What Is Inflammation?
If we injure ourselves then our body will immediately react to help repair the damage and keep us safe from infections. When an intruder does make its way into the body then the same mechanism will help to deal with the intruder before it can do us any harm. As helpful as this is for us, it can also cause some rather unwelcome side effects.
These defensive actions will sometimes cause some considerable discomfort for us. It can cause considerable pain in the short term, and it can cause a lot of discomfort in the long term. Regardless, it is a process that is still necessary for our overall wellbeing. The side effects of these defensive actions are known as inflammation.
1. Inflammation
Inflammation is a very common condition. Indeed, it is something that affects all of us. While we are often trying to treat inflammation, it is actually a very important process for us. Without it, we would not be able to heal quickly, and we would be more prone to infections.
Inflammation is caused because lots of white blood cells rush to a problem area to help protect us against unwelcome intruders. This causes the flow of blood to increase, and this causes the area to become red and warm. The white blood cells will also release chemicals, and these irritate the tissues, potentially causing pain.
2. Acute Vs Chronic
Inflammation can be broken down into two main types: Acute and chronic. Acute inflammation develops quickly, is relatively short lived, and tends to be found after we have sustained injuries. Acute inflammation can be very painful, especially to begin with, but it will usually pass completely within a week or two.
Chronic inflammation develops more slowly, but it will also remain in the long term. The good news is that although it does last longer, it is usually not anywhere near as uncomfortable as acute inflammation is. Chronic inflammation can still be quite uncomfortable, however, and it tends to be caused by certain medical conditions.

3. Causes
There are numerous potential causes of inflammation. As mentioned, one of them is an injury. Something like an ingrowing toenail can also become very inflamed. Other potential causes include certain medication, and you should speak with a doctor if any medication does cause an unwanted reaction, although it is a known and expected symptom in many cases.
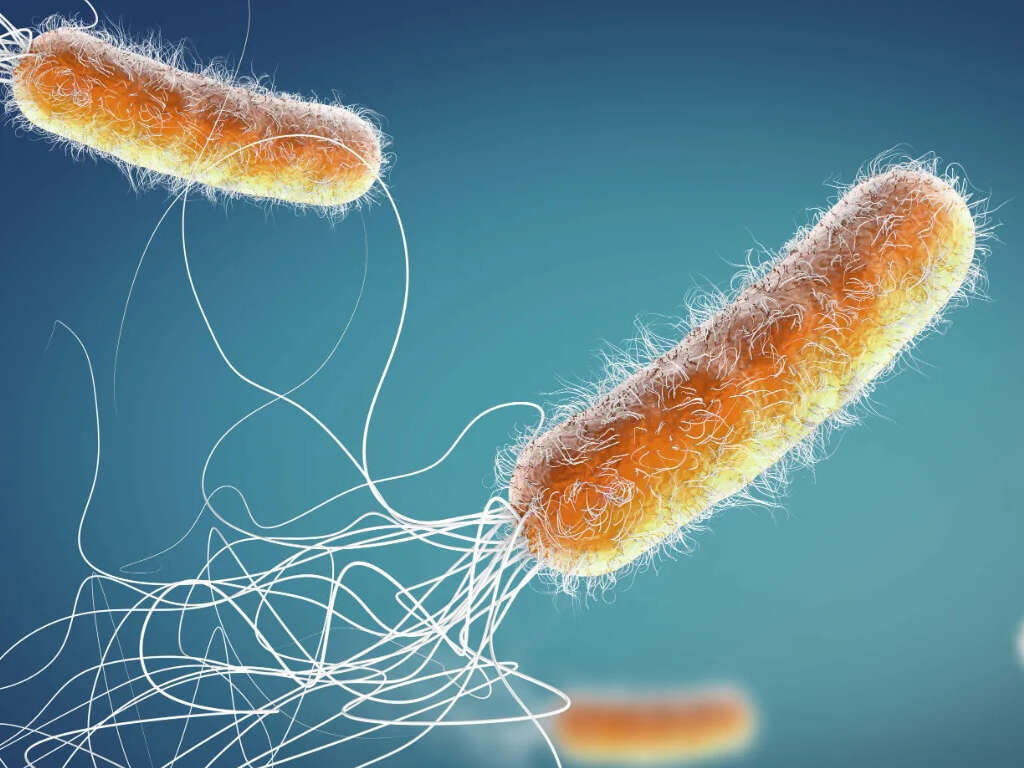
Another potential cause is being exposed to irritants such as chemicals, while exposure to allergens will also cause inflammation in some people. Infections will also sometimes cause inflammation, and something like a sore throat is usually down to inflammation in response to a virus or bacteria.

