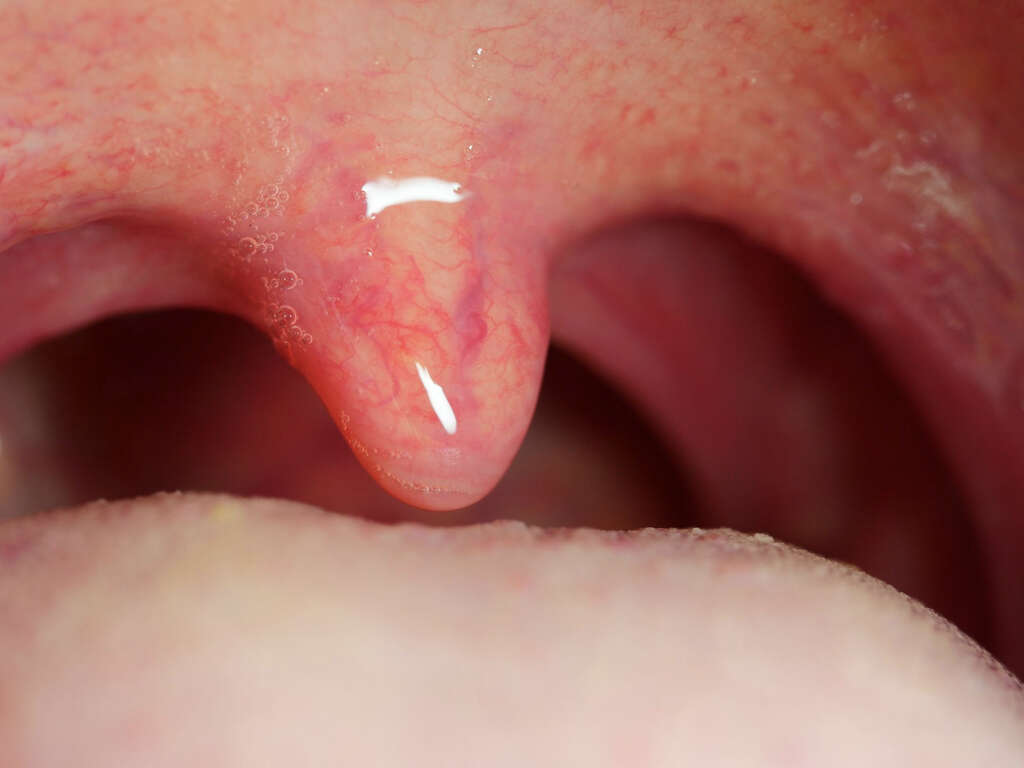
What Is Uvulitis?
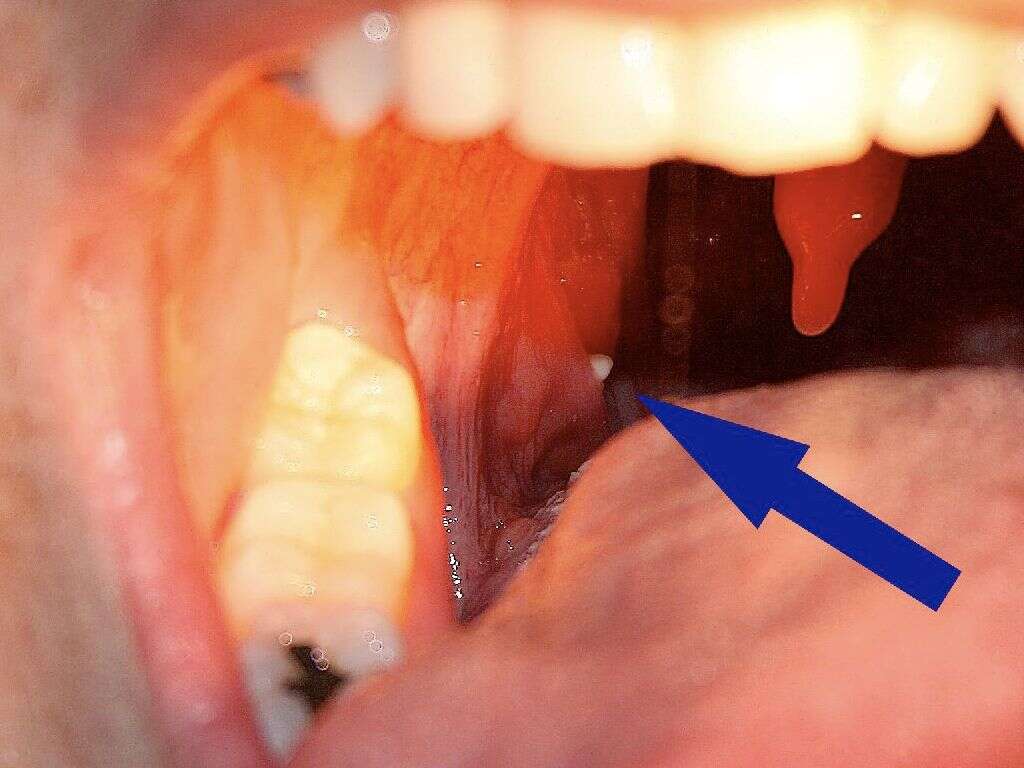
Uvulitis is a term used to refer to the inflammation of the uvula. The uvula is a small, tongue-shaped organ, extending from the soft palate, and hanging down the back of the mouth. The organ works together with the soft palate to close off the nasal cavity when swallowing. It also plays a part in speech.
Similar to other parts of the oral cavity, the uvula is exposed to pathogens and other irritants that can cause inflammation and swelling. This usually affects the uvula and surrounding tissues and is usually mild. However, the otherwise temporary condition can become more severe. This can lead to difficulty in swallowing and breathing.

