What Is Pulmonary Tuberculosis?
There are numerous conditions that can affect our lungs. Some of them can have very mild effects, while others can be rather more uncomfortable. We rely on our lungs for the oxygen that we need so serious lung conditions can be dangerous to us. One example of such a condition is pulmonary tuberculosis.
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a condition that should be taken very seriously if you catch it. It can be very serious and, in some cases, it will lead to a fatality. Thankfully, it is not a common condition, but that does not mean that reasonable precautions should be taken.

1. Once Rare
Tuberculosis used to be a rare condition in the developed world, and it was only really people that travelled that were likely to get it. This is because, despite being potentially dangerous, most people have an immune system that is strong enough to protect them against it. This changed in developed countries in the 80s, however, thanks to the emergence of another serious infection: HIV.
HIV leads to AIDS, which stand for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. As the name suggests, it causes peoples’ immune systems to fail. This made victims more likely to develop diseases, including tuberculosis. This caused numbers of TB to surge, although they were controlled again in the 90s. It is still a disease that needs to be treated with caution.

2. Causes
Tuberculosis is caused by the mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium. It is a contagious condition but it still does not spread easily, which is one of the reasons why it is not more common than it is. There is also a vaccine for the disease, but this is not commonly used in the United States.
Pulmonary tuberculosis is spread from person to person. It can be passed on in droplets when infected people cough, sneeze, or speak. That it is difficult to catch also means you are most likely to catch from somebody you are physically close to, or even intimate with.
3. Weakened Immunity
As mentioned, our immune systems are mostly quite resilient to pulmonary tuberculosis. This is great news for people who have strong immune systems, but not so great for those that don’t. Some medical conditions can weaken the immune system, and some medications can also make the immune system weaker.
As well as HIV/AIDS, kidney disease, diabetes, and some cancers can weaken the immune system. The very young and very old are also at risk, as well as people that are suffering from malnutrition. Some drugs to deliberately weaken the immune system are sometimes used, such as when somebody has just had a transplant operation.
4. Drug Resistance
Bacteria and viruses will evolve just like all other organisms do. This can lead to some very serious problems when it comes to treating infections. This is because some pathogens can evolve to be resistant to certain medicines. This is one of the reasons that pulmonary tuberculosis can be deadly: Some medications lose their effectiveness over time.
Many of the standard treatments for tuberculosis no longer work in most cases, so specialized medications need to be developed to overcome the resistance. Medical professionals need to use medication with care to help prevent the bacterium from developing further resistance to new drugs.
5. Latent vs. Active TB
Another reason why TB is not more prevalent is that it is not always active even in people that have caught the disease. In latent TB, the bacterium will be present but causes no symptoms and is not contagious. It can become active, however, which means that it is important the condition is treated regardless of the patient’s symptoms.
As the name suggests, active TB can make people sick, and it can also be spread to other people. In some cases, the condition will become active just weeks after catching the bacterium. In others, it can take several years for it to become active.
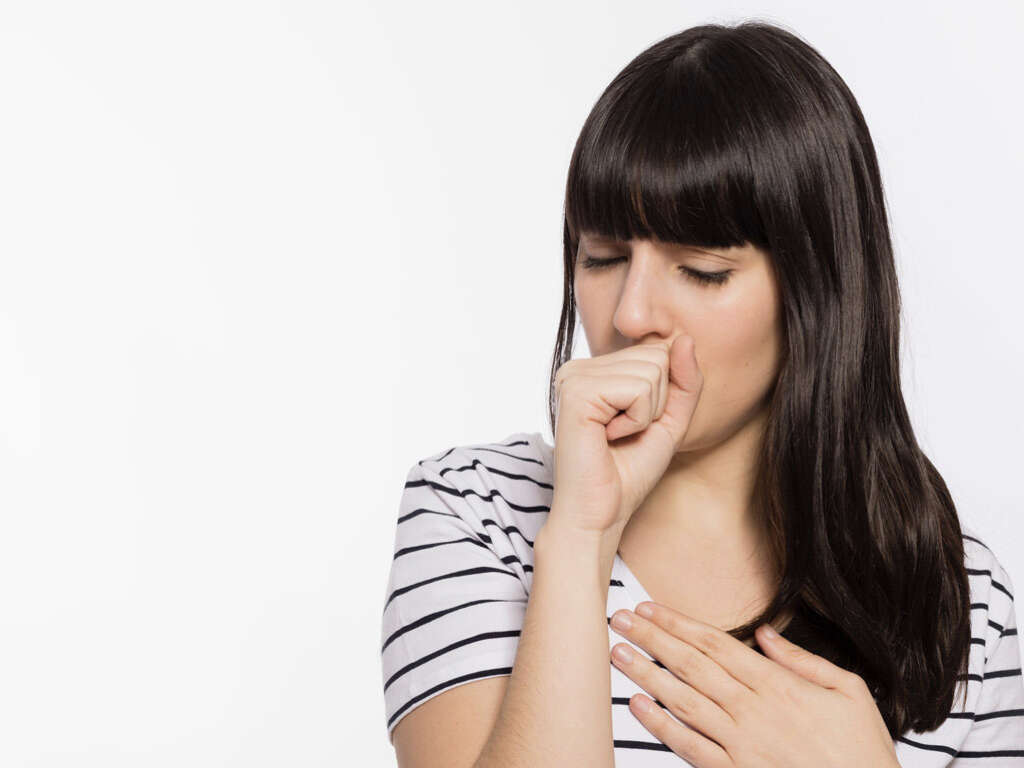
6. Coughing
Pulmonary tuberculosis attacks the lungs. As such, coughing is the most common symptom when people have active TB. The patient is likely to be coughing for 3 weeks or more, and it is likely to be quite painful for them. Not only can the coughing be painful, but many will also find it painful just to breathe.
Some patients will also cough up blood. This is a sure sign that something is seriously wrong and that you should find medical attention if you have not done so already. Remember also that coughing helps to spread infections, so you should always try and cover your mouth where possible.

