What Is Influenza B?
Viruses are not considered to be living things, according to who you ask. They are tiny packages of RNA or DNA in a protective shell and they are unable to reproduce on their own. To reproduce they need to hijack a host’s cells, implant their own RNA/DNA, and have the host cell produce new viruses for them.
Although viruses are not strictly living, they still evolve just like other living organisms. As a result, there are numerous different types of virus, and also sub types. Some have evolved to be able to infect different species, including people. One type that many of us will be exposed to at some point is the influenza B virus. Viruses are not considered to be living things, according to who you ask. They are tiny packages of RNA or DNA in a protective shell and they are unable to reproduce on their own. To reproduce they need to hijack a host’s cells, implant their own RNA/DNA, and have the host cell produce new viruses for them.
Although viruses are not strictly living, they still evolve just like other living organisms. As a result, there are numerous different types of virus, and also sub types. Some have evolved to be able to infect different species, including people. One type that many of us will be exposed to at some point is the influenza B virus.
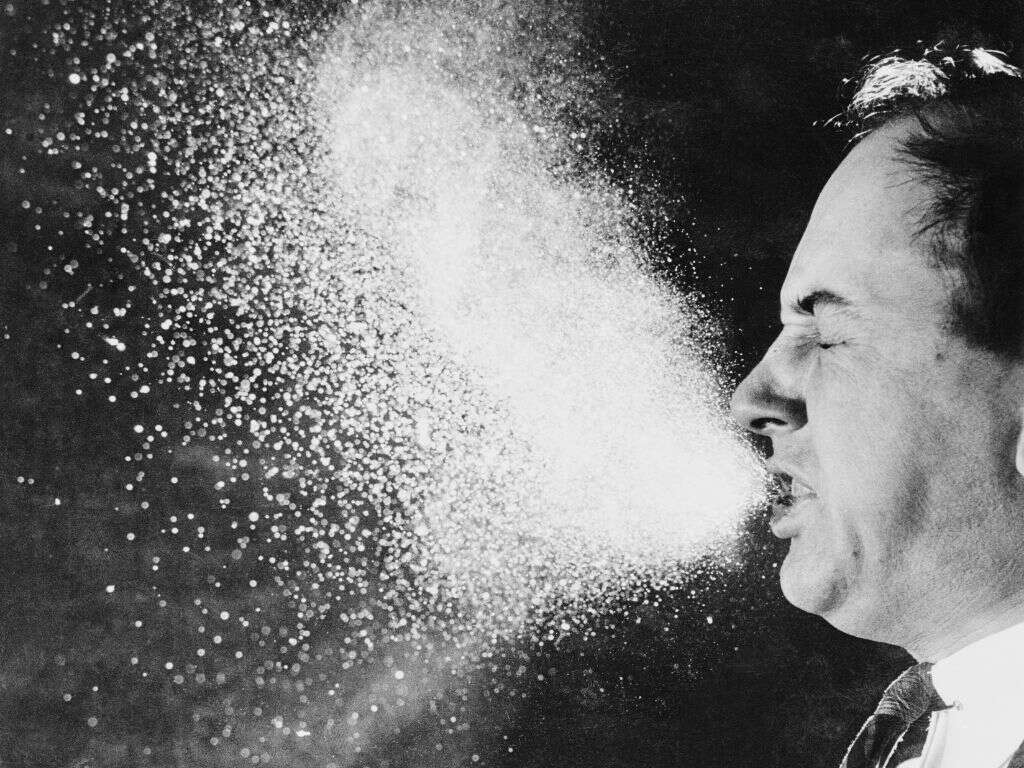

1. Influenza
Influenza, often simply referred to as ‘the flu’, is one of the most common diseases that people are likely to catch. In the past it used to be dangerous and it has been responsible for taking countless lives throughout history. Modern medicine has made it less of a threat to us, but still, it remains a threat to vulnerable people.
The flu is a type of respiratory infection, meaning it infects the lungs and the airways. In most people, the disease will be uncomfortable but it is not usually something to be overly concerned about. However, it is advised that vulnerable people have flu shots as recommended, and they should be monitored if they do have the disease.