4. Dietary Causes
A lot of people will need to be rather careful about what they eat to help prevent inflammation. Certain types of food can cause inflammation in the digestive system. This is especially the case in people who have inflammatory conditions of the digestive system, like irritable bowel syndrome.
Certain foods can also cause inflammation elsewhere in the body, including in places like the joints. Some foods can also cause inflammation indirectly, such as in instances of gout. This is a condition where microscopic uric crystals embed themselves in the patient’s joints, and this will result in the joint becoming inflamed.

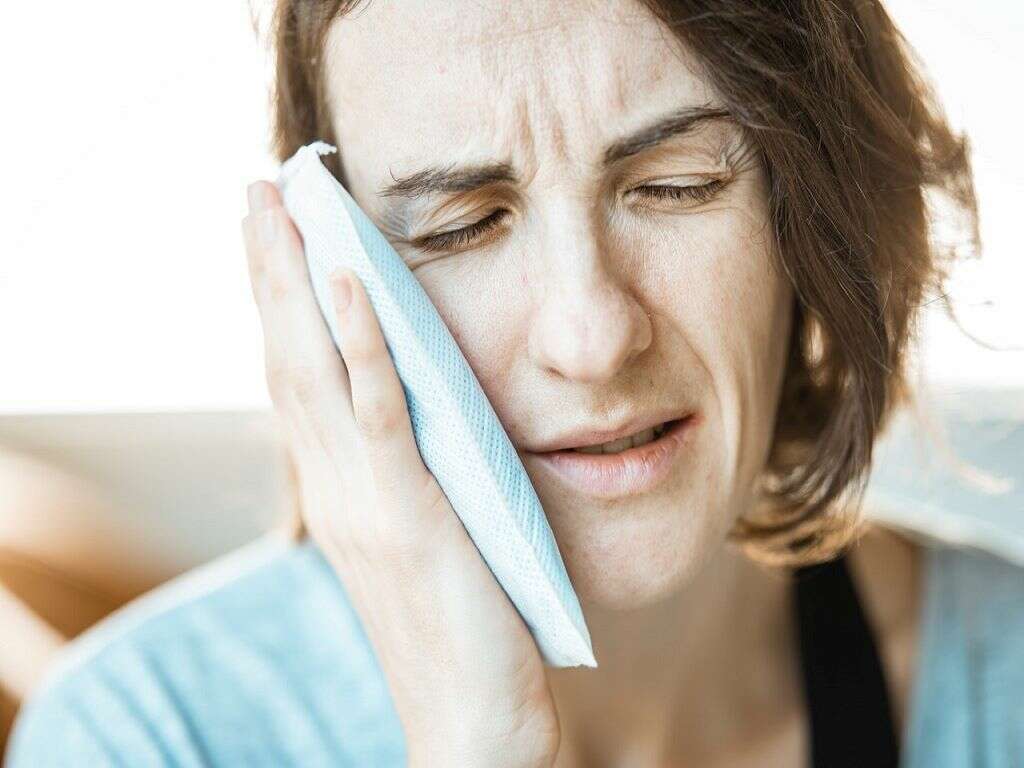
5. Acute Inflammation Symptoms
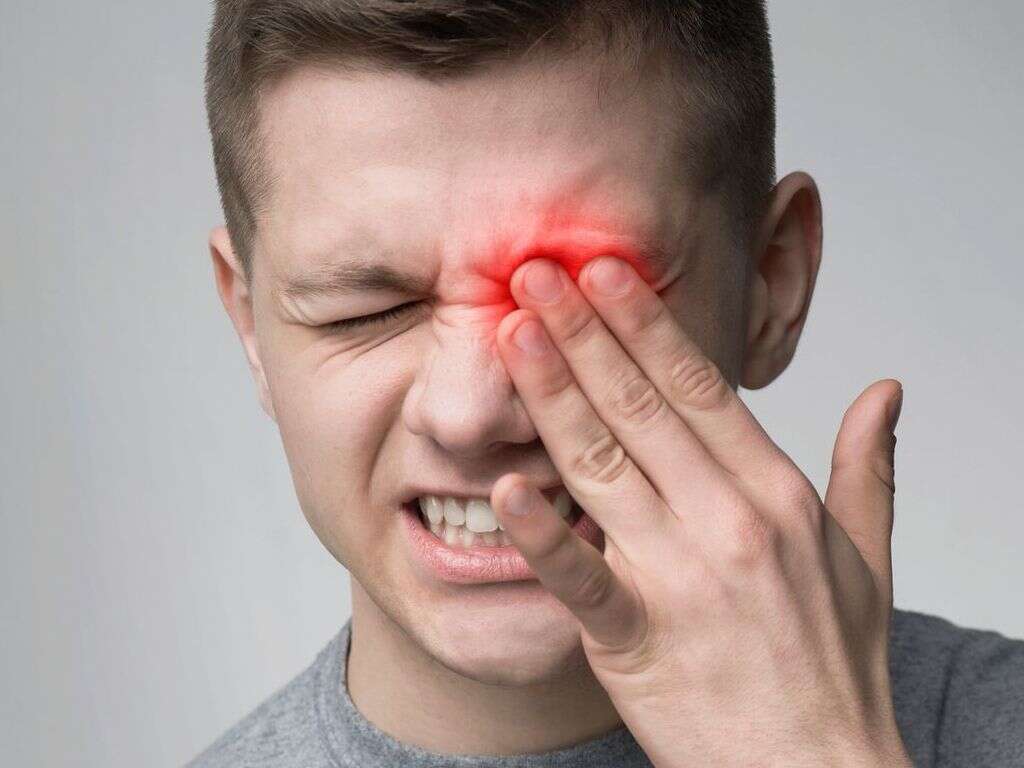
