver disease or viral inflammation of the liver are two possible reasons why people may experience these symptoms when jaundiced.
Both nausea and vomiting cause discomfort. Excessive vomiting can lead to other issues if not promptly managed, such as dehydration and weight loss.
Advertisement