What Is Molluscum?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Meza-Romero, Rodrigo et al. “Molluscum contagiosum: an update and review of new perspectives in etiology, diagnosis, and treatment.” Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology vol. 12 373-381. 30 May. 2019, doi:10.2147/CCID.S187224
- 2. Nandhini, G., Rajkumar, K., Kanth, K. S., Nataraj, P., Ananthakrishnan, P., & Arunachalam, M. (2015). Molluscum contagiosum in a 12-year-old child - report of a case and review of literature. Journal of international oral health : JIOH, 7(1), 63–66.
- 3. Leung, Alexander K C et al. “Molluscum Contagiosum: An Update.” Recent patents on inflammation & allergy drug discovery vol. 11,1 (2017): 22-31. doi:10.2174/1872213X11666170518114456
Molluscum is the infection that can happen when a person catches the molluscum contagiosum poxvirus. The infection usually appears on the skin, causing lesions to develop and trigger irritation all over the infected regions. While a treatable condition, some cases of this infection can take up to four or five years to run their course.
Because there are many different kinds of rashes that can develop over the skin, focusing on the underlying causes and additional symptoms of molluscum is crucial to recognize it. These questions illustrate important factors involved with diagnosing and treating this infection.
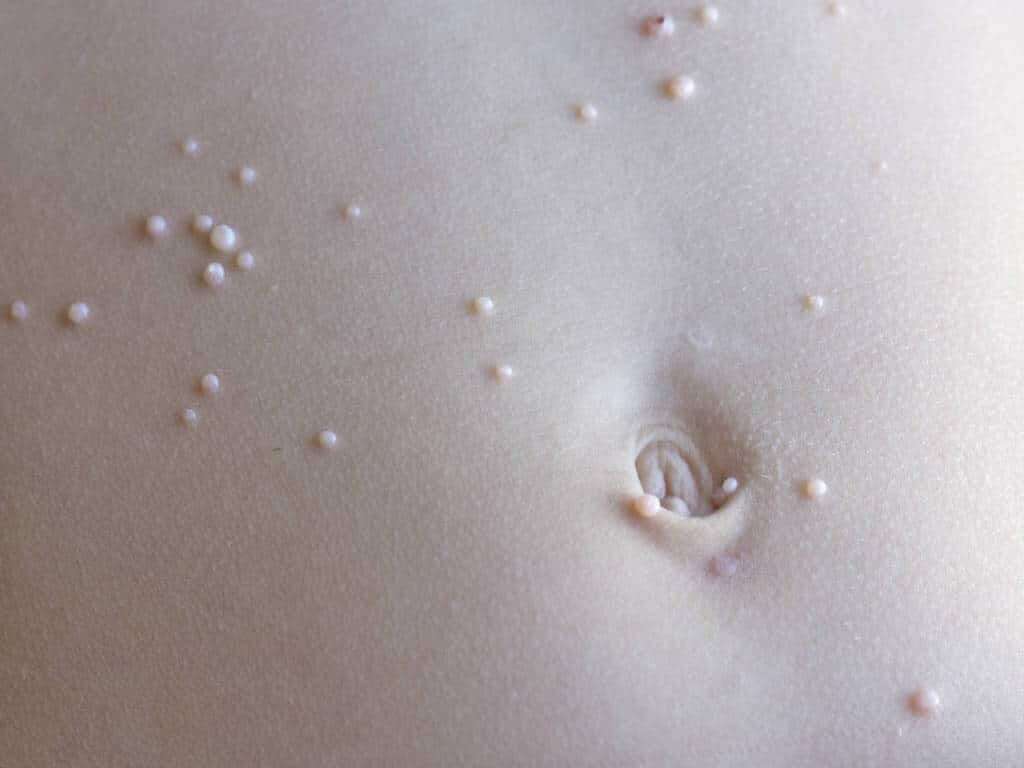
1. What Are the Symptoms of Molluscum?
Someone who has come in contact with the molluscum contagiosum virus is likely to see the symptoms of infection anywhere between one and six months from the first point of contact. It takes several weeks for the virus to intubate, meaning you may not realize there is even an infection for a good chunk of time.1Meza-Romero, Rodrigo et al. “Molluscum contagiosum: an update and review of new perspectives in etiology, diagnosis, and treatment.” Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology vol. 12 373-381. 30 May. 2019, doi:10.2147/CCID.S187224
The first symptoms of molluscum are small lesions on the skin. Molluscum causes a specific type of skin rash, and any part of the body can develop these lesions. Typically, the bumps appear in groups of up to 20. The lesions are usually the same color as a person’s flesh, or else a bit lighter or pinkish.