2. InfluenzaType B
There are 3 main types of the influenza virus that can infect people, one of which is type B, which accounts for around 25% of all cases of the flu. The type B influenza virus can be found in people only. It is not a particularly severe type of the flu, but it can still pose a very real risk to some people. It is also highly contagious.
This type of flu can be found all year round and it will occasionally result in seasonal outbreaks. However, influenza type B viruses do not cause pandemics and they are not classified by subtype. Symptoms of influenza type B virus will typically last for up to 7 days, first appearing up to four days after the patient has been exposed to the virus.
3. Influenza Type A
Influenza is the most common variety of the flu in people, and it can be transmitted from animals to humans. One example of type A virus is the avian flu, also known which is as bird flu. Swine influenza, also known as swine flu, is another variety of influenza type A.
It is not normal for these examples to be passed on to people, but it will happen in a small number of cases. When people do catch influenza type A, the symptoms are likely to be harsher than the symptoms of influenza type B. Influenza type A mutates rapidly and it is also responsible for pandemics occasionally.
4. Influenza Type C
Of all the types of influenza virus that can infect people, type C is the mildest. People infected with this type are unlikely to experience harsh symptoms and an infection will often be mistaken for the common cold. However, it can lead to more severe infections like pneumonia and bronchitis in a small number of cases.
Influenza type C is also not responsible for pandemics. Another type of influenza virus is influenza type D which has only been discovered relatively recently. This type primarily infects cattle and some other animals and it is not known to infect people as far as we know.
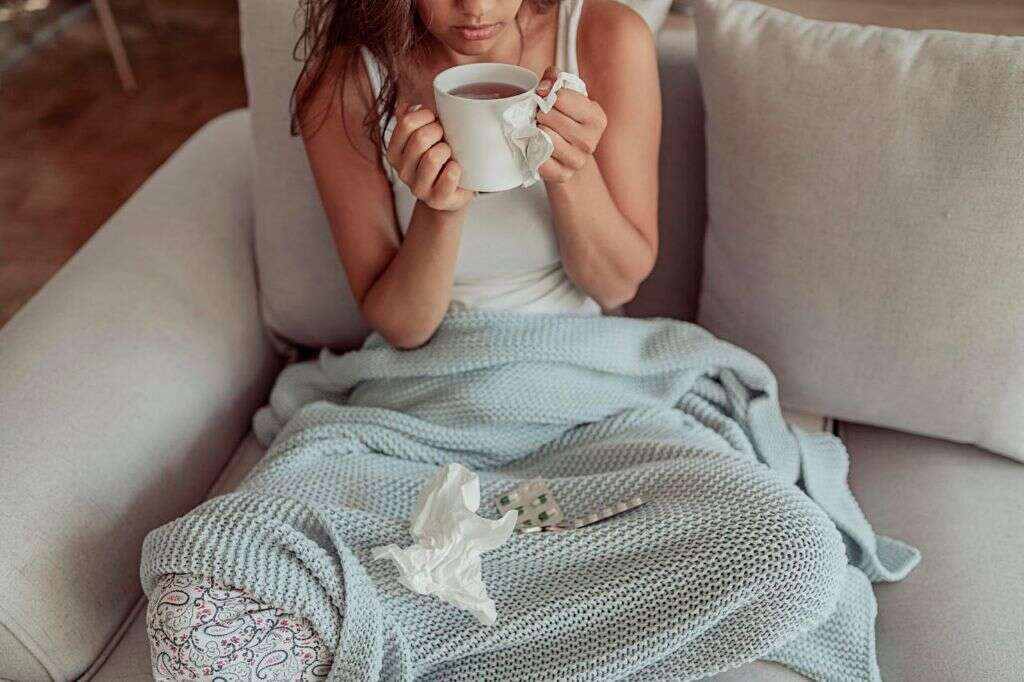

5. Transmission
Influenza B is very contagious, which means it is fairly easy for an infected person to infect somebody else. It is transmitted in the same way that the other influenza viruses are transmitted. This mostly means through the droplets of bodily fluids of an infected person.
These droplets are typically ejected from the body when the infected person coughs and sneezes and these droplets can infect people up to 6 feet away. It is one reason why people are advised to cover their mouth and nose. The virus can also be transmitted when somebody comes into contact with surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus.

6. Symptoms
The symptoms of influenza type B will not be severe in the vast majority of cases. They will typically include a fever and chills. The patient is also likely to experience aches and pains in the joints and muscles. Other symptoms include sneezing and a runny nose, coughing, fatigue, and weakness.
Some of the less common symptoms of influenza type B include nausea and vomiting. The patient will also sometimes have discomfort in their abdomen, and they may also lose their appetite. While the condition is rarely a threat to us, it will cause complications in a small number of cases.
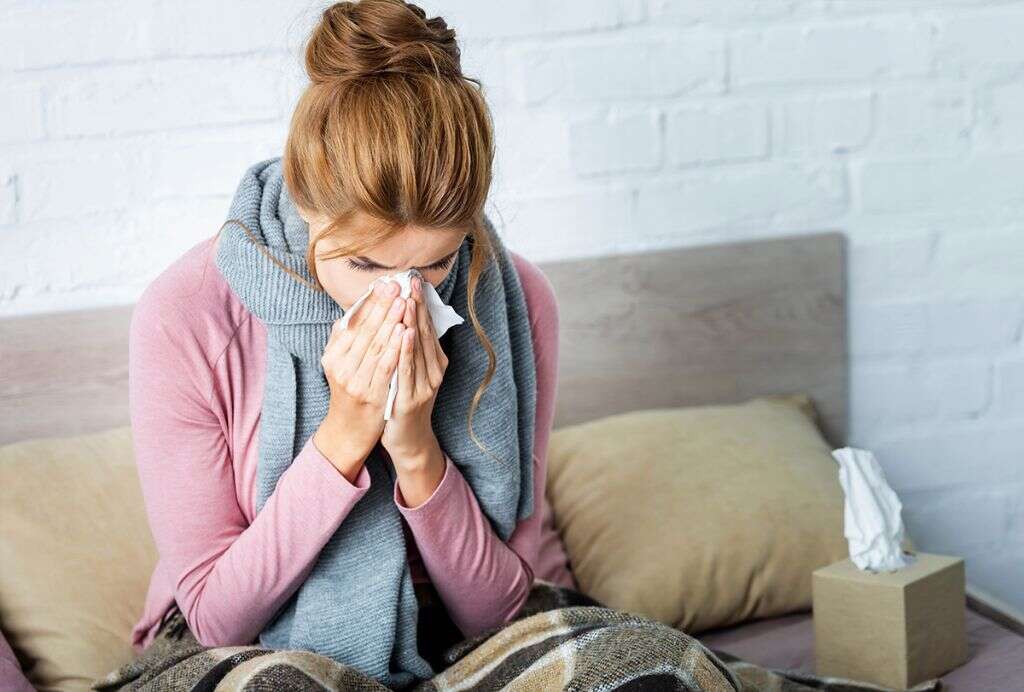

