What Is PTSD?
Most of us will experience a tragic event at least once in our lives, and this will usually involve the loss of a loved one. It is a part of life and it is largely a matter of grieving and then moving on. Some events will be even more traumatic, however, and a period of grieving will not be enough in some cases.
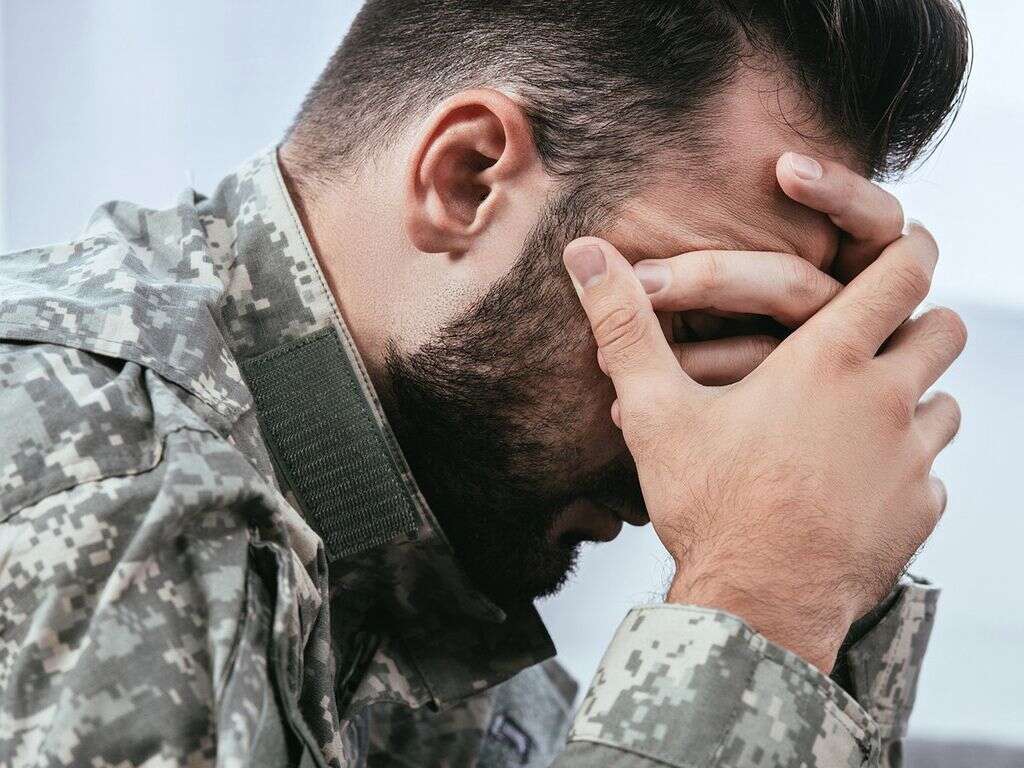
PTSD is a condition where the patient is struggling to cope with extreme events that have happened in their lives. It is often associated with people that serve in the military, but it can affect people from all walks of life. The good news is that treatment is available that can help patients with the condition.

1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
PTSD is the acronym for post-traumatic stress disorder. It is a condition that tends to affect people that have been through extremely traumatic experiences in their past. The condition causes the patient to suffer from anxiety over the event and it can have a considerable negative impact on their quality of life.
For many people, PTSD is temporary and the symptoms will lessen as time goes by. For other people, however, PTSD is something that can be with them for the rest of their lives. Treatment is available that can help the patient to manage the condition and its symptoms.

2. Causes
As mentioned, PTSD is something that tends to affect people that have undergone traumatic events in their lives. There are some other factors that can contribute to the condition, however. One of these is an inherited vulnerability to some mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
People that have certain personalities or temperaments are also more or less likely to develop PTSD. People that are naturally nervous, for example, might be more prone to developing the condition after events that other people will cope with better. How the individual’s brain and body responds to stress is another potential factor in who develops the condition.

3. Symptoms
For many people, the symptoms of PTSD will begin to show within a few months of a traumatic event. For others, it may be years. The symptoms can also vary in severity from person to person, and they can also vary within individuals. Some patients will tend to have no symptoms for much of the time, only for them to appear after certain triggers.
For some people, the trigger might be atmospheric factors that remind them of traumas they have experienced. For others, being stressed in general can trigger the symptoms and make existing symptoms worse. Even seeing something on TV can trigger the symptoms in some people.

