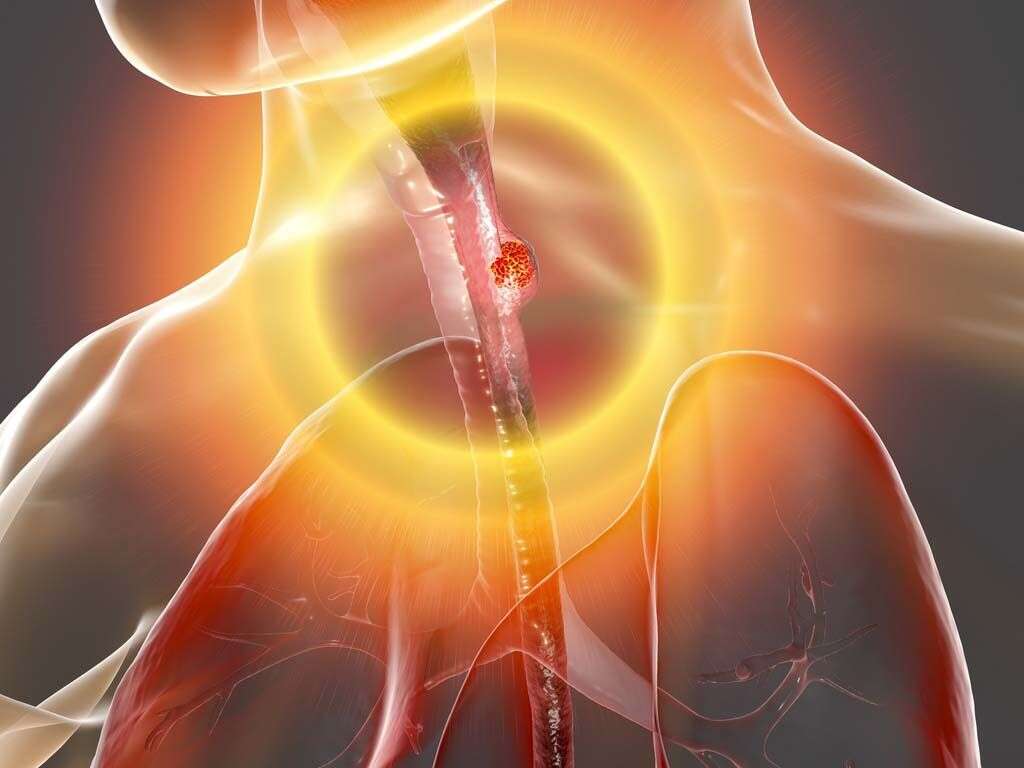
What Is Barrett's Esophagus?
8. Management of High Grade Dysplasia and Ablative Therapy
The management of high grade dysplasia is controversial. The first step would be confirmation of the diagnosis by a certified pathologist who specializes at reading esophageal biopsies. Based on available literature, it is estimated that as many as 40% of patients who undergo esophagectomy (surgical removal of part of the esophagus) for high grade dysplasia were found to have concomitant cancer in the specimen that was resected.
There are three management options for high grade dysplasia: surveillance endoscopy with intensive biopsy, endoscopic ablation, or surgical resection. In ablative therapy, the goal is to destroy the Barrett’s epithelium to eliminate intestinal metaplasia and promote regrowth of squamous epithelium. Some options include radiofrequency ablation, photodynamic therapy, argon plasma coagulation, multipolar electrocoagulation, laser ablation, and cryoablation.
Advertisement