What Is Oxidized Cholesterol?
2. What Is the Difference Between LDL and HDL Cholesterol?
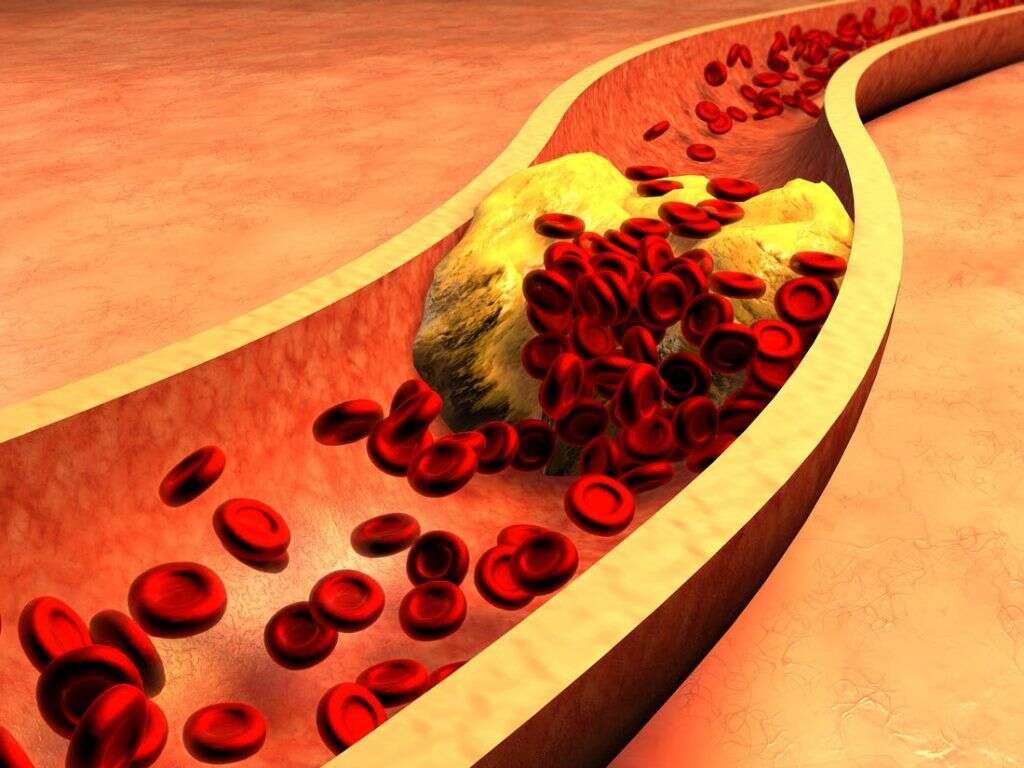
In the same way that oil and water do not mix, cholesterol does not dissolve in blood. To navigate through the bloodstream, cholesterol must be carried on molecules called lipoproteins, which are made of proteins and fats. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) transport cholesterol to the liver for removal. They reduce inflammation, produce nitric oxide to dilate blood vessels, and prevent clotting. High levels of HDL are considered beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) are the primary carriers of cholesterol, and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) also carry a small amount. High levels of VLDL and LDL cholesterol in the blood can lead to the formation of plaques, which are a combination of cholesterol, fatty acids, calcium, connective tissue, and cellular debris. The presence of these plaques is called atherosclerosis and can result in heart attack, stroke, or lack of blood flow to other organs like the kidneys.
Advertisement