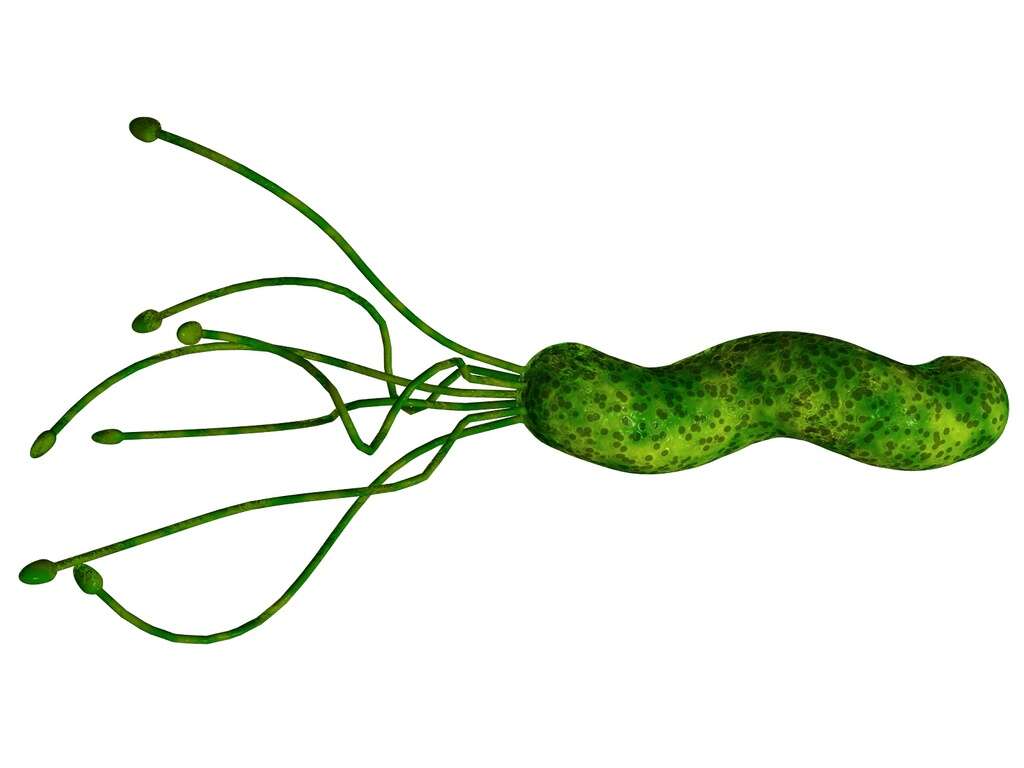
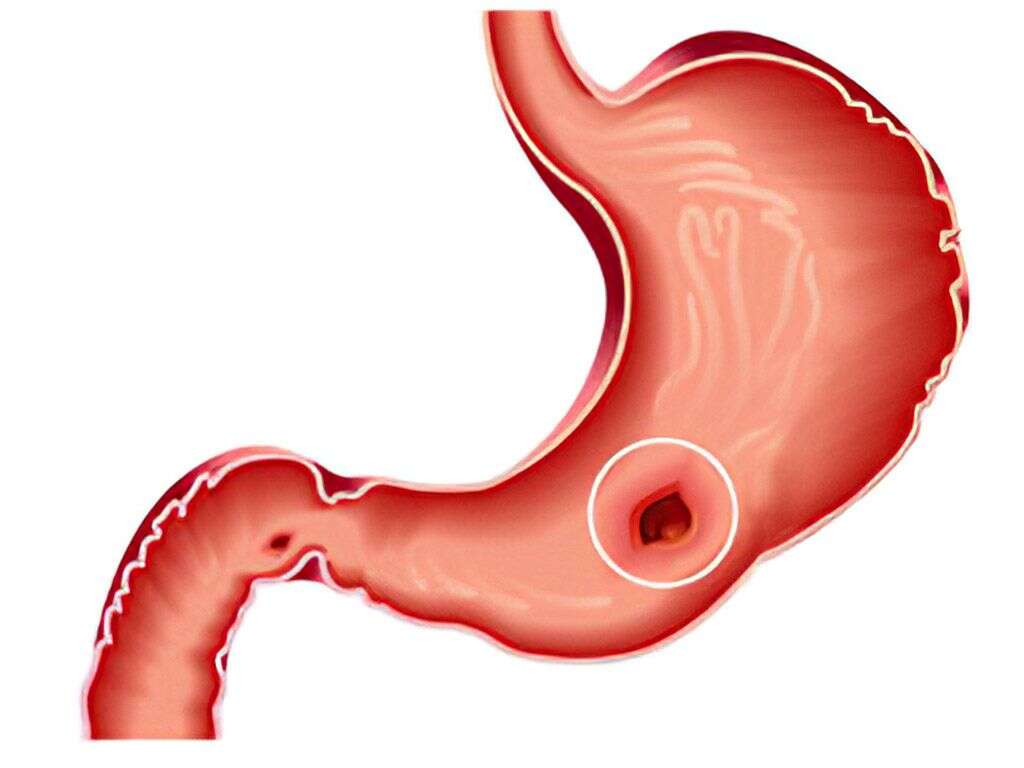
What Is H. Pylori?