1. Symptoms of Uvulitis
The most common symptom of uvulitis is an irritating feeling like you have something stuck in the back of the mouth. You may also experience some degree of breathlessness and difficulty in swallowing.
Other symptoms include sore throat, pain, and excessive saliva production. Your tone of voice may also change, and a look at the back of the mouth using a mirror will show swelling and redness of the throat and the uvula. The tonsils may also be swollen.

2. Causes of Uvulitis
Environmental and lifestyle factors, infection, trauma, and genetics are the most common causes of uvulitis. Environmental causes include exposure to allergens such as dust, pollen, and certain foods.
Dehydration can also lead to uvulitis due to insufficient lubrication of the uvula, especially in alcoholics. Some chemicals, such as tobacco, and some medications can also irritate the uvula and cause uvulitis.

3. Infections
Infections, especially those caused by viruses, and bacteria can also lead to uvulitis. Such infections include the common cold, croup, mononucleosis, strep throat, tonsillitis, and STDs.
When these infections affect the oral cavity, they can irritate any of the tissues here, including the uvula and the throat. Cases due to an infection like the common cold are usually short-lived, and go away within a few days.

4. Trauma
Trauma to the uvula can also cause uvulitis. Such trauma can result from conditions such as GERD, whereby stomach acid injures the throat, including the uvula.
Trauma to the uvula can also occur during surgical procedures such as removal of the tonsils or the insertion of a tube to deliver oxygen into the lungs.

