What Is Pericardial Effusion?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Colombo, A. et al. Etiology and prognostic implications of a large pericardial effusion in men. Clinical Cardiology vol. 11,6 (1988):389-94. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960110606.
- 2. Sagristà-Sauleds, Jaume et al. Diagnosis and management of pericardial effusion. World Journal of Cardiology vol. 3,5 (2011): 135-43. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i5.135.
5. Signs & Symptoms
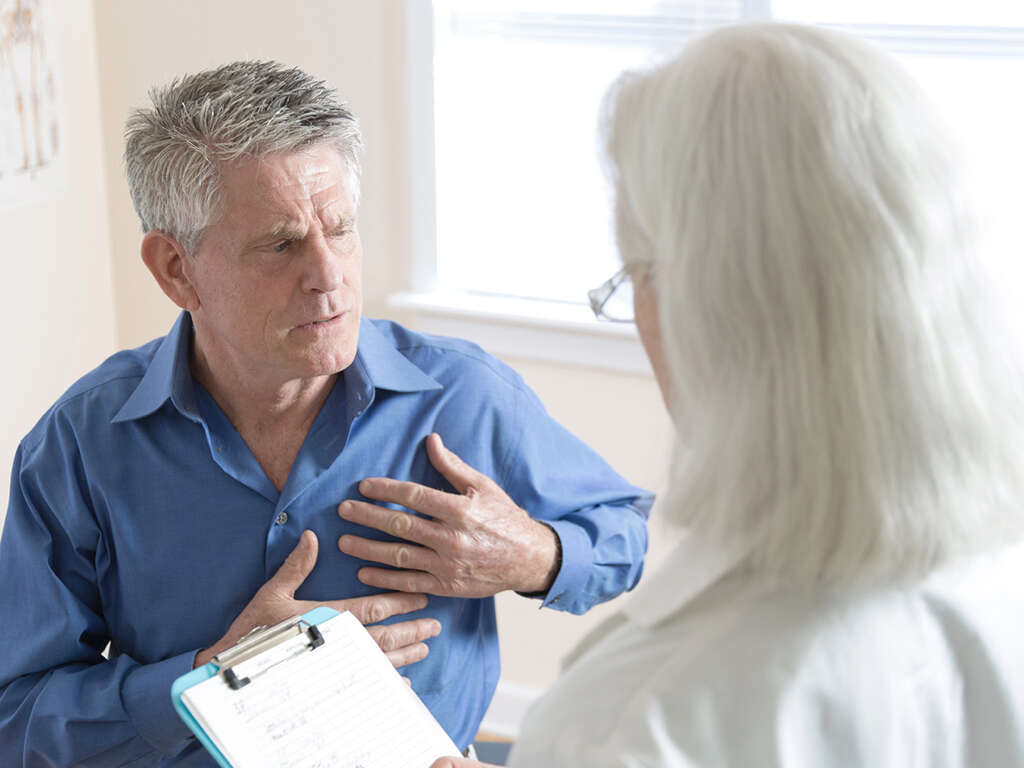
This condition ranges from mild to severe. A small pericardial effusion is indicative of a mild case, while a large one is severe. A majority of those who have pericardial effusion do not have any symptoms, including those with large, chronic pericardial effusion.2Sagristà-Sauleds, Jaume et al. Diagnosis and management of pericardial effusion. World Journal of Cardiology vol. 3,5 (2011): 135-43. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i5.135. This is particularly true when the condition develops slowly, with fluid buildup occurring over time.