The symptoms of acute inflammation will typically develop rapidly, usually within just a few minutes. It can be very painful, unbearably so, and people in an emergency will often be given medication to help soothe pain caused by inflammation, among other things.
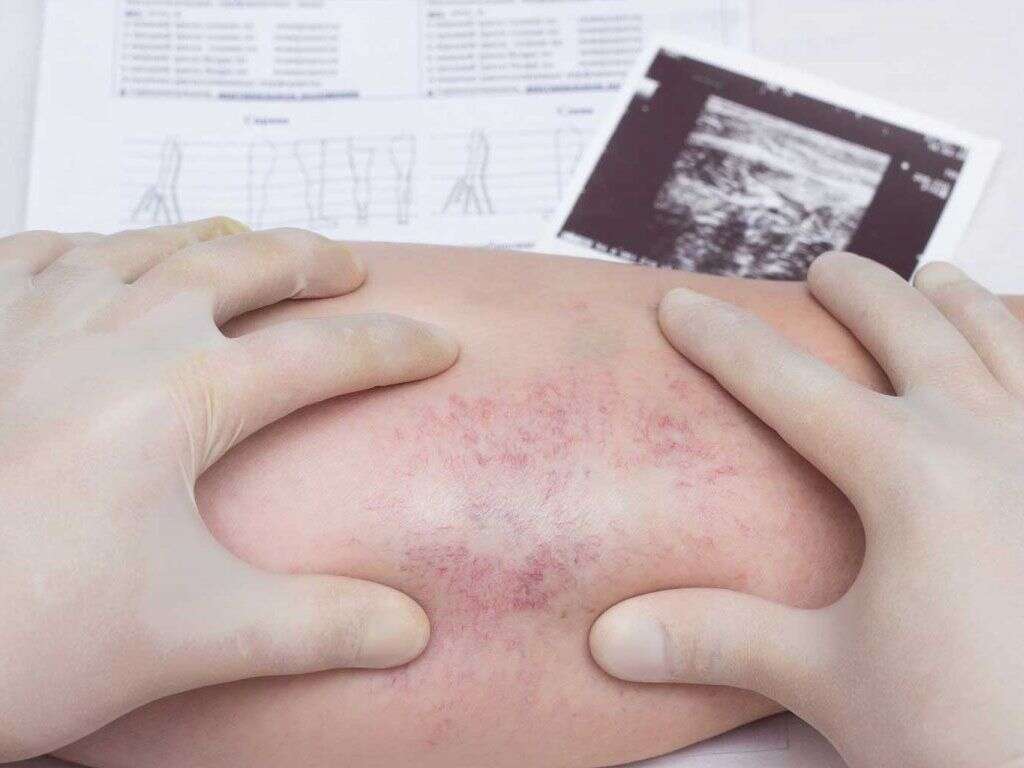
The affected area can also become very swollen, and the swelling can cause the skin to become tight as it is stretched. The area will also likely become very red, and it will also likely be warm to the touch. The patient is also likely to temporarily lose function in the affected area, and affected joints will become very difficult to move.
6. Chronic Inflammation Symptoms
Chronic inflammation will also likely cause pain, and it can be very uncomfortable. However, it is unlikely to be as intense as the pain that comes with acute inflammation. Chronic inflammation can also cause pain in a generalized area rather than in a specific area. Chronic inflammation can also affect people’s skin, and it can also affect organs and other bodily tissues.