5. Genetics and Uvulitis
Genetics may play a part in some cases of uvulitis. A rare condition called hereditary angioedema can make your throat, face, hands, feet, and uvula swell.
Another rare condition leads to an elongated uvula that is larger than normal. However, although the condition resembles uvulitis, it is not uvulitis, and the only way to treat it is through a surgical intervention known as uvulectomy.
6. Uvuritis Risk Factors
Uvulitis can occur in any person, no matter the age or gender. However, the condition is more common in children than in adults. Some people are also more likely to get uvulitis than others.
Such people include those who have allergies, smokers, those who are constantly exposed to irritating chemicals and other irritants, and those with a weak immune system that makes them vulnerable to infections. If you are at risk of getting uvulitis, especially due to allergies, discuss your condition with a doctor.
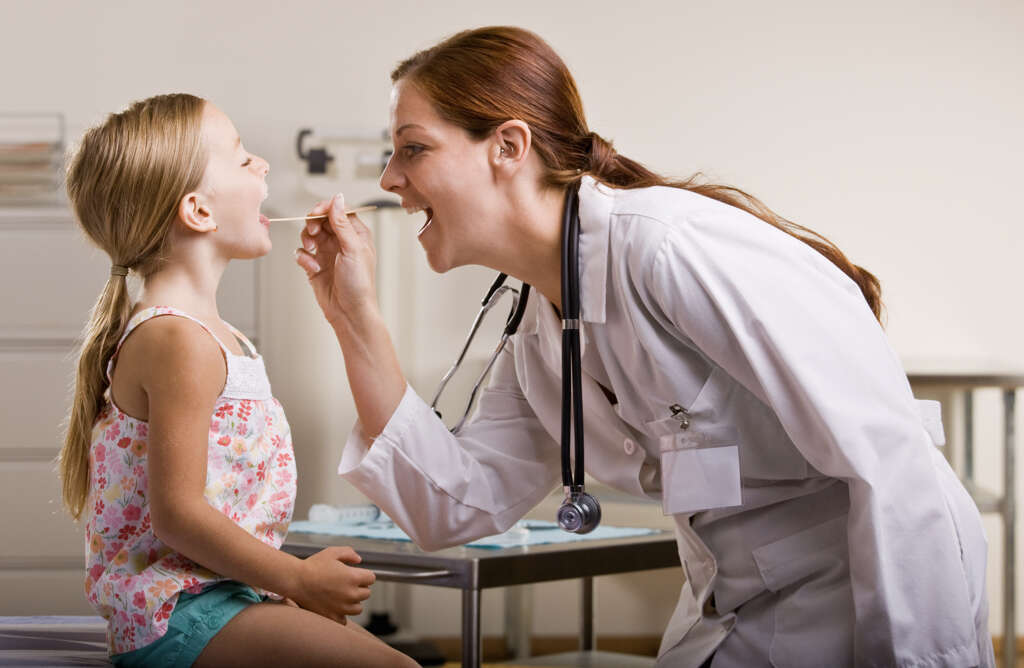
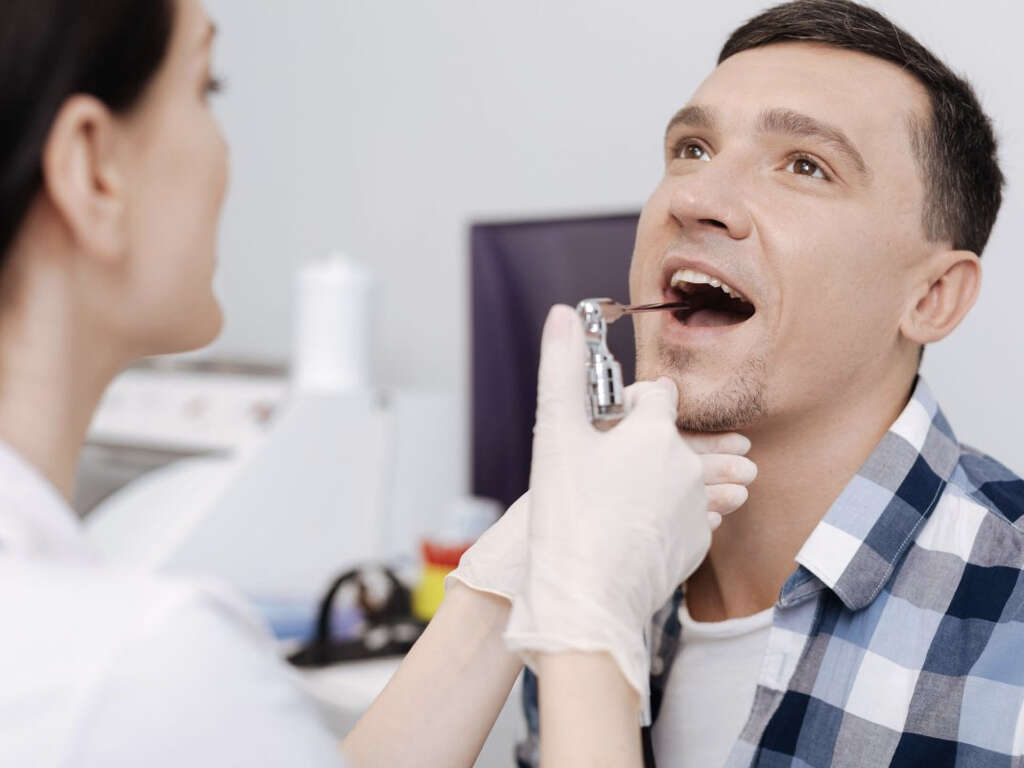
7. Diagnosis of Uvulitis
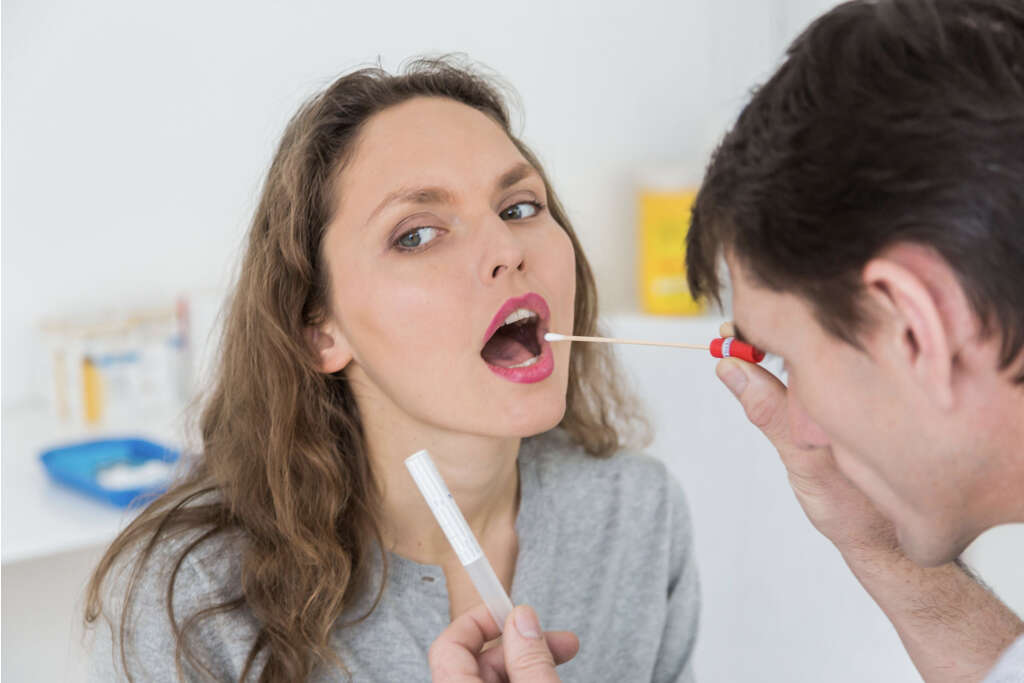
Upon visiting your doctor, they will interview you to get a history of your condition. It is important that you inform the doctor of any related symptoms including colds, cough, fever, and abdominal pain. Other important information includes any new foods you have consumed, exposure to chemicals or other materials, and medication you have taken for the condition, including over-the-counter drugs and antibiotics. The doctor will carry out a physical examination and may also swab the uvula or the throat for a laboratory examination.
Your doctor may also ask for a blood test to see whether you have an infection or not and to rule out some infections. In some cases, all these tests can be inconclusive and you may need to see an allergist to assess your case. Provide the allergist with your blood and skin tests to be able to identify the substances and foods that may cause an allergy.