4. Symptom Types
The symptoms of PTSD are often broken down into four separate types. These are avoidance, intrusive memories, mood, and negative changes in thinking. As the name suggests, avoidance means the patient will try and avoid thinking about the event, and avoid anything they fear might trigger more distress.
Intrusive memories mean that the patient will have flashbacks and dreams of the event, and suffer distress over reminders of the event. Mood symptoms include the patient having negative feelings about themselves, feeling numb emotionally, memory problems, and feeling detached. Changes in thinking include feeling shame or guilt, difficulty sleeping and concentrating, self-destructive behavior, irritability, and always being guarded.

5. Complications
The symptoms of PTSD can be enough to be incredibly disruptive to the patient’s life. Their careers can be adversely affected, as can their relationships with family and with other people. What’s more is that their physical health can also deteriorate, and the patient is less likely to take part in activities that they used to enjoy.
PTSD will result in some patients developing eating disorders, while some will develop problems with alcohol and substance abuse. The condition will also cause some people to develop anxiety and depression. In other cases, the patient may even attempt to take their own life.
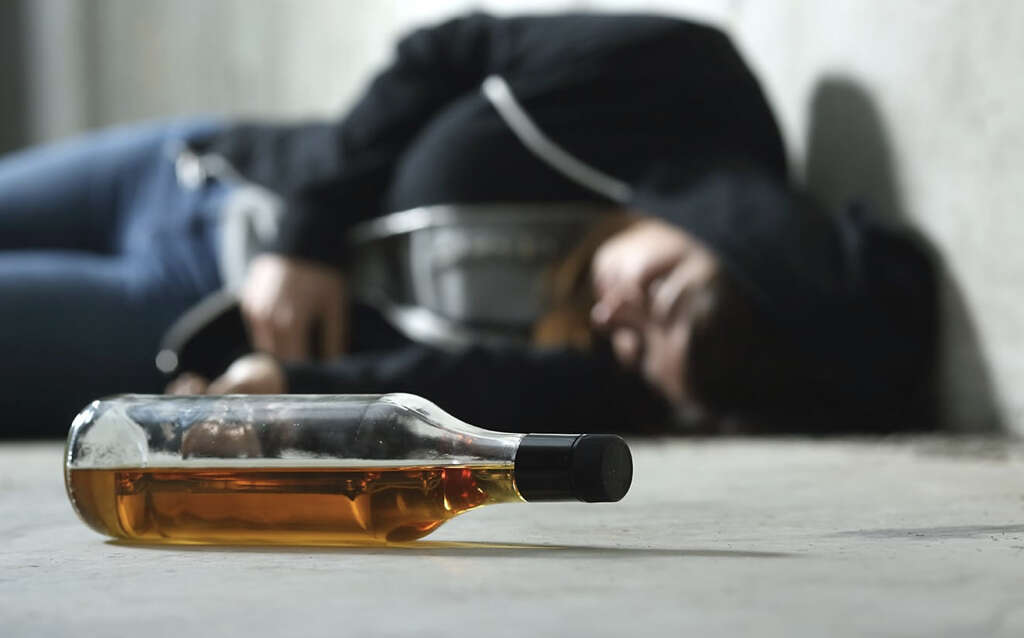

