Swollen Eye Causes, Treatments & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Lowth, Dr Mary. 'Swollen Eyelid: Causes, Treatment and Pictures.' Patient.info, 7 Mar. 2018, patient.info/eye-care/swollen-eyelid.
- 2. Christopher J. Brady, et al. 'Eyelid Swelling - Eye Disorders.' Merck Manuals Consumer Version, Merck Manuals, www.merckmanuals.com/home/eye-disorders/symptoms-of-eye-disorders/eyelid-swelling.
- 3. Russa. 'Puffy Eyes: What Causes Them and What To Do About It.' Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, 13 Oct. 2020, health.clevelandclinic.org/puffy-eyes-what-causes-them-and-what-to-do-about-it/.
- 4. 'Eye Swelling.' Seattle Childrens Hospital, www.seattlechildrens.org/conditions/a-z/eye-swelling/.
- 5. Turbert, David. 'What Are Eye Allergies?' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 31 July 2020, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/allergies.
- 6. Turbert, David. 'Eye Allergy Diagnosis and Treatment.' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 10 Sept. 2019, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/allergies-diagnosis.
- 7. Boyd, Kierstan. 'Conjunctivitis: What Is Pink Eye?' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 17 Dec. 2020, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/pink-eye-conjunctivitis.
- 8. 'Blocked Tear Duct Symptoms.' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 23 Jan. 2018, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/blocked-tear-duct-symptoms.
- 9. 'Blocked Tear Duct Treatment.' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 27 Mar. 2018, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/treatment-blocked-tear-duct.
- 10. Porter, Daniel. 'What Is a Black Eye?' American Academy of Ophthalmology, 23 Mar. 2021, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/black-eye.
- 11. Lowth, Dr Mary. 'Blepharitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment.' Patient.info, 2 May 2018, patient.info/eye-care/swollen-eyelid/blepharitis.
- 12. 'Edema.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 1 Dec. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20366493.
- 13. 'Orbital Cellulitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001012.htm.
- 14. 'Retinoblastoma: MedlinePlus Genetics.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8 Sept. 2020, medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/retinoblastoma/.
- 15. 'Retinoblastoma.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 14 Dec. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinoblastoma/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351013.
Composed of loose, stretchy skin less than 1 millimeter thick, eyelids protect the eyes from dust, dirt, irritants and injury. The Meibomian glands are located in the eyelids, producing an oily substance that lubricates the eyes and eyelids.1Lowth, Dr Mary. ‘Swollen Eyelid: Causes, Treatment and Pictures.’ Patient.info, 7 Mar. 2018, patient.info/eye-care/swollen-eyelid. If fluid accumulates in eyelid tissues, swelling may develop in the eyelids, sometimes accompanied by pain or itching.2Christopher J. Brady, et al. ‘Eyelid Swelling - Eye Disorders.’ Merck Manuals Consumer Version, Merck Manuals, www.merckmanuals.com/home/eye-disorders/symptoms-of-eye-disorders/eyelid-swelling.
In some cases, swelling dissipates on its own in a day or two. To alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling, a person with a swollen eye should remove contact lenses, rinse the eye with cool water and apply a cool compress to the eye.3Russa. ‘Puffy Eyes: What Causes Them and What To Do About It.’ Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, 13 Oct. 2020, health.clevelandclinic.org/puffy-eyes-what-causes-them-and-what-to-do-about-it/.

1. When to See a Doctor
If swollen eyes don't return to normal within 48 hours, it's best to seek medical care. People should also see a health care provider if they experience moderate or severe swelling in one eye and if the eyelid is red or painful. Swollen eyelids accompanied by fever, swollen feet or ankles or sinus pain also require medical evaluation.
Immediate emergency medical attention is necessary if a person experiences severe swelling of both eyelids or if a fever accompanies severe swelling and redness of a single eyelid. People should also obtain immediate medical care if they experience vision loss or double vision.4‘Eye Swelling.’ Seattle Childrens Hospital, www.seattlechildrens.org/conditions/a-z/eye-swelling/.
2. Diagnosing the Cause of Swollen Eyes
To diagnose the cause of swollen eyes, the health care provider reviews the person's medical history and symptoms then conducts a physical examination. They ask how long the eye has been swollen and what other symptoms are present. They inquire about any recent injuries, insect bites and exposure to any new over-the-counter products or household items.
The provider also asks about accompanying symptoms and any pre-existing disorders, such as heart, kidney or liver disease. In some cases, they may order imaging tests.2Christopher J. Brady, et al. ‘Eyelid Swelling - Eye Disorders.’ Merck Manuals Consumer Version, Merck Manuals, www.merckmanuals.com/home/eye-disorders/symptoms-of-eye-disorders/eyelid-swelling.<a></a>

