What Is Post Polio Syndrome?
Our bodies are interlaced with nerve cells that help to relay messages throughout the body. These messages include those that allow us to feel pain and other sensations, and those that send commands for our muscles to make certain actions.
If something was to go wrong with these nerve cells, then it can have a profound negative impact on our lives. It can affect how we feel, our ability to move, and even the ability to use essential organs. It can be very dangerous and it can be the result of different underlying causes, one of which is post polio syndrome.

1. Polio
Polio is a disease that used to be common even in developed nations. However, the introduction of a vaccine in the late 1970s has seen the disease become all but extinct in many parts of the world. The disease can still be found in some parts of the world where vaccine programs are not standard, however.
Polio a disease caused by the poliovirus. The disease causes damage to the nerves, resulting in a number of unwelcome symptoms. The patient can begin to lose control over their limbs and develop difficulties breathing, and the disease will also be fatal in some cases.

2. Post-Polio Syndrome
Polio is not serious for all people who catch it, and some will not even have been aware they had the disease at all. Others will have had symptoms like paralyses and muscles weakness, only for the symptoms to disappear after the patient recovers from the disease. The symptoms will return for some people, however.
Post-polio syndrome is a condition where the symptoms return decades after the disease had apparently passed. The condition can cause any symptoms that did remain to get worse. It is a poorly understood condition and is also rare, especially considering polio itself is also rare in developed nations.

3. Causes
We are not completely sure why post-polio syndrome occurs, but there are some strong candidates. One is to do with the way that the body compensates for nerve cells that were destroyed by the virus. These nerve cells are known as motor neurons, and they help carry messages to and from the central nervous system.
To compensate for the loss of motor neurons, the remaining motor neurons will grow new fibers that act as branches between nerve cells. This will help to restore functionality to the patient, but it will also be more demanding on each individual motor neuron. It is thought that post-polio syndrome is caused by this extra demand eventually causing the remaining motor neurons to fail.

4. Symptoms
Post polio syndrome will result in a number of unwelcome symptoms. The symptoms are likely to be very mild at first only for them to develop gradually as time goes by. One of the first symptoms the patient might experience is that they become exhausted more easily than they usually would do.
The patient muscles can also become weaker, and they can also feel pain in their muscles and joints. Their muscles can begin to shrink, and they can also become less tolerant of the cold. The condition can also cause some sleep disorders, and it can also develop difficulties breathing.

5. Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is caused when food particles are accidentally inhaled into the lungs. The particles are likely to contain bacteria and these bacteria can take hold in the lungs, causing an infection in the organs. It can happen in people with post polio syndrome because they can develop difficulties chewing and swallowing.
This can happen in people that had bulbar polio particularly, which affects the nerves that help control chewing and swallowing. Difficulties performing these actions can cause further problems because the patient is unable to eat and drink. They can become dehydrated and malnourished, both of which can be dangerous.
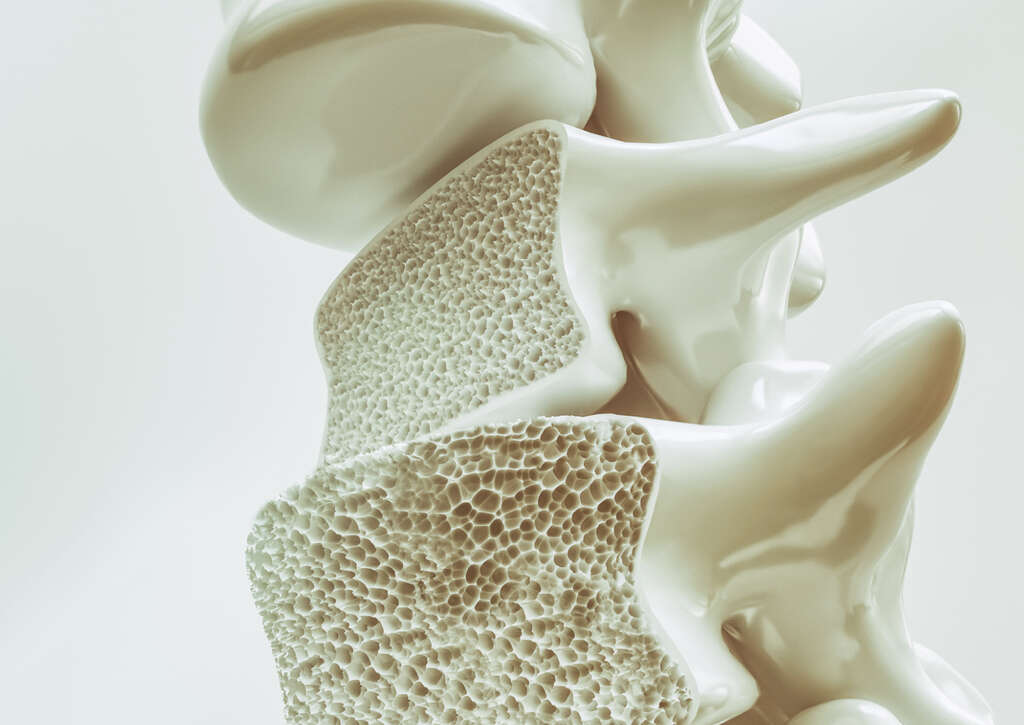
6. Osteoporosis
Post polio syndrome can also cause osteoporosis, which causes the patient to lose their bone density. This can happen partly because the patient is experiencing long periods of inactivity. The loss of bone density means that the bones will lose their strength, meaning breakages are more likely.
This is often made worse by the fact that post polio syndrome will also often cause the patient’s muscles to become weaker. This can mean they lose their balance and this can lead to falls, further increasing the likelihood of broken bones. Broken bones themselves can result in even further complications such as infections.
7. Chronic Respiratory Failure
In order to breathe, our chest muscles have to be working hard to enable our lungs to inhale and exhale. Post polio syndrome can affect this ability, and this can make it harder for us to breathe. Weak chest muscles also mean it is harder for us to cough, which also means that fluid can accumulate in the lungs.
With fluid in the lungs, the lungs cannot absorb as much oxygen as they would usually be able to, and this further makes breathing difficult. Low oxygen levels in the blood can be dangerous for the patient, and they will likely need an oxygen mask to help them breathe.

8. Risk factors
Post polio syndrome can only occur in people that have had polio in the past, but anybody that has had polio can develop the syndrome. Some former polio suffers are more likely to develop the syndrome than others are, however. One factor is the severity of polio when they had it, with those who were more ill more likely to develop post polio syndrome.
People who caught polio as children are less likely to develop post polio syndrome than those who caught when they were teenagers or adults. Those that made more of a complete recovery are also in a higher risk group, as are people who perform heavy exercise more often.
9. Diagnosis
There is no test that can confirm post polio syndrome. However, the patient’s medical history can be taken into account to help doctors be confident about what is causing the patient’s symptoms. This includes looking at factors like whether or not they had polio, how long ago it was, and whether or not the progression of the symptoms is gradual.
Although there are no tests to diagnose the syndrome, there are tests that can help to eliminate other possible causes. This includes blood tests, imaging tests, muscle biopsies, and tests that help to read the electrical activity in the patient’s body.
10. Treatment
As things stand, no treatment is available for post polio syndrome. However, it is often possible to help manage the patient’s symptoms to help maintain their quality of life. This includes physical therapy that helps to strengthen the patient’s muscles, while also limiting any additional stress on the patient’s motor neurons.
It can also be important for the patient to learn how to limit how much energy they spend, and also to use devices that assist them where necessary. Speech therapy can help the patient to learn to swallow where needed, and medication can help to ease any pain the patient might be experiencing.