2. What Are the Causes of Molluscum?
As with a majority of skin infections, direct contact with infected skin is the easiest way to develop an infection yourself. Still, skin-to-skin contact is not the only way that people can become exposed to the virus. Touching a contaminated object like a towel or article of clothing can also put you at risk.
Sexual contact with someone who has been infected by the molluscum contagiosum virus is another way to contaminate yourself. You may also find that it is easy to spread the virus around your own skin by scratching at an infected area. It is advised to avoid scratching at the lesions and to seek a consultation by a dermatologist at the first sign of such bumps.
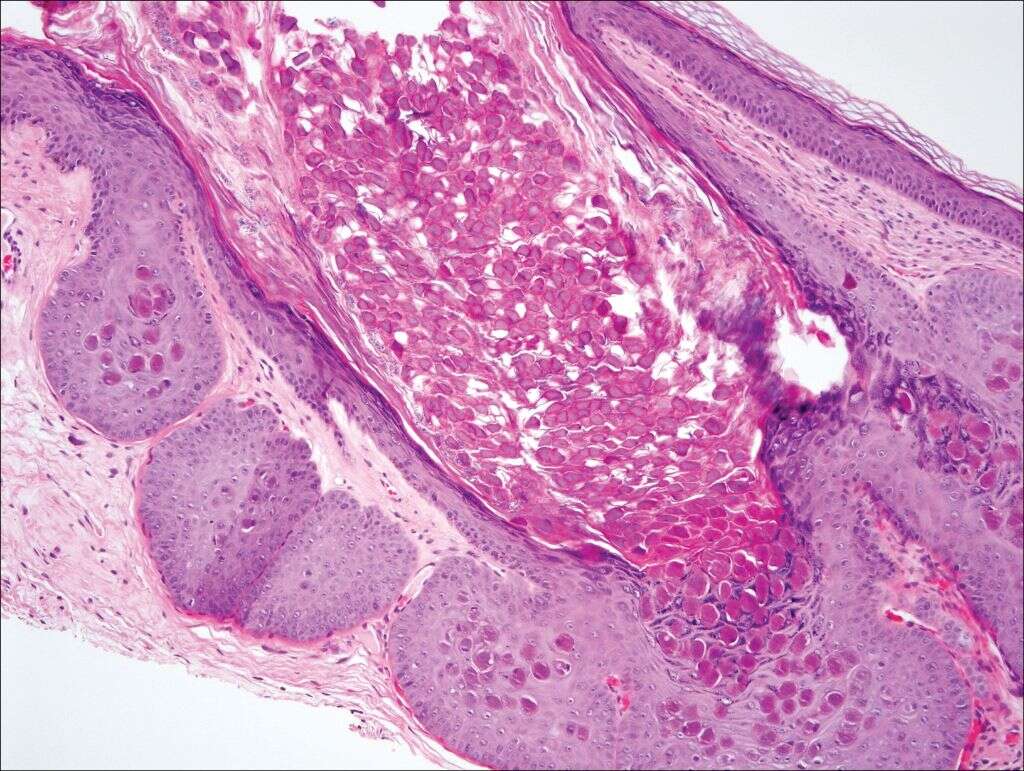
3. Who Is Most at Risk for Molluscum?
Though anyone can develop this infection if exposed to this virus, there are a few at-risk groups. Since children are often in close contact and have little reservations when it comes to touching another child while playing, they are most likely to come in contact with an infection of the skin like molluscum.
Adults who engage in contact sports or physical performances on stage may also experience the lesions associated with molluscum. Also, any adults with weakened immune systems may be the most likely to develop an infection after being exposed to the virus.2Nandhini, G., Rajkumar, K., Kanth, K. S., Nataraj, P., Ananthakrishnan, P., & Arunachalam, M. (2015). Molluscum contagiosum in a 12-year-old child - report of a case and review of literature. Journal of international oral health : JIOH, 7(1), 63–66.

