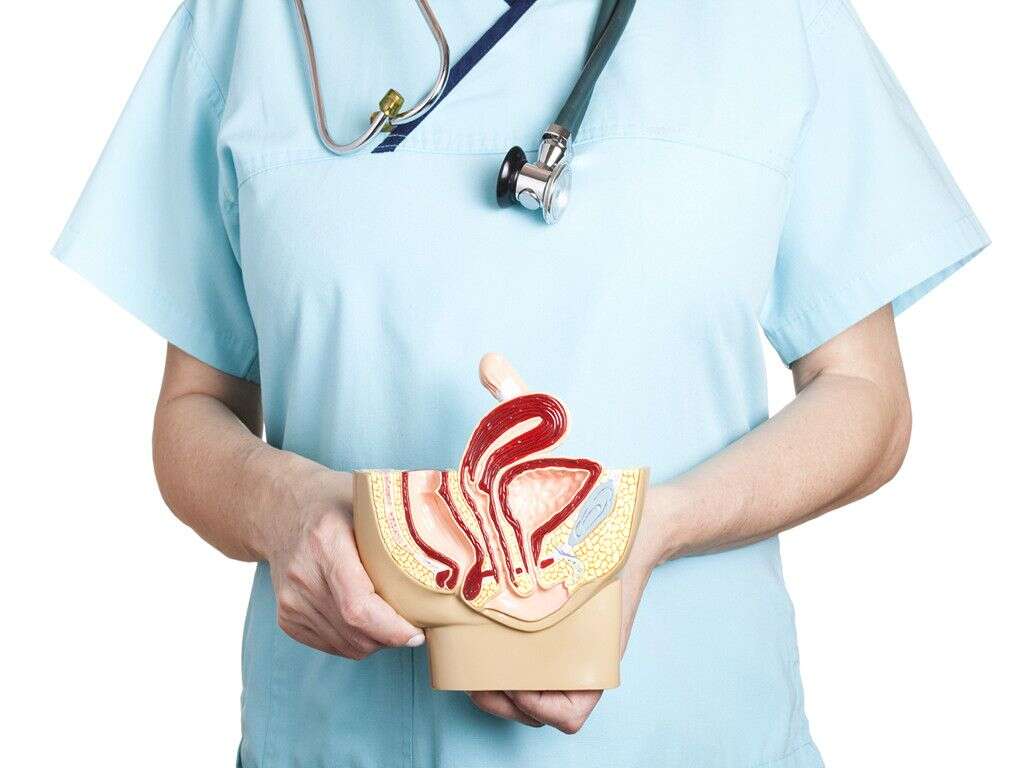
10 Cervicitis Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Cervicitis.' Harvard Health, 2 Jan. 2019, www.health.harvard.edu/a/to/z/cervicitis-a-to-z
- 2. 'Cervicitis, Cervix Inflammation: Diagnosis, Tests Management and Treatment.' Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15360-cervicitis
- 3. 'Frequent or Painful Urination: Colorado Urology Associates.' Urology Associates of Colorado | Denver Urologists, denverurology.com/urology/bladder-urinary-conditions/frequent-or-painful-urination/
- 4. 'Cervicitis.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cervicitis
- 5. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/womens-health/what-causes-a-woman-to-bleed-after-sex/
- 6. 'Cervicitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001495.htm
- 7. 'Bacterial Vaginosis.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 1 May 2019, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bacterial-vaginosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352279
Bleeding After Intercourse
Bleeding after intercourse is generally a sign something is wrong, like cervicitis. There are, however, some exceptions to this rule. For example, many women find they bleed after the first time they have sex. In women who have already been sexually active, bleeding shouldn't generally occur after sex.
Infections like cervicitis or pelvic inflammatory disease can potentially cause bleeding after intercourse. Other potential causes include tears in the vagina or vulva, polyps or cancer.5NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/womens-health/what-causes-a-woman-to-bleed-after-sex/
Advertisement