What Is Myopathy?
The onset of sudden muscle weakness or discomfort can take you by surprise. It may mean you are dehydrated or that your body lacks potassium. However, there are times when muscle weakness, along with other symptoms, may signal the development of a possible chronic condition.
Myopathy is a term the medical community uses to refer to an illness or disease that impacts the muscles. It typically results in the weakening of muscles over time. Some types of myopathy can cause involuntary muscle movement. Depending on the diagnosis, myopathy may result in the immobility of some muscle groups.

1. Causes of Myopathy
There are two main categories of myopathy: acquired and inherited. Acquired myopathy occurs as a result of something else. For example, some autoimmune disorders cause muscle spasms and weakness. When muscles are fatigued or deficient in essential nutrients, myopathy can also occur. Acquired myopathy can happen at any time in a person’s life. It may be temporary or chronic.
Inherited myopathy is genetic. The symptoms may not present immediately at birth, and in some cases, they may come on later in life. However, if a parent or close relative has myopathy, then doctors will likely categorize it as genetic.

2. Risk Factors for Developing Myopathy
Some factors may put you at risk for developing myopathy at some point. If a close relative has myopathy, you have a greater chance of carrying the genetic markers for a disorder. While you may not experience the same signs, symptoms or condition as your family member, you may have a higher probability of experiencing some variation.
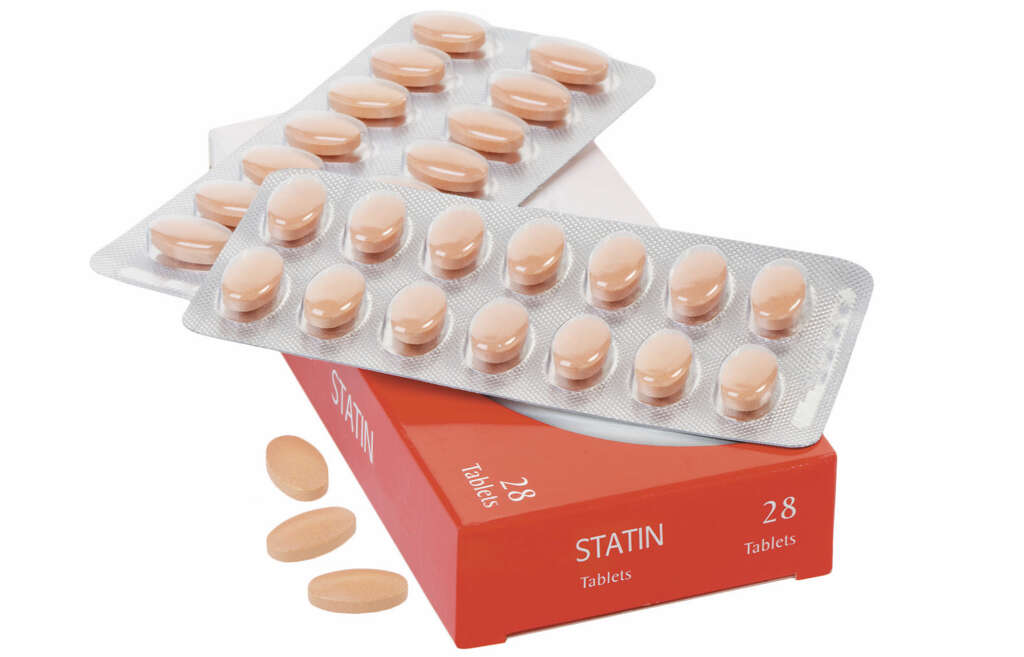
Certain medications may also put you at an elevated risk of getting myopathy. Statin drugs, such as those used to control heart disease, may produce the side effect of weakening the muscles. If you are an athlete and do not maintain the proper nutritional regimen required of your sport, you may also develop acute myopathy after a particularly difficult event.
3. Symptoms of Myopathy
You should be on the lookout for several signs and symptoms if you know you have a genetic predisposition for developing myopathy. Acute myopathy may onset in much the same fashion, so understanding these signs may help your doctor get a quicker diagnosis.
The most common sign of myopathy is a weakening of the muscles in the upper arms and/or legs. The muscles may cramp or spasm without warning. You may also feel fatigued, and the urine often appears dark yellow or brown. In the most extreme cases of myopathy, you may have temporary paralysis of certain large muscle groups.

4. Diagnosis of Myopathy
When you visit the doctor for your symptoms, you will likely undergo a physical exam that includes several tests to determine your muscle strength. These tests usually involve the doctor or medical provider placing pressure on the limbs to see if you can resist or push back.
Other testing includes an EMG or electromyography. This measures the electric impulses transmitted to the muscles and their relative reaction. It is painless and helps to measure the progression of an ongoing myopathy diagnosis.
5. Myositis
Myositis categorizes the onset of inflammation of the muscles used to move the body. An underlying autoimmune disease, an infection or an injury can bring on this condition. Age may also play a factor in its development.
Myositis is further diagnosed as polymyositis, dermatomyositis or sporadic inclusion body myositis. Polymyositis usually manifests as a generalized weakness in those muscles closest to the torso. Dermatomyositis may often exhibit a localized rash in the area of the muscle cramping or weakness. Sporadic inclusion body presents in those over 50 and includes a decreased ability to walk.