Patients with chronic inflammation are also more likely to develop problems like diarrhea, constipation, and heartburn. It can cause the patient to develop infection more frequently than they otherwise would, and it will also sometimes cause weight gain. Chronic inflammation can also cause fatigue, which can be made worse with difficulties sleeping.
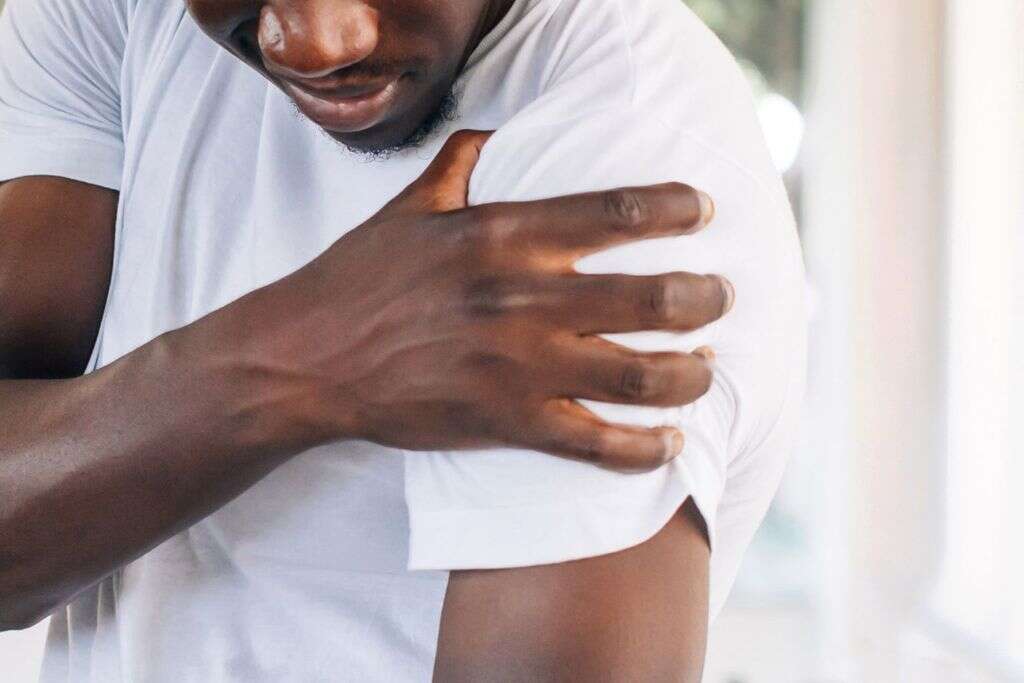

7. Rheumatoid Arthritis
One of the best examples of a chronic inflammatory disease is rheumatoid arthritis. This is a condition where the patient’s joints can become inflamed, and this can cause symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and immobility. There is, so far, no known cure for the condition, but the symptoms can be treated to some degree.