3. Allergies
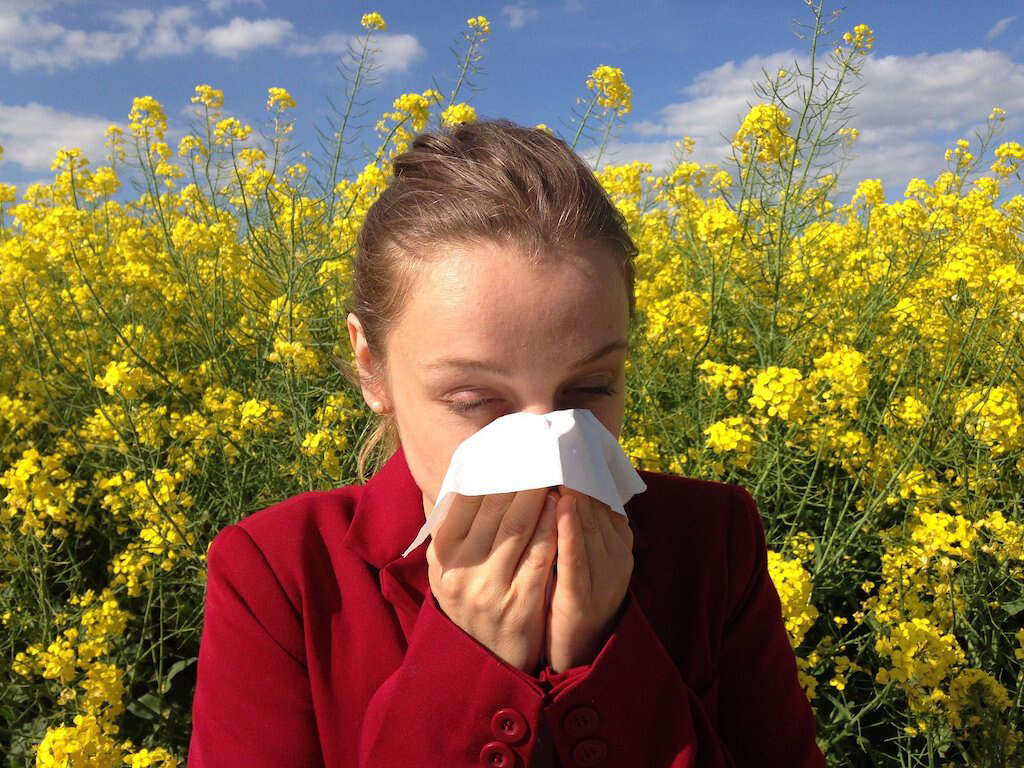
One of the most common causes of swollen eyes is allergies. The eyes may also be red, itchy and watery, and they may be sensitive to light. Many people have allergies to dust, pet dander, mold, smoke and pollen, and others experience reactions to perfumes, cosmetics, medications, certain foods and insect bites.5Turbert, David. ‘What Are Eye Allergies?’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 31 July 2020, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/allergies.
Applying eye drops containing artificial tears, antihistamines or corticosteroids may help alleviate swollen eyes caused by allergies. Oral antihistamines and immunotherapy injections are other potential treatment options.6Turbert, David. ‘Eye Allergy Diagnosis and Treatment.’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 10 Sept. 2019, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/allergies-diagnosis.

