What Is Photosensitivity?
Photosensitivity refers to the amount of reactivity an object has when it receives photons, especially in situations when there is visible light. In medicine, photosensitivity is a term used to describe abnormal reactions the skin has when there is light. It can be divided into photoallergy and phototoxicity.
Photosensitivity has been observed in both humans and animals. In humans, it can take various forms. Some are more sensitive while in others, it is due to a side effect of medications (such as tetracycline antibiotics, sulfonamides, and heart drugs like amiodarone). There are also dietary supplements that can lead to photosensitivity. Some conditions such as porphyria, systemic lupus erythematosus, and xeroderma pigmentosum are also more sensitive to light. In animals, photosensitivity has been observed in horses, bovine, and sheep. It can be due to ingestion of plants such as St John’s wort, buckwheat plants (horses), and biserrula (in sheep).
1. Photoallergy
Photoallergy, photodermatitis, or sun poisoning is a form of photosensitivity. It occurs when the allergen is activated by light to result in an allergic response such as a rash or other effects. It can cause issues such as burning sensation, swelling, itchy rash where there is peeling of the skin, and difficulty breathing. Some patients may also experience nausea. In the affected areas, a brown or orangish tint may form. Photoallergy may be caused by various medications (such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, retinoids, oxybenzone, psoralens, tetracycline antibiotics), and plants (such as giant hogweed, common rue, burning bush). Prevention includes avoidance of exposure, using protective clothing like gloves, avoiding sunlight, and wearing sunscreen.
2. Phototoxicity
Phototoxicity is also a form of photosensitivity. It is also sometimes known as photo-irritation. This is a chemically induced irritation that requires the presence of light. The affected area resembles an exaggerated sunburn.
The chemical involved can enter the skin through topical administration, oral ingestion, or parenteral administration (not through swallowing). The chemical involved will react to light and cause toxicity. This includes many cold-pressed citrus oils such as bergamot and plant juices such as lime and parsley.

3. Drug-Induced Photosensitivity
Drug-induced photosensitivity refers to the abnormal reaction seen due to the combined effects of light and a chemical. This means that exposure to either light or chemical on its own will not be sufficient to cause any issues. These reactions can occur in both oral and topical medications.
These reactions occur due to the damage caused by the compounds present on cell membranes. It should not be confused with photoallergic reactions that are caused by the effect of the immune response to a light-activated compound. The incidence of photoallergy is less than phototoxicity.
4. Statistics
The incidence of drug-induced photosensitivity is unknown. However, phototoxic reactions were observed to be significantly more common compared to photoallergic reactions. It can occur in any race, especially among those with heavily pigmented skin.
It is also more common among men compared to women. Drug-induced photosensitivity can occur in individuals of any age.

5. Signs and Symptoms
Patients may present with complaints about being unable to tolerate sunlight. A normal person would be able to tolerate minutes or hours of exposure to the sun. However, those with sensitivity will start exhibiting skin lesions that appear like a sunburn or dermatitis. In those with pseudoporphyria, the affected area has a bullous reaction (fluid-filled blister) while in lichenoid reactions, there are plaques and papules that appear.
The skin can also become erythematous (red) and scaly. These lesions are often only seen on areas that are exposed to the sun. Once healed, there is often hyperpigmentation that takes weeks or months to resolve. Separation of the nail can also be seen in the use of systemic medications such as chloramphenicol, psoralen, and more.
6. Investigations
Some of the investigations that may be useful include assessing urine porphyrin levels, and determining anti-Ro (SS-A) antibody and antinuclear antibody (ANA) levels. Other tests include photopatch testing, and phototesting with ultraviolet (UV) A, UVB, and visible light. In photopatch testing, two sets of suspected photoallergens are applied to the back. One set will be removed after 24 hours and both sets evaluated after 48 hours.
There is a positive reaction if there is the presence of vesicles, edema, and erythema. In phototesting, small areas on the back or inner forearm are treated with increasing doses of light. The minimum dose of light required to cause a reaction is called the minimum erythema dose (MED).