In addition to being an inflammatory disease, rheumatoid arthritis is also an autoimmune disease. This means that the joint tissues are being attacked by the patient’s own immune system. It is this that causes the inflammation, and autoimmune conditions tend to go hand in hand with inflammatory diseases.
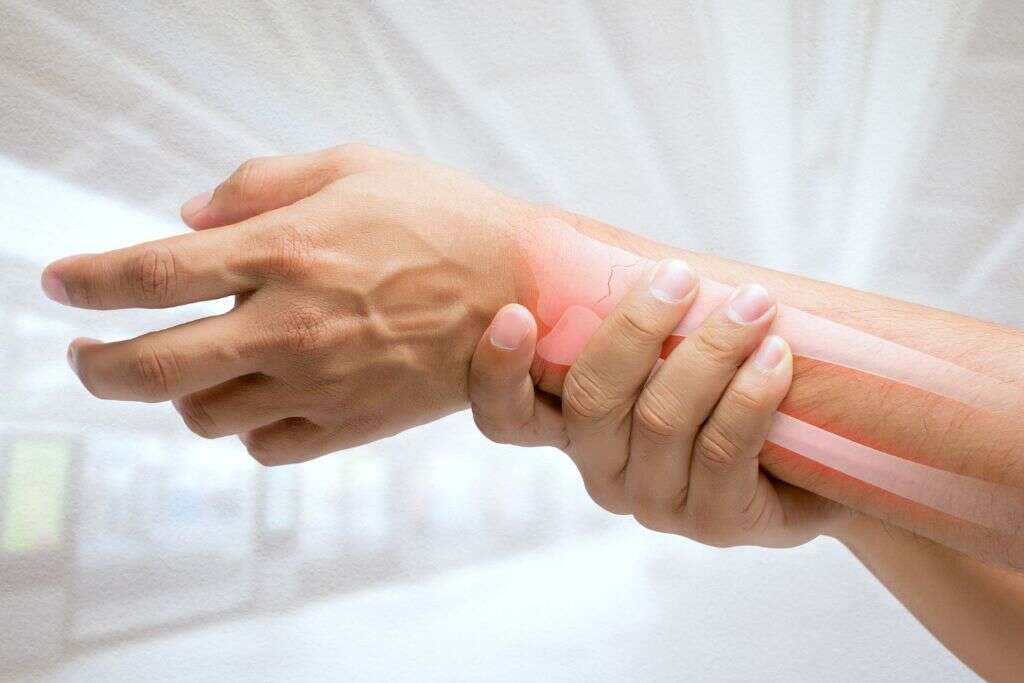
8. Diagnosis
Your doctor may need to perform a brief physical exam, depending on the nature of the condition. They will also need to know about your medical history and they will need to ask about your symptoms. Tests will need to be performed, and there is no single test that can confirm the diagnosis.
Blood samples may be taken and the blood can then be analyzed for signs of inflammation in the body. In some cases, imaging technology may be used to get a visual look inside the patient’s body to look for signs of inflammation. If an inflammatory condition of the digestive system is suspected then a colonoscopy or similar may be performed.
