What Is Orthopnea?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Vaskar Mukerji: 'Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea.' Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd Edition. 1990, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK213/
- 2. 'Pulmonary edema.' Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009
- 3. Rakesh K. Pai, MD, FACC; Martin J. Gabica, MD; E. Gregory Thompson, MD; Adam Husney, MD; Stephen Fort, MD, MRCP, FRCPC: 'Heart Failure Symptoms.' UMHS Michigan Medicine, August 31, 2020, https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tx4082abc
- 4. Biykem Bozkurt; Douglas L. Mann: 'Shortness of Breath.' AHA Journals, July 15, 2003, https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.0000075956.36340.78
- 5. Cara Martinez: 'Shortness of Breath: When to See Your Doctor.' Cedars-Sinai, September 30, 2019, https://www.cedars-sinai.org/blog/shortness-of-breath.html
- 6. 'Heart Failure: Risk Factors.' University Health Care System, https://www.universityhealth.org/heart-failure/risk-factors/
6. Complications
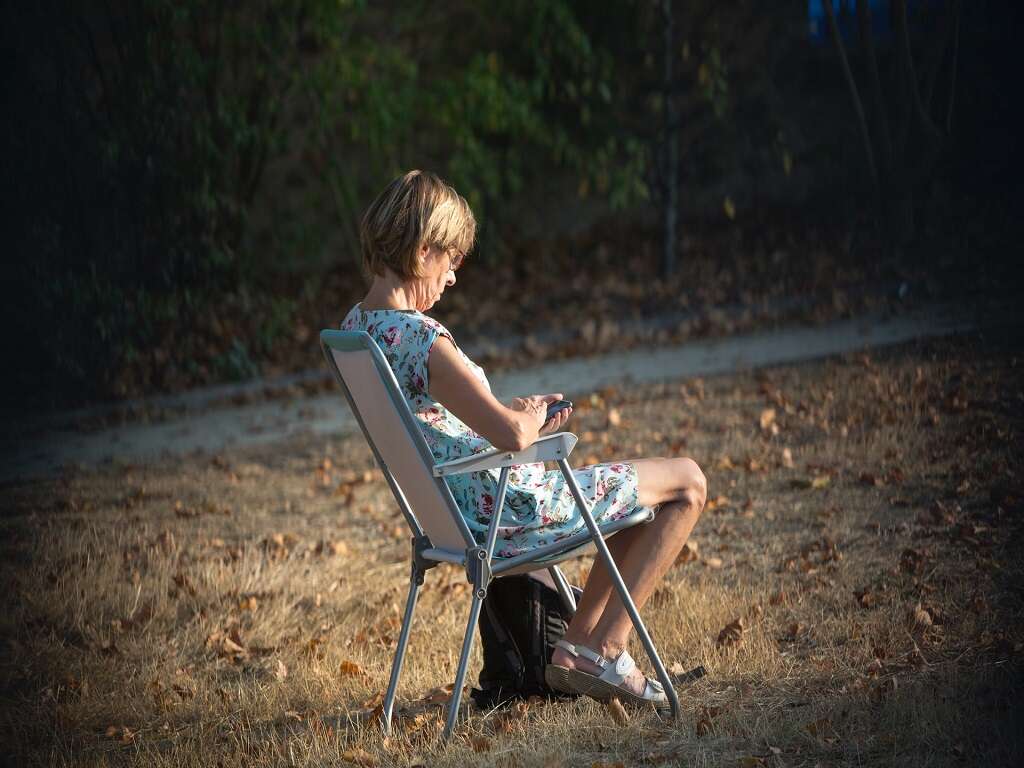
Orthopnea can lead to fatigue during the day and weight gain. As the orthopnea gets more extreme, many people are unable to sleep in bed at all. Instead, they can only rest while sitting in a chair.
Other complications are tied to the cause of an individual’s orthopnea. In serious cases, such as heart failure, if the person doesn’t seek treatment, it can lead to severe complications. The results may be severe heart failure and death.
Advertisement