7. Complications
Although rare, influenza type B does have the potential to be dangerous for us. The more severe cases can develop into bronchitis, which will make it harder for the patient to breathe. It can also cause pneumonia, which causes the alveoli in the lungs to become filled with fluid.
The virus can also cause the heart to become inflamed in a condition known as myocarditis, and it can even result in kidney failure. Respiratory failure is also possible, which is itself a very dangerous condition. Sepsis may also occur, which is a dangerous reaction by the immune system to the infection.

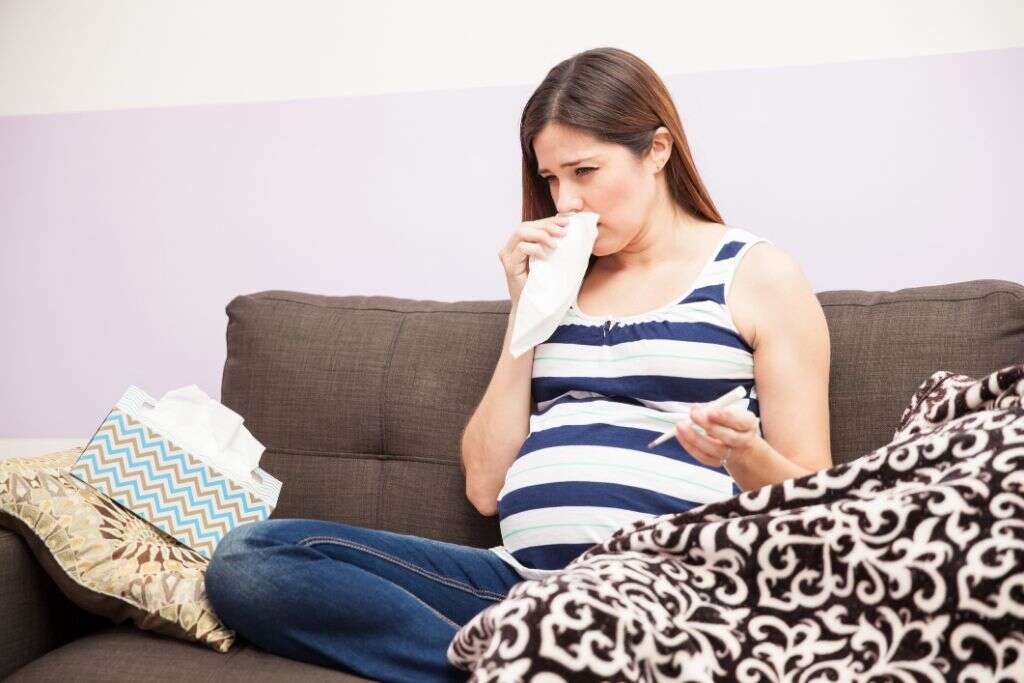
8. Who’s At Risk
Influenza type B is common in people of all ages and all walks of life. However, it is more likely to be found in the young and the old as their immune systems are less likely to be resistant. People with weakened immune systems for other reasons are also in a high risk category.
Other factors include people with certain chronic medical conditions, and people of certain ethnic backgrounds. Pregnant women are also at a higher risk of catching influenza type B. Not only are people in higher risk categories more likely to catch the virus, but there is also a greater risk of the symptoms being severe for them.

9. Prevention
Perhaps the most effective way of preventing influenza type B is to get a vaccination against the virus. Everybody can also follow some simple rules that can help slow the spread of the virus considerably. One of these is to try and make sure your mouth and nose are always covered whenever you cough or sneeze.
Another way to help slow the spread of the disease is to wash your hands regularly. You should also try using soapy water and/or hand sanitizers as they can help to kill viruses and other pathogens. You should try and encourage children to maintain high hygiene standards also.

10. Treatment
As things stand, there is no known treatment for influenza type B, or any other type of influenza virus. The patient is often asked to get as much rest as they can and make sure that they get plenty of fluids. In the majority of cases, the patient’s immune system will deal with the virus and the patient will make a full recovery.
If the symptoms are particularly bad or if the patient is not recovering then you should speak with a doctor. Although the virus cannot be treated directly, medication is available that can at least help to ease the patient’s symptoms. In the most severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary and some patients may need to be put on a ventilator.