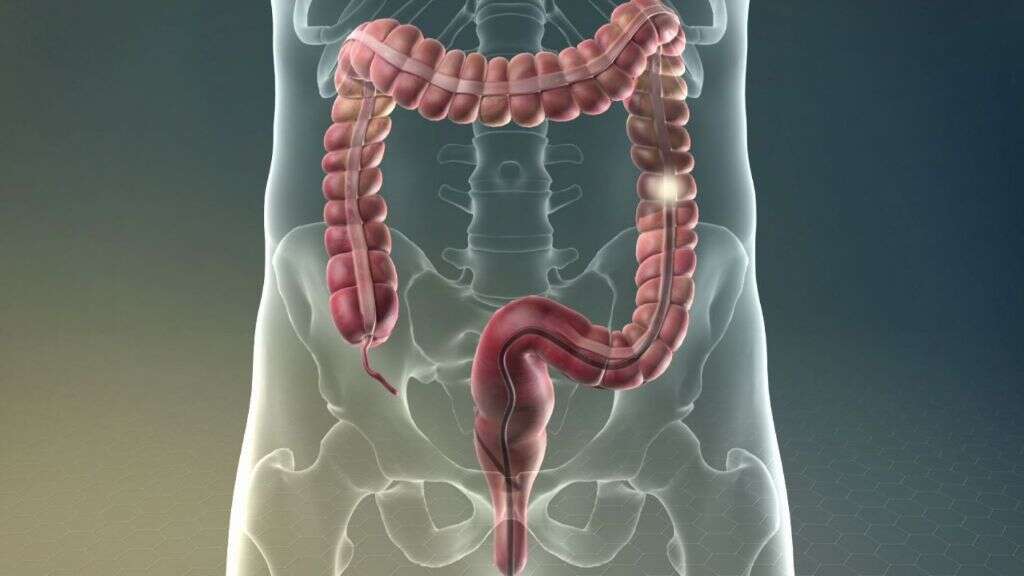
9. Treatment
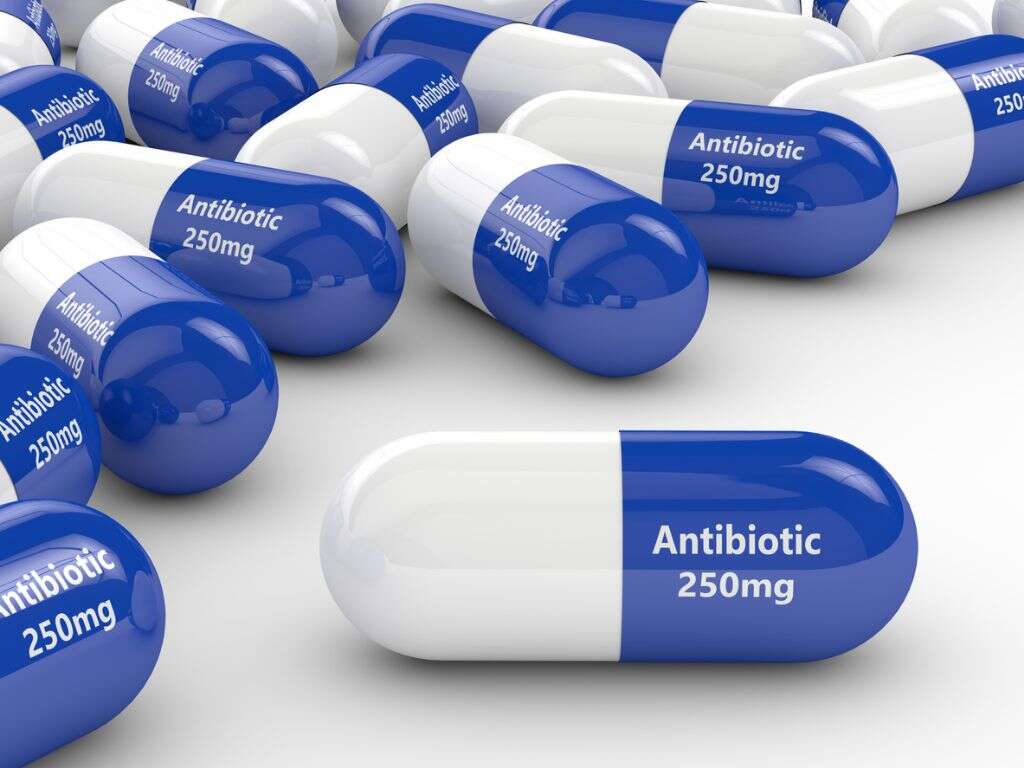
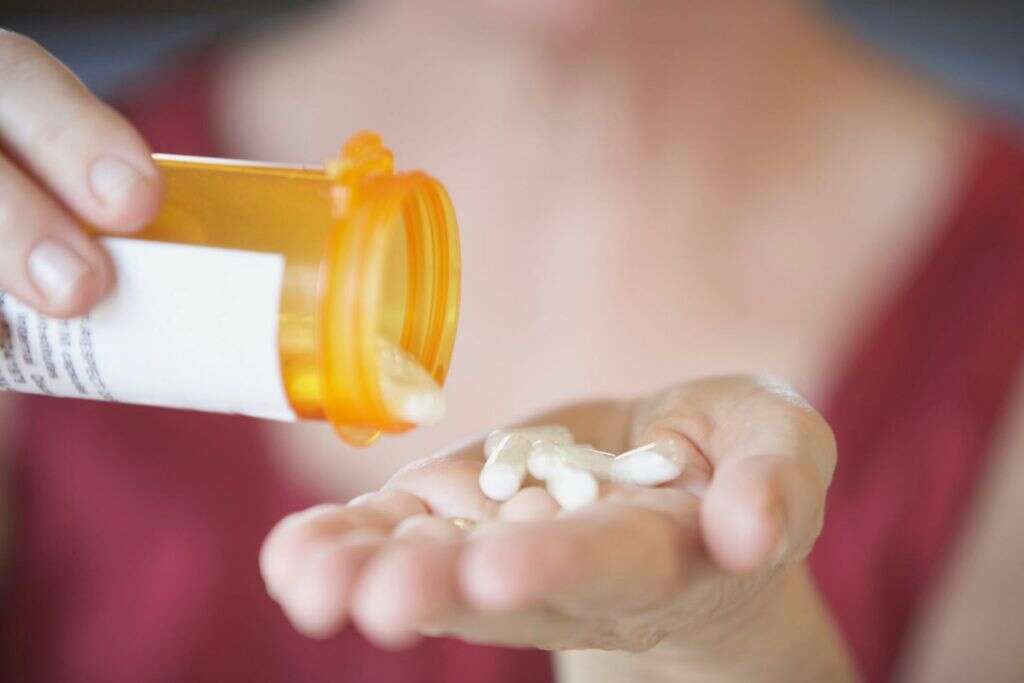
In cases of acute inflammation it is usually a case of waiting for the condition to pass. However, any wounds and fractures should be seen to, and the patient may be given pain killers to help relieve the symptoms. Anti-inflammatory medication may also be prescribed depending on the nature of the condition.
Chronic conditions tend to be treated with anti-inflammatory medication, including aspirin and NSAIDs like ibuprofen. Corticosteroids are also sometimes used, and they can be used in a variety of forms from topical creams to injections. If the inflammation is caused by an autoimmune disease then the patient may be prescribed medication that will suppress their immune system.
10. Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, there are various home remedies the patient can use to at least help make them feel more comfortable. One of these is to avoid foods that cause inflammation, and focus instead on eating foods that fight inflammation. If the patient smokes then quitting smoking may make a considerable difference.
Some people will find that exercising will help, and avoiding stressful situations is also very effective for some people.
Using heat may help to increase blood flow and relieve pressure, while a cold compress could help reduce swelling and relieve pain. Different remedies will work for different people, and it may take some trial and error before the patient finds the best solution for them.