What Is Charcot Foot?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Kaynak, Gökhan et al. “An overview of the Charcot foot pathophysiology.” Diabetic Foot and Ankle vol. 4 (2013): 10.3402/dfa.v4i0.21117.
- 2. Roberts, Lee C. et al. “The Charcot Foot in Diabetes.” Diabetes Care, vol. 34(9) (2011): 2123-2129.https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-0844
- 3. Shah, Mrugeshkumar et al. “Charcot Arthropathy.” Medscape Drugs and Diseases (2020): https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1234293-overview
3. Symptoms
The primary symptom is a “rocker-bottom” foot in which the arch has collapsed, creating a convex sole on which it is difficult to walk.2Roberts, Lee C. et al. “The Charcot Foot in Diabetes.” Diabetes Care, vol. 34(9) (2011): 2123-2129.https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-0844 This deformity can range from mild to debilitating.3Shah, Mrugeshkumar et al. “Charcot Arthropathy.” Medscape Drugs and Diseases (2020): https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1234293-overview However, most patients report feeling much less pain than would be expected, due to being insensate in the affected area.3Shah, Mrugeshkumar et al. “Charcot Arthropathy.” Medscape Drugs and Diseases (2020): https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1234293-overview
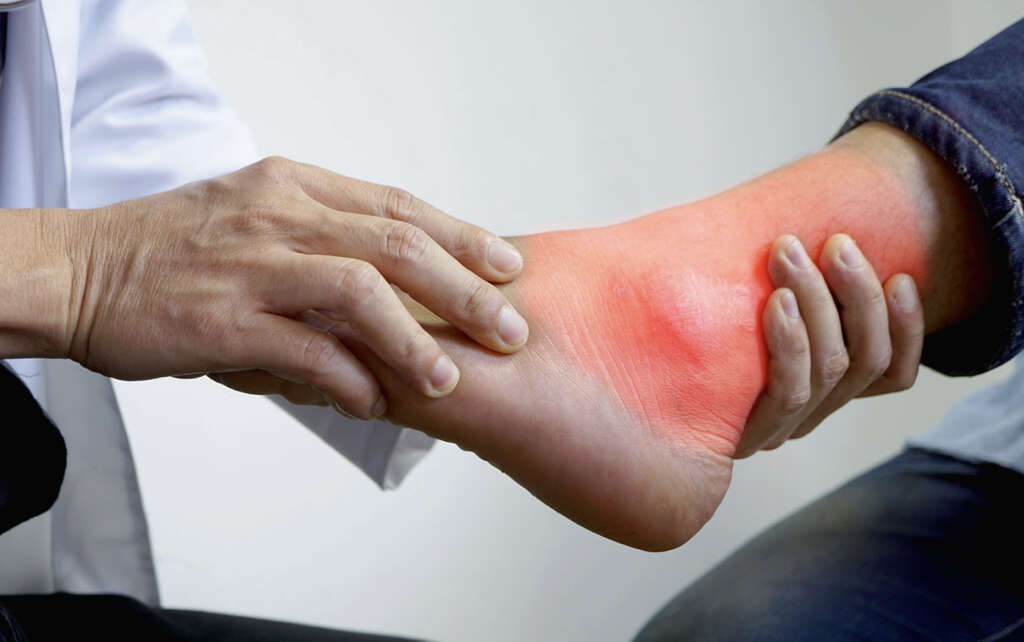
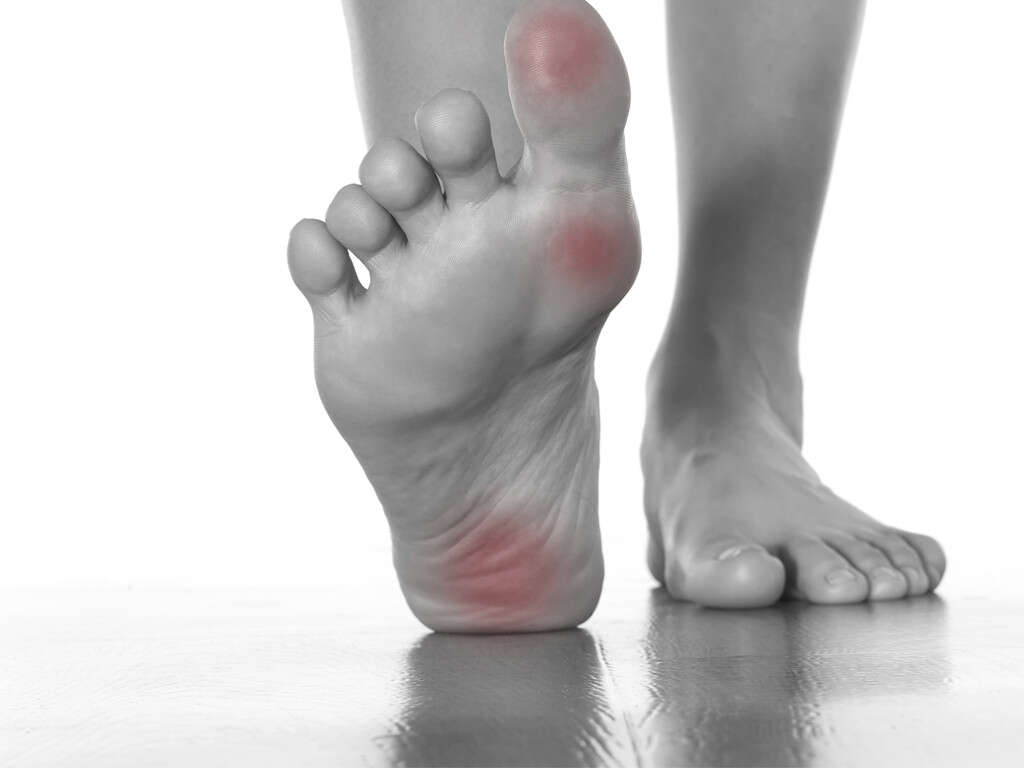
Signs of inflammation that may precede bone deformities are swelling, redness, and warmth in one foot.2Roberts, Lee C. et al. “The Charcot Foot in Diabetes.” Diabetes Care, vol. 34(9) (2011): 2123-2129.https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-0844 Other symptoms include joint effusion, joint instability, and bone resorption. Foot ulcers and callused areas are common on the skin of the foot, especially covering places where bones protrude.3Shah, Mrugeshkumar et al. “Charcot Arthropathy.” Medscape Drugs and Diseases (2020): https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1234293-overview
Advertisement