8. Home Remedies for Uvulitis
If you have uvulitis, or a sore throat, your body is telling you that there is something wrong. Some home remedies can help soothe your swollen uvula and sore throat. These include sucking on ice chips or frozen juice bars, or ice cream. You can also try gargling with warm salt water.
Getting adequate sleep, and sleeping in comfortable surroundings, free from irritants, can also help your body recover and fight any infections. You should also keep your throat and body hydrated by sipping on warm water throughout the day. This will reduce the irritation of your throat.

9. Medical Treatment for Uvulitis
Treating uvulitis depends on the cause of the condition. Once the cause is resolved, uvulitis will also clear. Some medical conditions, like the common cold, can go away without treatment. Uvulitis due to such conditions clears up once the infection goes away. If, however, the condition causes a lot of discomfort, you can take pain medication and wait for the swelling to reduce. Cases of bacterial infection are treated with antibiotics. Make sure that you complete the course of treatment even after you get relief from the symptoms.
If uvulitis is a result of an allergy, seek a doctors assistance to determine the allergen so you can avoid it. Antihistamines or steroids are used to treat allergies. Uvulitis due to hereditary angioedema can be treated with C1 esterase inhibitors, plasma kallikrein inhibitor, bradykinin receptor antagonist, or androgens.
10. Long-Term Outlook for Uvulitis
Uvulitis is an uncommon condition that is usually a result of an underlying problem. For this reason, once the cause is dealt with, uvulitis resolves without further treatment. Home remedies, including avoiding trigger foods and other substances and keeping your throat hydrated, can also help.
Serious uvulitis is treated with medication. Discussing your condition with a doctor can help determine the best management plan depending on your condition.