6. Congenital Myopathy
Congenital myopathy is usually detected and diagnosed at birth. A child born with this muscle condition will appear limp or floppy and have difficulty sucking and breathing. Babies with this condition also lag behind other children in developmental milestones.
In some cases, what starts as a muscle disorder may morph into issues with the skeletal system. Scoliosis is often found in children who were born with congenital myopathy.

7. Muscular Dystrophy
One of the most severe forms of myopathy is muscular dystrophy.1Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ‘What is Muscular Dystrophy?’ Undated. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/musculardystrophy/facts.html. These are genetic disorders that cause the muscle systems in the body to weaken and degrade as time goes on. They may appear early in a person’s life, or symptoms may come on gradually over time.
Muscular dystrophy is rare. Individuals who are diagnosed and progress through this type of degradation often deal with a loss of mobility through a period of time. Some types of dystrophies may attack and weaken certain muscle groups, such as the arms and legs. Others may eventually cause a shutdown of all muscle function. There is no known cure for this type of myopathy.

8. Drug-Induced Myopathy
Prescription medication and other substances may cause muscle weakness. Those medications prescribed for lowering lipids and helping heart health may inhibit muscles. Leg cramps and overall weakness may result during treatment. Drugs for controlling certain psychological issues may also suppress nerve impulses to the body, including stimulus to large muscle groups.
The long-term consumption of alcohol may cause muscle weakening. Myopathy due to alcohol use is rare in those who are casual or occasional users. However, in longstanding alcoholics, spasms, numbness and atrophy of some muscles may occur.

9. Treatment of Myopathy
Genetic myopathy is incurable, but physicians manage the symptoms in a number of ways. Doctors may be able to prescribe drugs to help reduce the inflammation of the areas affected. Aside from oral medication, creams and ointments may also help restore blood flow to an area of the body.
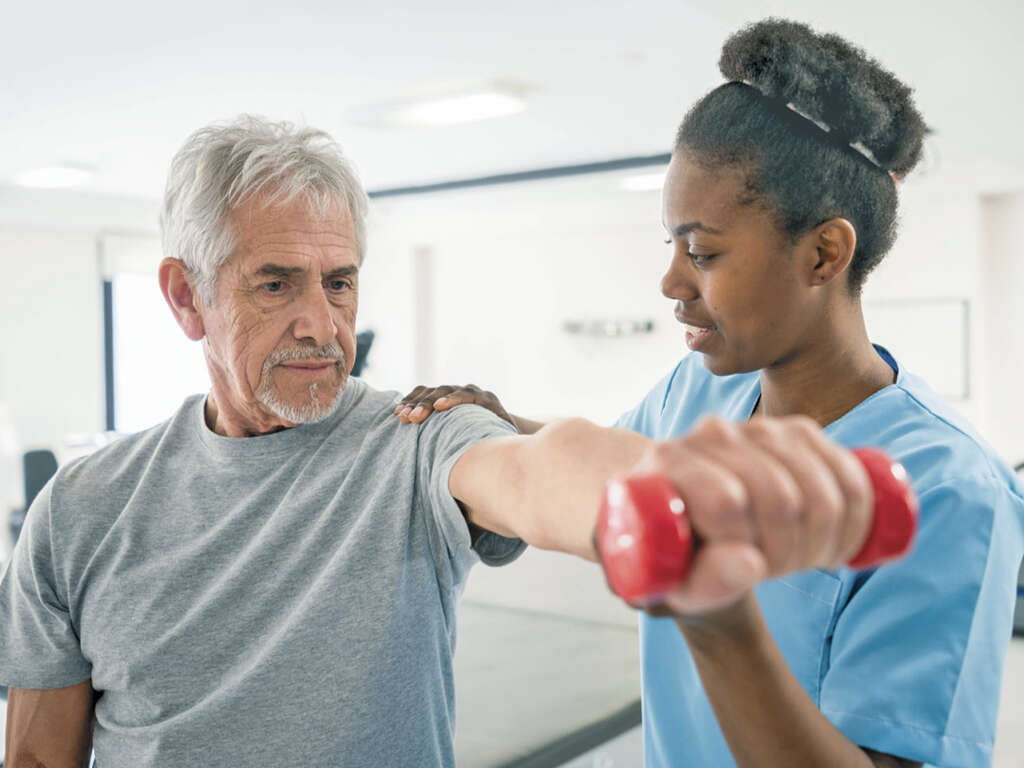
Exercise is one way to help alleviate the progression of many myopathies. It can help increase muscle size and vitality, improve cardiovascular strength and enhance flexibility. Heat therapy to the muscle group can also help increase circulation and bring fresh blood to the area.

10. Prognosis
The prognosis for people dealing with myopathy varies based on the type and stage of the disease. If you are diagnosed with a genetic condition that causes myopathy, you may still go on to lead a long and fulfilling life without more than minor impacts on your daily routine. If your condition is the result of another underlying condition, treatment of that issue on an ongoing basis may help keep the symptoms of myopathy at bay.
While there is no cure for some forms of myopathy, there are successful treatment plans and programs. If you become immobilized due to the atrophy that can occur over time, scientists have made great strides in assistive devices. Living with myopathy can be a matter of making adjustments, ongoing therapy and maintaining an overall healthy lifestyle.