4. Conjunctivitis
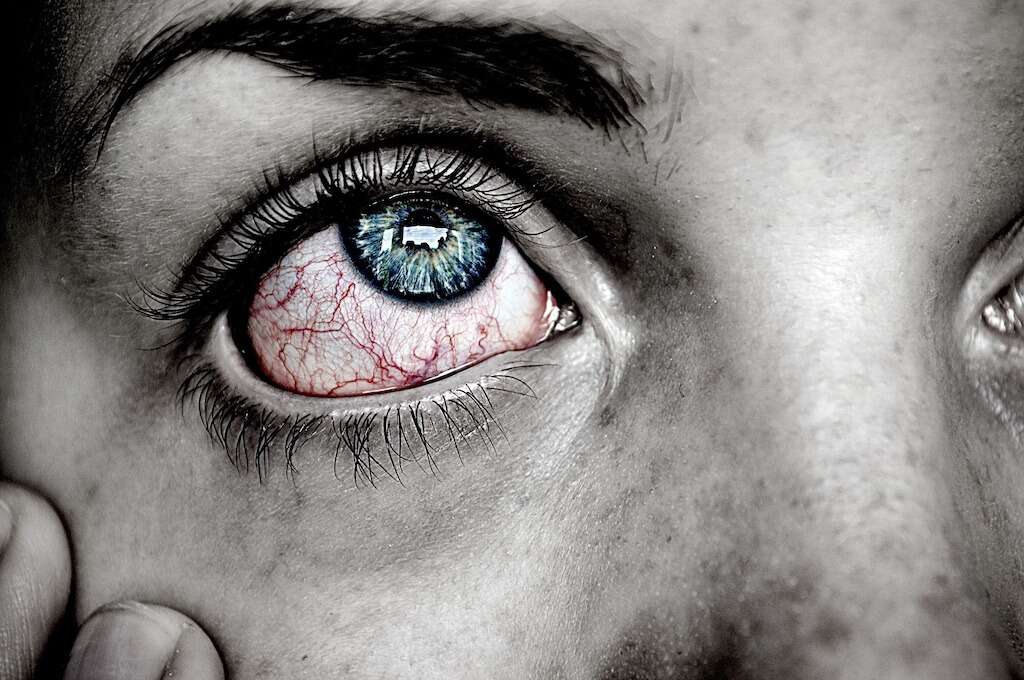
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is a contagious viral or bacterial eye infection that causes swelling and redness. Sometimes a sticky discharge is present as well. Other symptoms include a gritty sensation in the eye, itching, burning, light sensitivity and blurred vision.
Viral conjunctivitis dissipates on its own. Using cool compresses can alleviate discomfort. To treat conjunctivitis caused by bacteria, a health care provider may prescribe antibiotic eye drops, depending on the severity of the symptoms.7Boyd, Kierstan. ‘Conjunctivitis: What Is Pink Eye?’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 17 Dec. 2020, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/pink-eye-conjunctivitis.

5. Blocked Tear Duct
If a tear duct becomes blocked, bacteria may get trapped in the eye and cause an infection. The eye may be swollen, red and tender, vision may be blurred and the eyelashes may be crusty. Fever may be present, and there may be a mucus discharge from the eye.8‘Blocked Tear Duct Symptoms.’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 23 Jan. 2018, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/blocked-tear-duct-symptoms.
Sometimes no treatment is needed, and the tear duct blockage resolves on its own. Gentle eyelid massage may help eliminate the blockage. Other cases require surgery to remove the blockage.9‘Blocked Tear Duct Treatment.’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 27 Mar. 2018, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/treatment-blocked-tear-duct.