4. Will Molluscum Go Away With Time?
For individuals with developed and strong immune systems, there is no treatment required for molluscum. The lesions will slowly go away on their own, usually taking between one and four years to fully vanish. The bumps should not leave behind any scars or unsightly blemishes, either.
Naturally, there are scenarios where you may wish to seek treatment anyway. If the bumps are big or on visible areas like your face or neck, you may feel reluctant to wait for the lesions to fade on their own. Those concerned about spreading the virus to others might also wish to seek more immediate treatment.
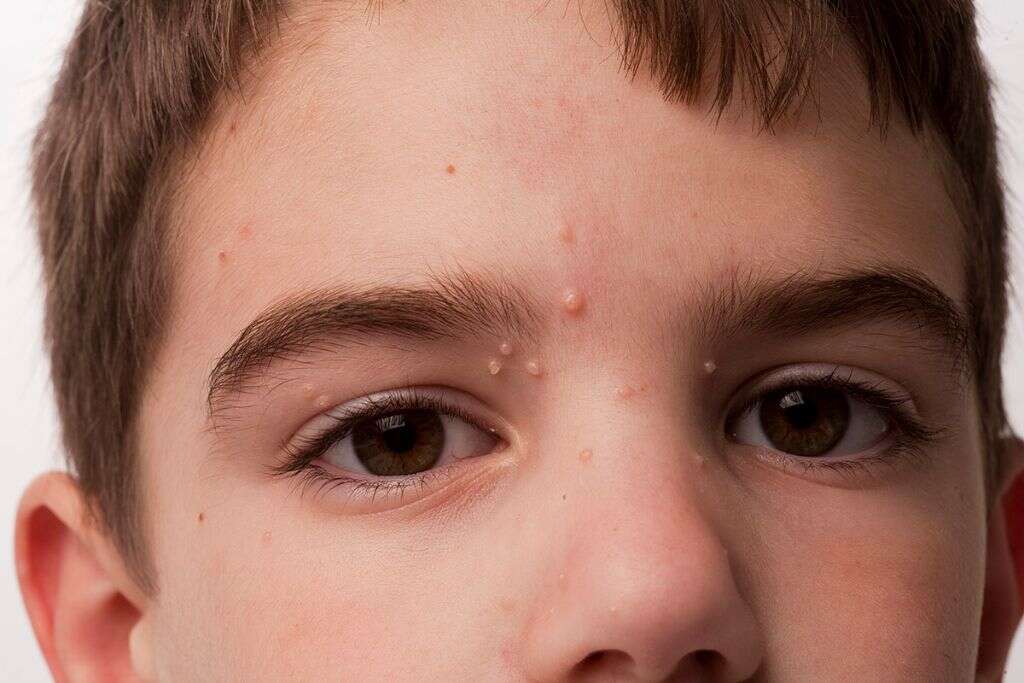
5. How Is Molluscum Typically Treated?
There are several medical options for those seeking assistance with molluscum. After assessing the severity of your infection, a doctor can offer the best possible solutions based on your case and medical history.
Typically, the most effective options available to patients are topical therapy in the form of creams and ointments. Cryotherapy and laser therapy can handle the bumps directly and quickly. Curettage may also be suggested by a dermatologist or other medical professional.

6. Can Anything Impact Treatment of Molluscum?
A few factors may affect the treatment options available to you for molluscum. If you are or are planning on becoming pregnant, there are a handful of medications that cannot be given to you. Certain prenatal medications and birth aids have bad interactions with molluscum medications.3Leung, Alexander K C et al. “Molluscum Contagiosum: An Update.” Recent patents on inflammation & allergy drug discovery vol. 11,1 (2017): 22-31. doi:10.2174/1872213X11666170518114456
Those undergoing treatment for cancer or taking medicine for HIV AIDS may also be limited in what treatment options are available. Antiretroviral therapy is often suggested for these cases, as this treatment can actually work to boost the immune system in general while handling the infection.

7. When Is Molluscum No Longer Contagious?
Depending on treatment, you may still be able to infect others with molluscum for a good amount of time after you have begun therapy. The skin is considered infected until all of the lesions have completely vanished. This can take upward of several years, which is why some seek more immediate treatment options.
It is possible to contract molluscum again after getting it once. Even if all the lesions have vanished, err on the side of caution at first. Infecting yourself by scratching mindlessly at an area that still is fighting off the virus can cause it to spread again.

8. Can Molluscum Be Prevented?
Unfortunately, there is only so much you can do to avoid coming in contact with molluscum. If you are an adult who plays sports or is constantly in close physical proximity to others, then you are more likely to develop the infection.
Still, it is possible to reduce the odds. Limit skin-to-skin contact as much as possible and always be thorough about laundering clothing and sheets. Allowing a wet towel to linger for too long in a bathroom can make it a breeding ground for all types of germs and bacteria.

9. Is There an Easy Way to Stop From Spreading Molluscum to Others?
After being diagnosed with molluscum, you may limit your contact with others to avoid spreading the rash. Keep the lesions covered at all times and be sure to avoid direct contact with exposed skin. Once treatment has begun, you may need to wait before safely touching someone again.
Avoid lending out personal items to anyone during the period of infection. A hoodie or towel that has been sitting in your home, even if it has been cleaned, may contain trace elements of the virus and cause it to spread.

10. What Practices Are Best for Minimizing the Spread of Molluscum?
Thoroughly and regularly washing your hands can stop molluscum from spreading around your own body. Use hand sanitizer and keep your hands free from any sign of the virus. Limit your scratching and look for a topical ointment that can reduce the itchiness of the infected area.
Because molluscum is a virus that spreads easily, you need to be diligent about containing it. While no direct treatment may be required for adults, be sure to follow the right practices to minimize the spread of the infection. With time, the molluscum should clear up and leave behind no trace.