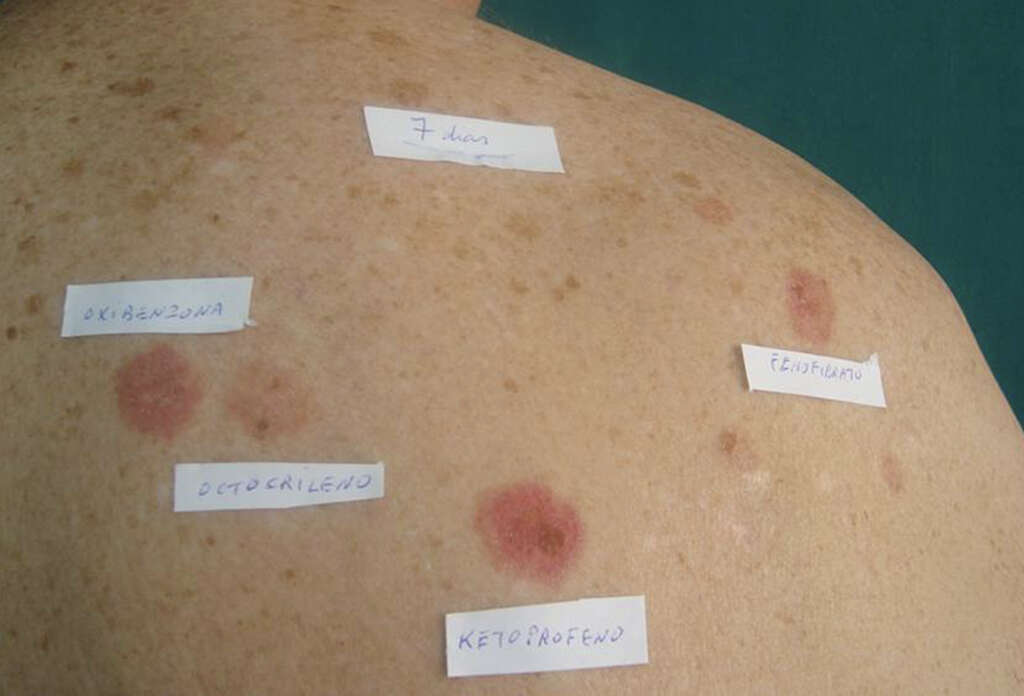
7. Care and Prevention
The main aim of treatment is to identify and avoid the causative agent, use sun protection, and provide symptomatic relief. This can be achieved using topical corticosteroids and cool compresses to reduce the redness and swelling. In more severe cases, systemic (oral) corticosteroids can be prescribed.
If sunscreens do not cause any issue, patients should be told to apply liberally. Since most cases of photosensitivity are caused by UVA, sunscreens that absorb UVA should be used. Sunscreens containing zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and autobenzone are generally more effective compared to others.
8. Medication
Medication can be used to reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
Corticosteroids that can be prescribed include clobetasol (increases the production of proteins that lowers inflammation), topical betamethasone (lowers inflammation by decreasing the permeability of the capillaries and migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes) hydrocortisone valerate (suitable for application to external mucous membranes and skin to lower inflammation), desonide (increases the production of enzymes that decreases inflammation), and fluticasone (very effective anti-inflammation and vasoconstriction).
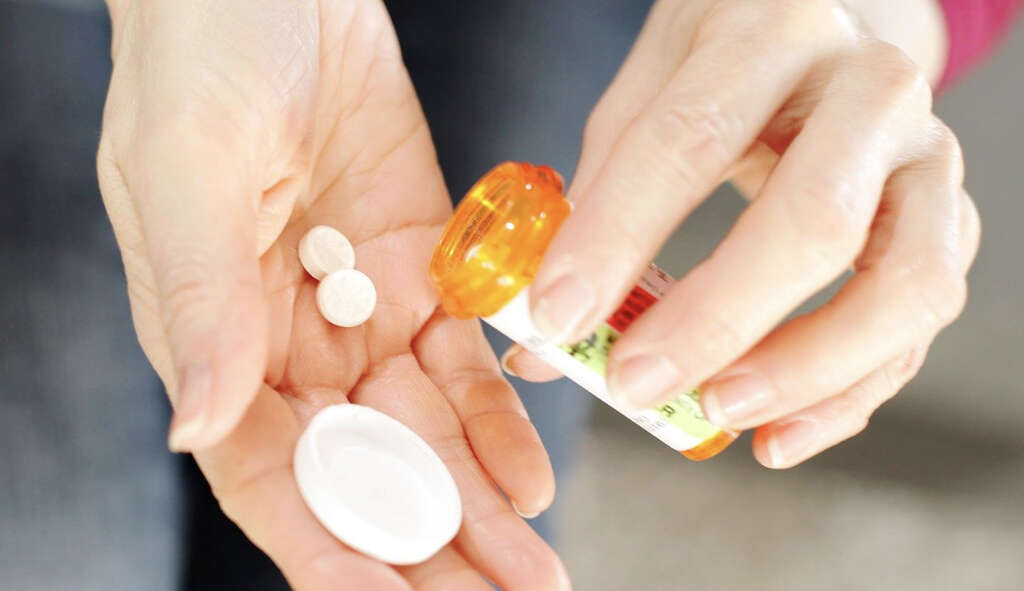
9. Complications
Chronic damage to the skin due to phototoxicity can lead to premature aging, skin cancer, and lentigines. It has been noted that there is an increase in the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. In persistent light reactivity, the photosensitivity can be present for months or years even after the offending agent has been eliminated.
it may progress to involve more parts of the skin. It can be debilitating as the patient would have to be confined to darkened rooms. Treatment usually involves avoidance of contact with triggers. Those without any improvement may be recommended for the prescription of immunosuppressive agents.
10. Prognosis and Patient Education
The prognosis (outcome) is excellent for most patients once the offending agent has been removed. However, resolution of the affected area can take weeks to months depending on the compound causing it. In some patients, they can have persistent reaction to light resulting in poor likelihood of resolution.
Drug-induced photosensitivity rarely causes death and only in those who have been taking large doses of psoralens and have subsequent exposure to large amounts of sunlight. Although death is rare, the condition can cause significant issues among some patients. These individuals should limit their exposure to light. Patients should be educated and counseled regarding possible photosensitivity for their medications. Using appropriate sun protection can also prevent these reactions.