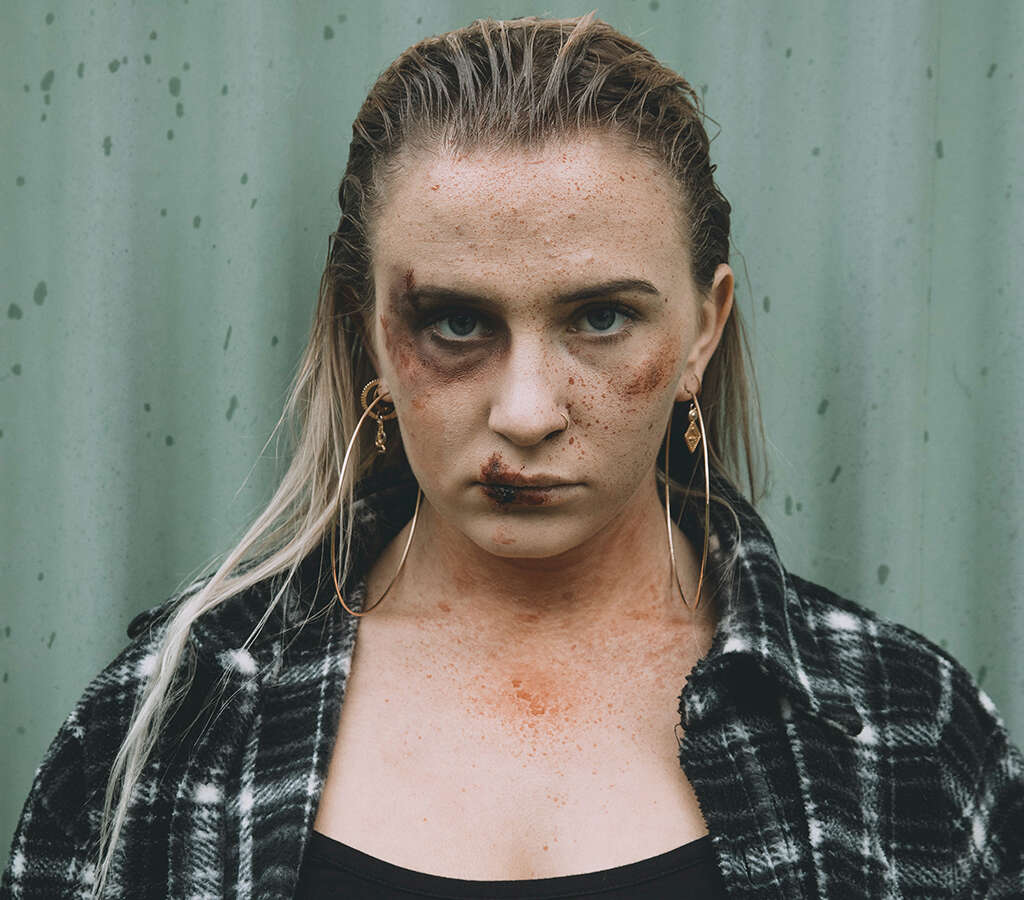
6. Black Eye
Trauma to the head or eye may lead to a black eye or bruising around the eye. Swelling, pain and blurred vision often accompany the bruising. A black eye may be indicative of a more serious injury, so a health care provider conducts a thorough examination that may include imaging tests.
In many cases, home care is all that's needed for a black eye. Applying ice to the affected eye helps reduce swelling and alleviate pain.10Porter, Daniel. ‘What Is a Black Eye?’ American Academy of Ophthalmology, 23 Mar. 2021, www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/black-eye.

7. Blepharitis
Blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelid, is associated with infections, seborrhoeic dermatitis or decreased oil production by the Meibomian glands. It usually affects both eyes and symptoms may include sore, swollen eyelids and gritty, itchy or burning eyes. A discharge may be present, and flakes or scales may appear on the eyelids.
There is no cure, but symptoms can be managed through hygiene that involves warming, cleansing and massaging the eyelids. Antibiotics, in the case of an underlying bacterial infection, and artificial tear drops may be helpful.[[11]

8. Edema
Swollen eyes may be associated with edema, swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the tissue. Underlying conditions that can lead to edema include heart failure or preeclampsia. Edema may also develop due to medical treatments, such as the administration of intravenous fluids and certain medications. In addition to swollen eyes, edema may cause swelling in other parts of the body, including the legs, feet, arms and hands.
Treating the underlying condition or discontinuing the responsible medical treatment or medication resolves the swelling.1Lowth, Dr Mary. ‘Swollen Eyelid: Causes, Treatment and Pictures.’ Patient.info, 7 Mar. 2018, patient.info/eye-care/swollen-eyelid.,12‘Edema.’ Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 1 Dec. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20366493.
9. Orbital Cellulitis
Orbital cellulitis is a serious infection of the fat and muscles surrounding the eye. It causes painful swelling and reddening of the eyelids, eyebrow and cheek. Fever and malaise may be present, it may be painful or difficult to move the eye and vision may be decreased.
Intravenous antibiotics treat orbital cellulitis, and sometimes surgery is necessary to alleviate pressure in the area around the eye. Without treatment, complications may include meningitis, septicemia and loss of vision or hearing.13‘Orbital Cellulitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001012.htm.
10. Retinoblastoma
A rare cancer of the eye, retinoblastoma affects young children and usually begins with a white spot in the pupil of the eye. Other symptoms include redness, swelling or soreness of the eyelids as well as crossed eyes or eyes that seem to point in different directions. Vision may be impacted in the affected eye.14‘Retinoblastoma: MedlinePlus Genetics.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8 Sept. 2020, medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/retinoblastoma/.
Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, laser therapy and cryotherapy. The affected eye may need to be surgically removed and replaced with an artificial eye.15‘Retinoblastoma.’ Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 14 Dec. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinoblastoma/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351013.