6. Risk Factors
People that have experienced some kind of traumatic event in their life are most at risk. The condition is often associated with people serving in the military, while first responders are also in a higher risk category. Other people at risk include those who had a traumatic childhood, and people that have other mental health conditions.
The type of events that can lead to PTSD are varied. However, many will include first responders responding to horrific events. Being involved in combat is another type. Being involved in a traffic accident or other serious accident is another potential factor. Physical and sexual assaults can also contribute.
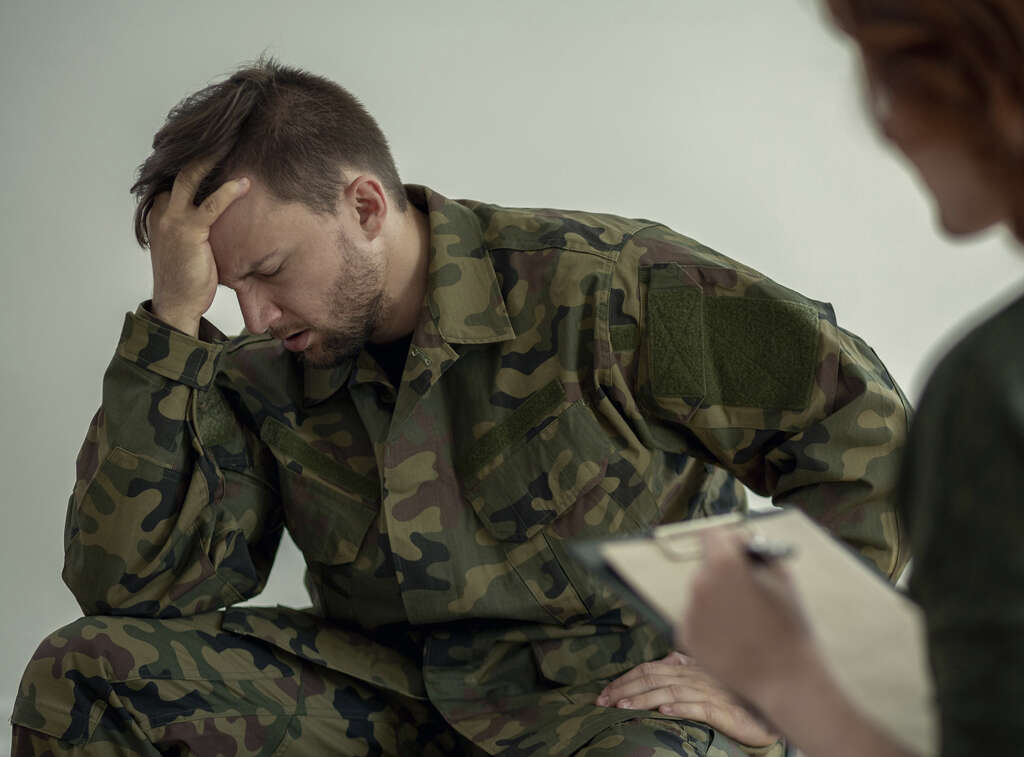

7. Prevention
There is no sure way to avoid being involved in a traumatic event. However, there are ways to help prevent the condition from developing in people that have experienced such events. Indeed, some people in jobs where they are likely to be exposed to traumatic experiences are given access to facilities that can help prevent the condition from developing.
It is quite normal for people to experience distress after traumatic events, and PTSD will sometimes progress from such reactions. If somebody is finding that they are struggling to cope then they should seek help. People that are developing substance abuse habits should also seek help to prevent the condition from worsening.

8. Diagnosis
One of the first steps of diagnosing the condition is for a doctor to perform a brief physical exam. This will help them look for signs of medical conditions that might be contributing to their symptoms. If PTSD or similar is suspected, then the patient will be referred to a specialist for a psychological examination.
The psychologist will need to ask the patient about their history and about any traumatic experiences they may have had. This may include questions about their life when they were young. The psychologist will also ask about the patient’s symptoms and the impact they have on their life. If the patient meets certain criteria, a diagnosis of PTSD will be reached.

9. Medication
There is no medication that can help to treat PTSD directly. However, medication is available that will help to treat the symptoms of the condition. This will often include antidepressants, which can help with sleeping and concentration. Antianxiety medication is also available for those that need it.
Medication is also available that can help to suppress nightmares in patients that suffer from them regularly. These medications can have some unwelcome side effects and you should let your doctor know if you have had reactions to medication in the past. Patients will also often be asked to undergo psychotherapy in addition to medicinal treatment.
10. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy involves an expert speaking with the patient about their symptoms and what is causing them. The treatment is aimed largely at helping the patient to understand the cause of their symptoms better, and to help them feel better about their self.
Psychotherapy is also largely about teaching the patient new skill that will help them to recognize their symptoms and to learn how to manage them better. It can also help the patient to recognize triggers of other problems like substance abuse, and help to prevent them from using substances. Psychotherapy treatment can be very effective in helping to improve the patient’s life overall.