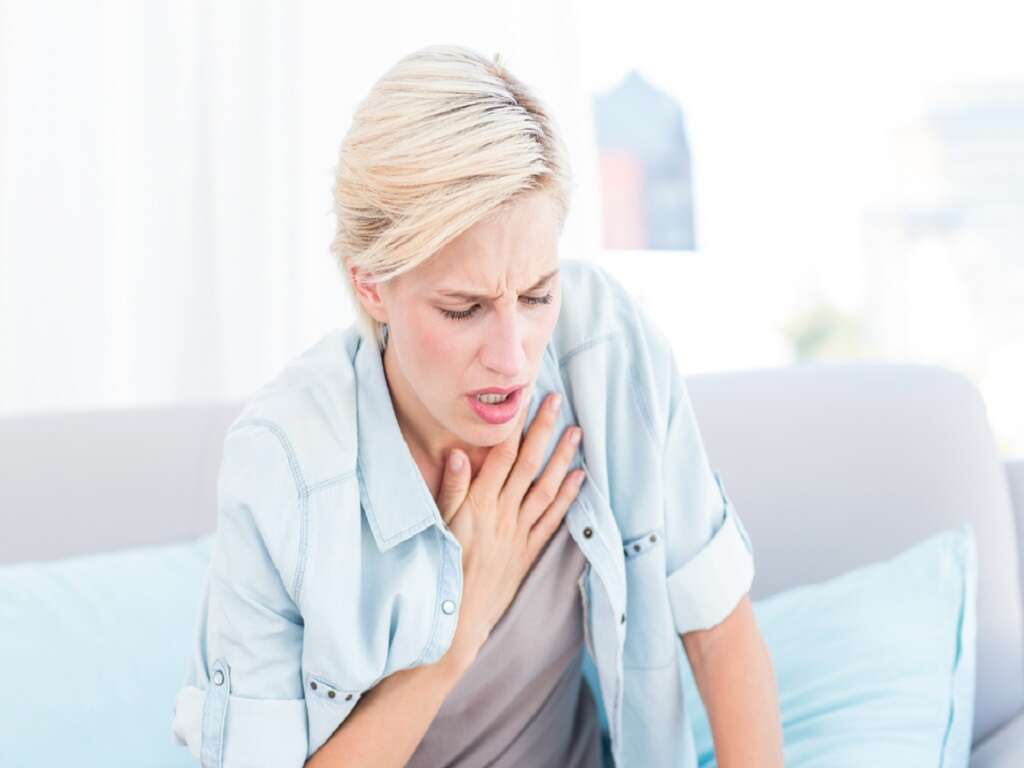
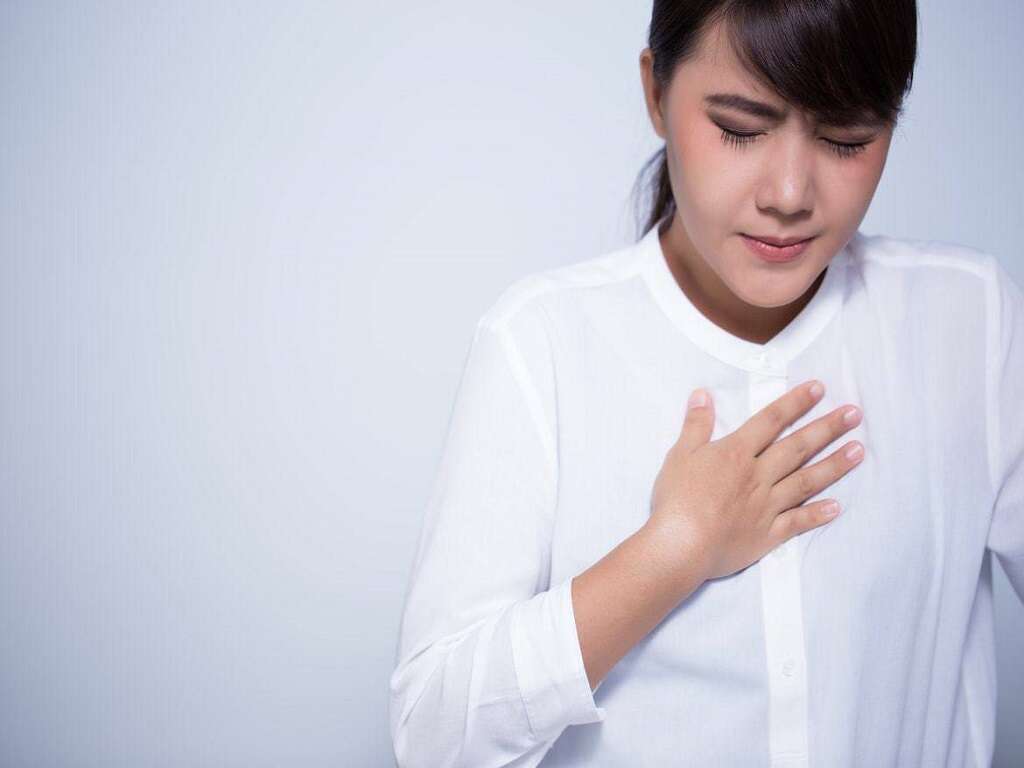
If symptoms do occur, it is usually after a significant amount of fluid has accumulated in the pericardium. At this time, the individual may experience chest pain or pressure, generally on the left side. Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing may also occur. Some people notice a feeling of fullness in the chest. There is the potential for swelling to occur in the legs and abdomen.
Advertisement