3. Patient History and Physical Examination
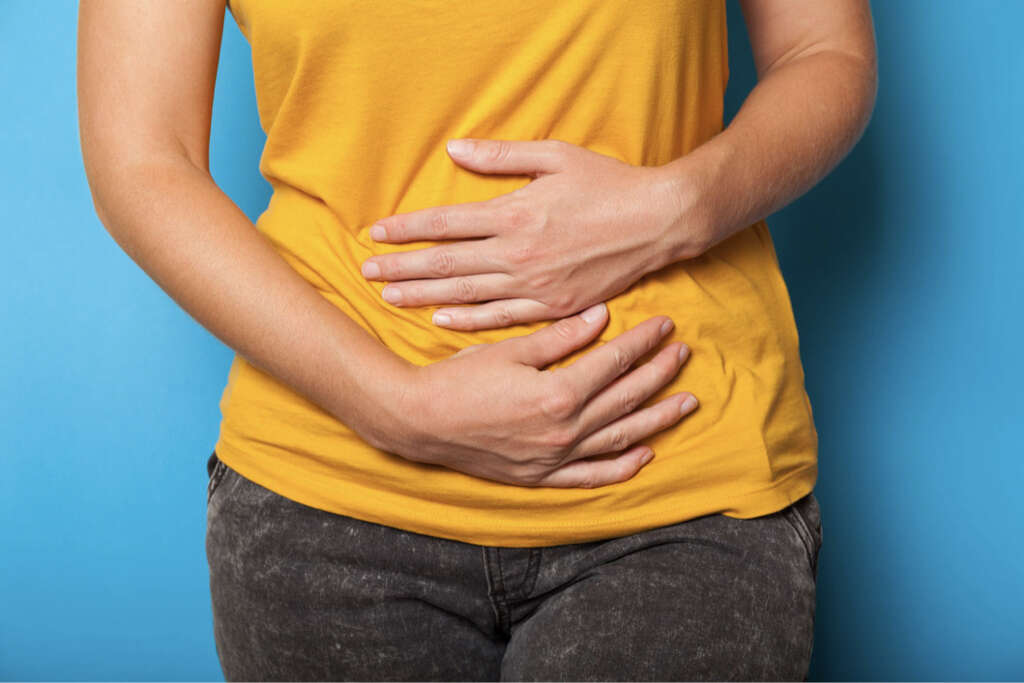
Patients with H. pylori infection are usually asymptomatic. No specific symptoms can be attributed to the disease. However, when the infection results in chronic gastritis, patients can experience acute abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and foul breath (halitosis).
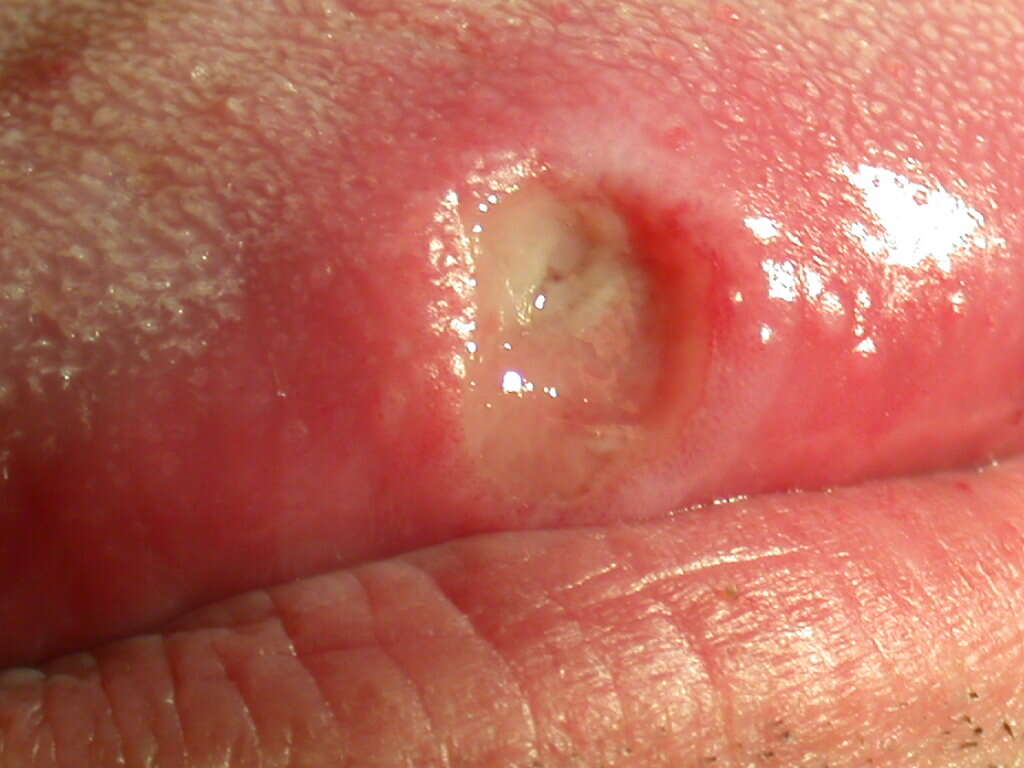
Furthermore, chronic gastritis may lead to peptic ulcers. In gastric or duodenal ulcers, pain in the upper half of the abdomen (epigastrium) can occur. Epigastric pain is more likely to occur when there is an empty stomach (i.e. early hours of the morning or between meals). Moreover, if hemorrhaging occurs, it can result in vomiting of blood or dark feces (due to presence of digested blood components). Those with the infection have an increased risk of peptic ulcers and gastric cancer (adenocarcimoma).
Advertisement