7. Fever
Pulmonary tuberculosis is like so many other infections in that it will probably cause a fever. This is a self-defense mechanism as the body tries to make the body too hot for comfort for the invaders. Chills and night sweats are also likely to happen.
The patient will also likely feel very fatigued. This is beneficial in a way because they will need to be getting as much rest as they can. It is common for patients to lose their appetite, while they can also begin to lose weight. Bear in mind that losing too much weight too quickly can be very bad for your health.

8. Complications
If sufficient treatment is not provided then pulmonary tuberculosis can go on to cause some very serious complications. Some patients can experience tuberculosis arthritis, while others can find that they develop pain and stiffness in their back. More serious problems include trouble with the liver and/or kidneys.
Meningitis is also a possibility and this can be very serious indeed. Meningitis can result in severe headaches, and it can be deadly if left untreated. The heart can also be infected in a small number of cases. The most serious complication of all: Tuberculosis can be fatal if the patient has not received sufficient treatment.

9. Risk Factors
Nobody is safe from pulmonary tuberculosis, unless they have been vaccinated. In addition to non-vaccinated people, there are also other people categories that are most at risk. This includes people that have a weakened immune system for reasons already mentioned.
People that work in health care are also more at risk as they are more likely to be exposed to it. Children that are around infected adults are also more likely to get TB. Traveling to developing parts of the world will also increase somebody’s chances of catching the disease. People that use drugs intravenously also put themselves at a higher risk.

10. Treatment
Pulmonary tuberculosis can be deadly, so treatment is essential. This generally means a course of anti-biotics and this is likely to last for 6-9 months, depending on a number of factors. Because TB can be resistant to some drugs, the patient will also often need to take several types.
When given antibiotics, we are often told that we should finish the full course regardless of symptoms, and this is especially important for pulmonary tuberculosis. This is because the bacterium infecting the patient may have developed a resistance to the drugs being used. This makes it very important that they are all killed to help prevent the evolved strain from spreading.





-06.jpg)